Method for improving embryonic stem cell to differentiate to cardiac muscle cell
A technology of embryonic stem cells and cardiomyocytes, applied in the field of promoting the differentiation of embryonic stem cells into cardiomyocytes, can solve problems such as shortage, limited service life, and limitation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] Embodiment 1 Culture and in vitro induced differentiation of embryonic stem cells
[0058] The mouse R1 embryonic stem (ES) line (Roder JC, Canada, purchased from ATCC, USA) was cultured on trophoblast cells, and the trophoblast cells were selected from primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts treated with mitomycin C (purchased from SIGMA) (derived from outbred Kunming white mouse, 13-15 days old embryo), cultured in DMEM, added 15% fetal bovine serum (purchased from Hyclone Company, ES cell qualified), L-glutamic acid, P-S (penicillin + streptomycin element), non-essential amino acids, (purchased from GIBCO, diluted 100X), β-mercaptoethanol (0.0007%), passaged for an average of 36 hours. 0.2% Trypsin-EDTA (purchased from GIBCO) was used for subculture.
[0059] The hanging drop culture method was used to induce differentiation in vitro, and the appropriate cell density (1.5-3.0×10 6 Cells / petri dish (diameter 60mm)) of mouse R1 embryonic stem cells (digested into a singl...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Example 2 Plasmid Construction and Transfection of ES Cells
[0061] Firstly, the vector plasmid pEGFP-N1 (BD, purchased from Clontech) was used to digest with the endonuclease AatII and then the large fragments were self-ligated to inactivate the original CMVIE promoter, and then the inactivated gene was cut with the endonuclease PstI. Carrier, and then the cloned myocardial-specific sodium-calcium exchange protein type I gene promoter (cloned from genomic DNA by conventional methods, or can be purchased from NIH / NIA Institute) was cut out with endonuclease PstI, and T4 Ligase ligation, the resulting clones were identified by digestion with PstI, SalI, and Asel, respectively, and positive clones that were correctly inserted were picked out, and a large number of amplified plasmids were used for transfection. The linearized plasmid was digested with Asel to obtain 15 μg of the linearized plasmid, and transfected into ES cells using an electroporator (BioRad, GenePulser)...
Embodiment 3
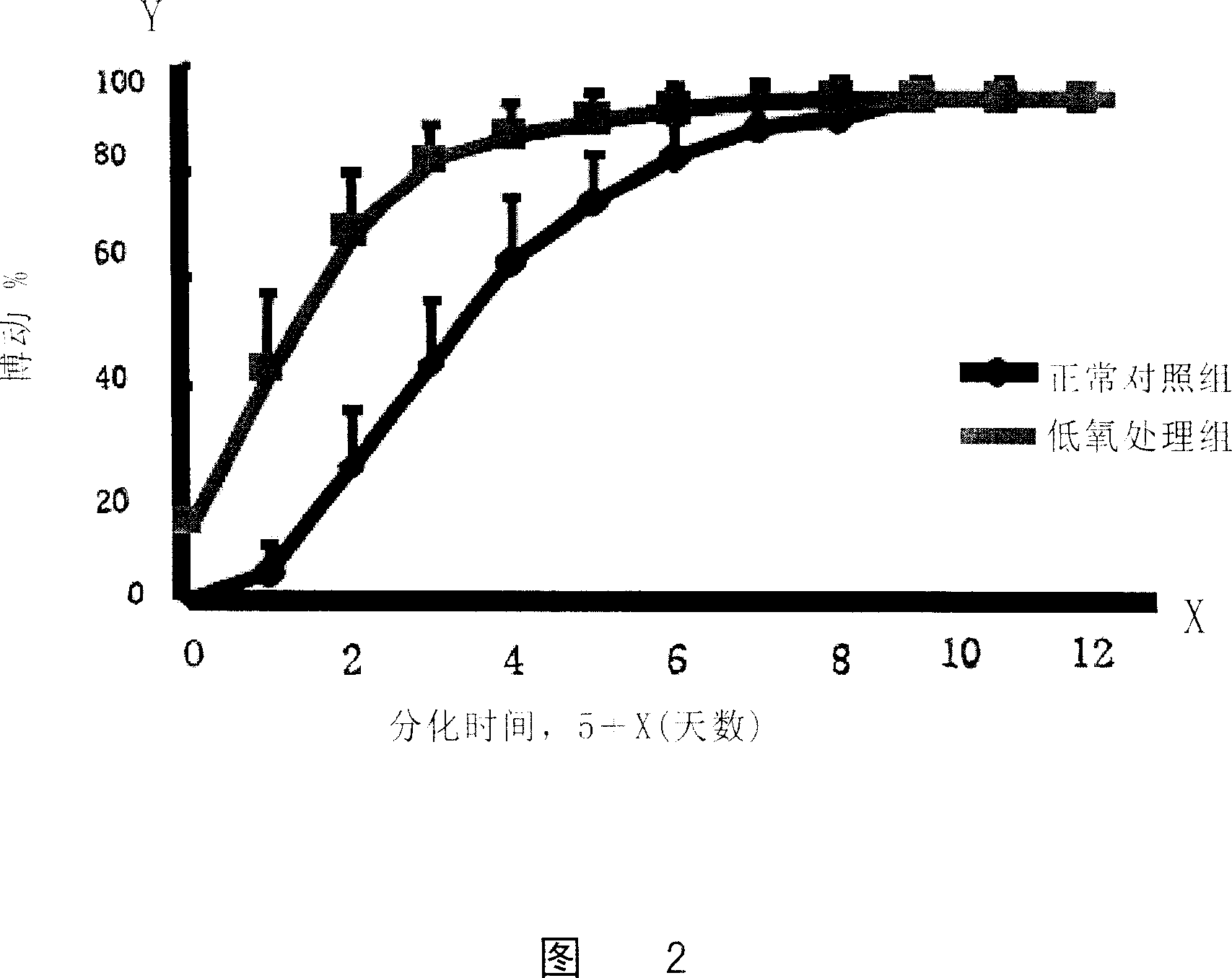
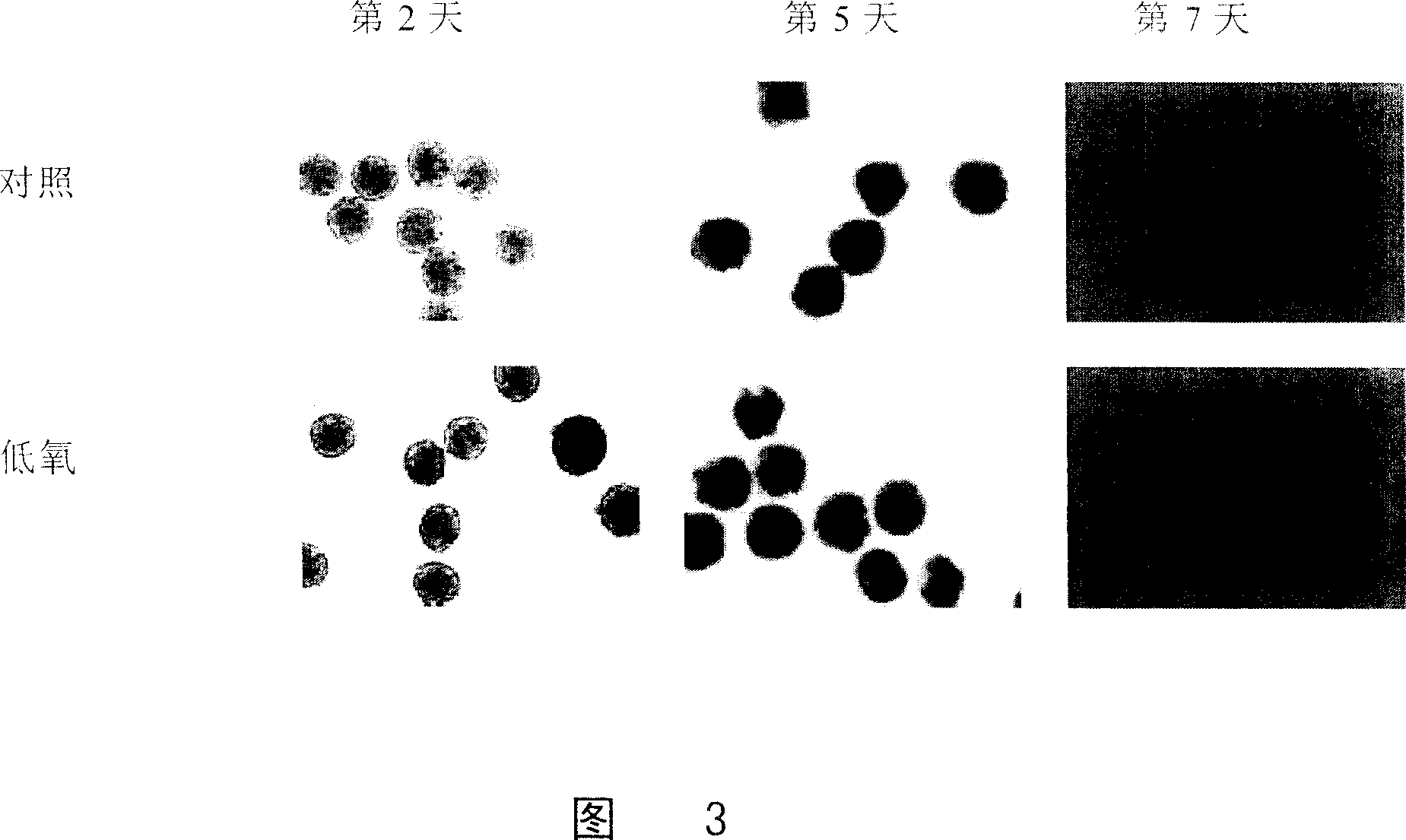
[0065] Example 3 Hypoxic culture of ES cells to induce differentiation
[0066] Normal cultured ES cells (ES cells transfected with a sodium-calcium exchange protein promoter to drive the green fluorescent protein (NCX1) gene) were made into hanging drops and divided into a hypoxic treatment group and a normal control group.
[0067] The cells in the hypoxic treatment group were cultured in a hypoxic incubator (Thermo Forma) with a culture condition of 3% O 2 , 5% carbon dioxide, and continued to culture for 48 hours (2 days), while the cells of the normal control group were in 21% O 2 , 5% CO 2 After the hanging drop culture, the two groups of cells were cultured under normal oxygen concentration conditions.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com