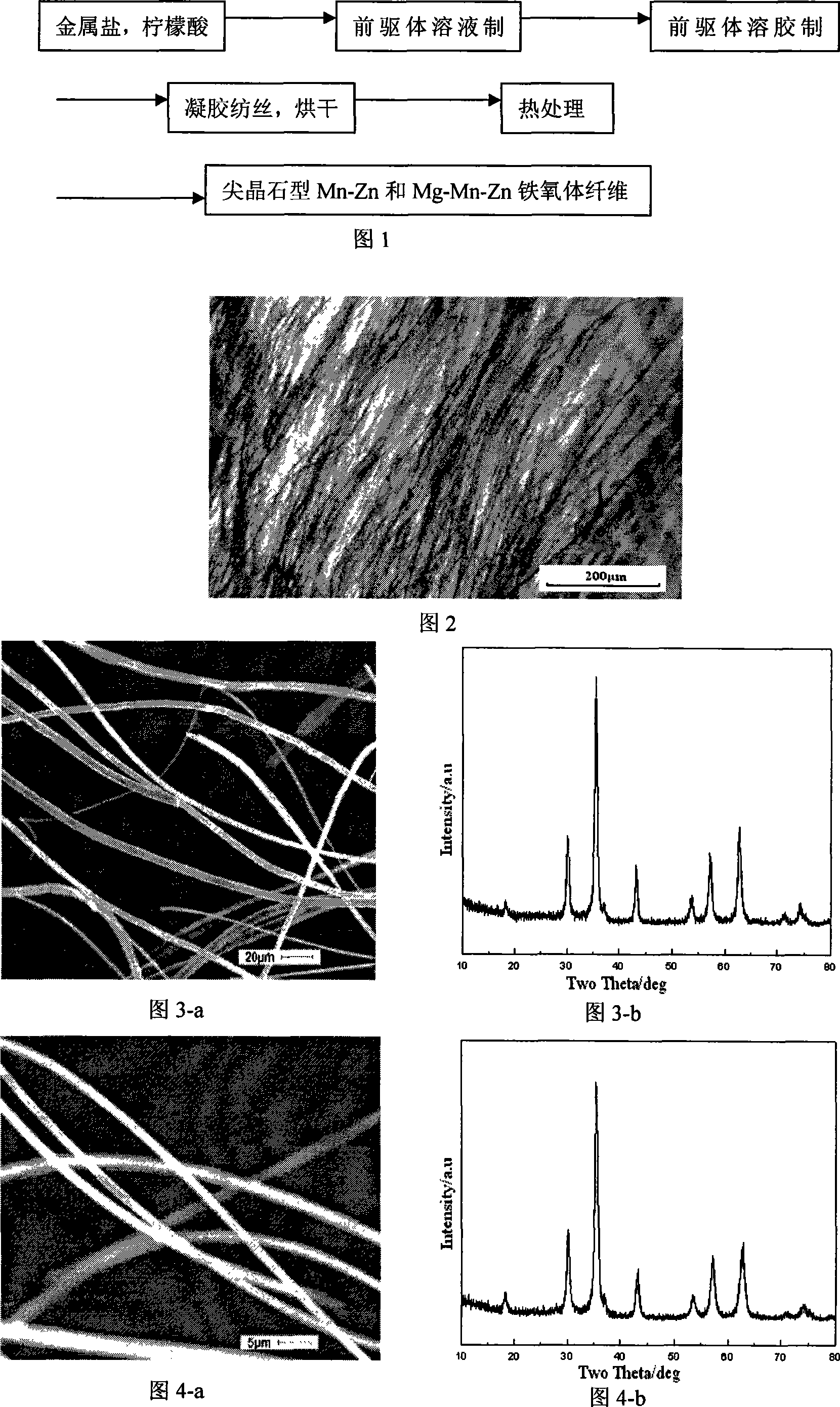
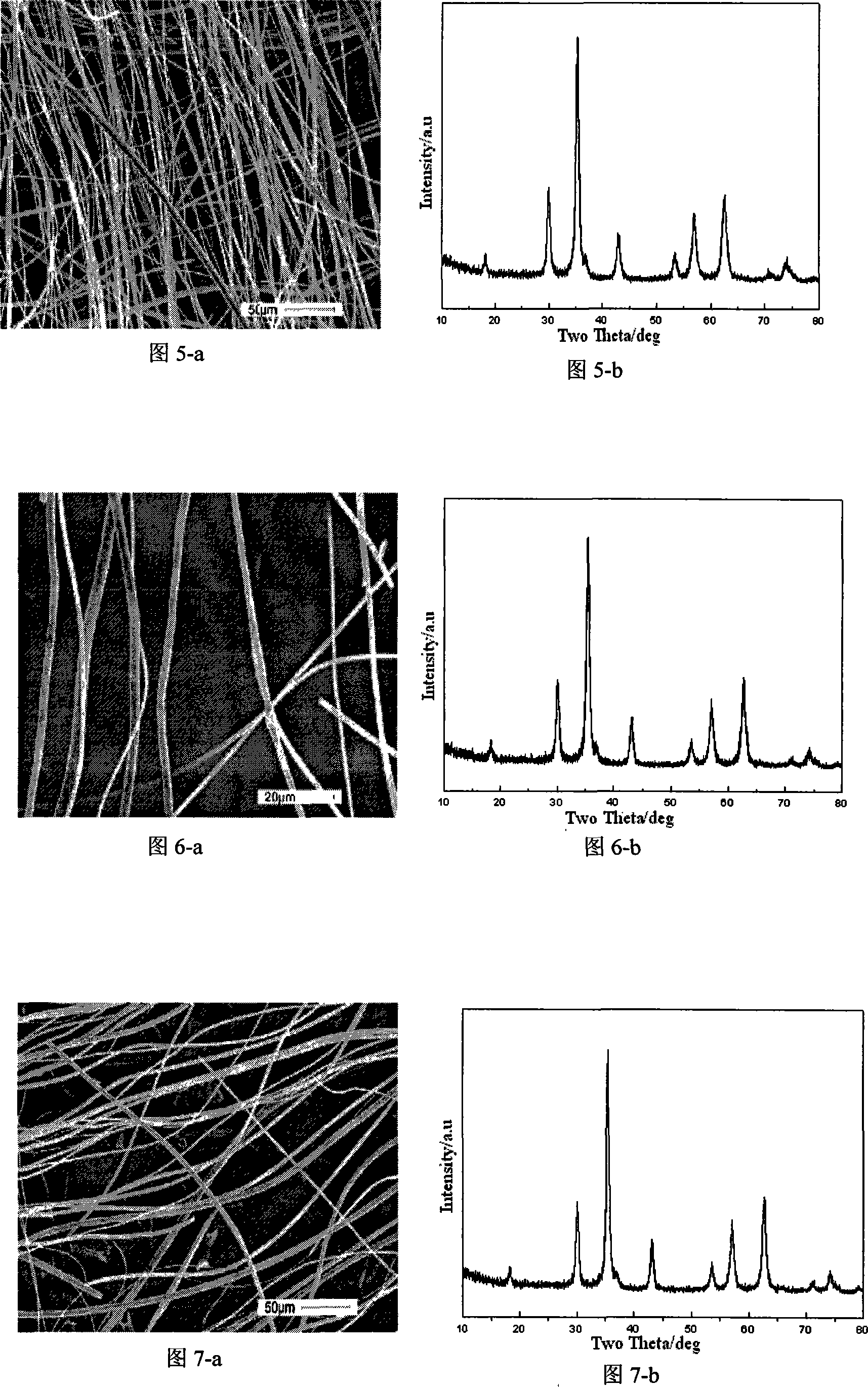
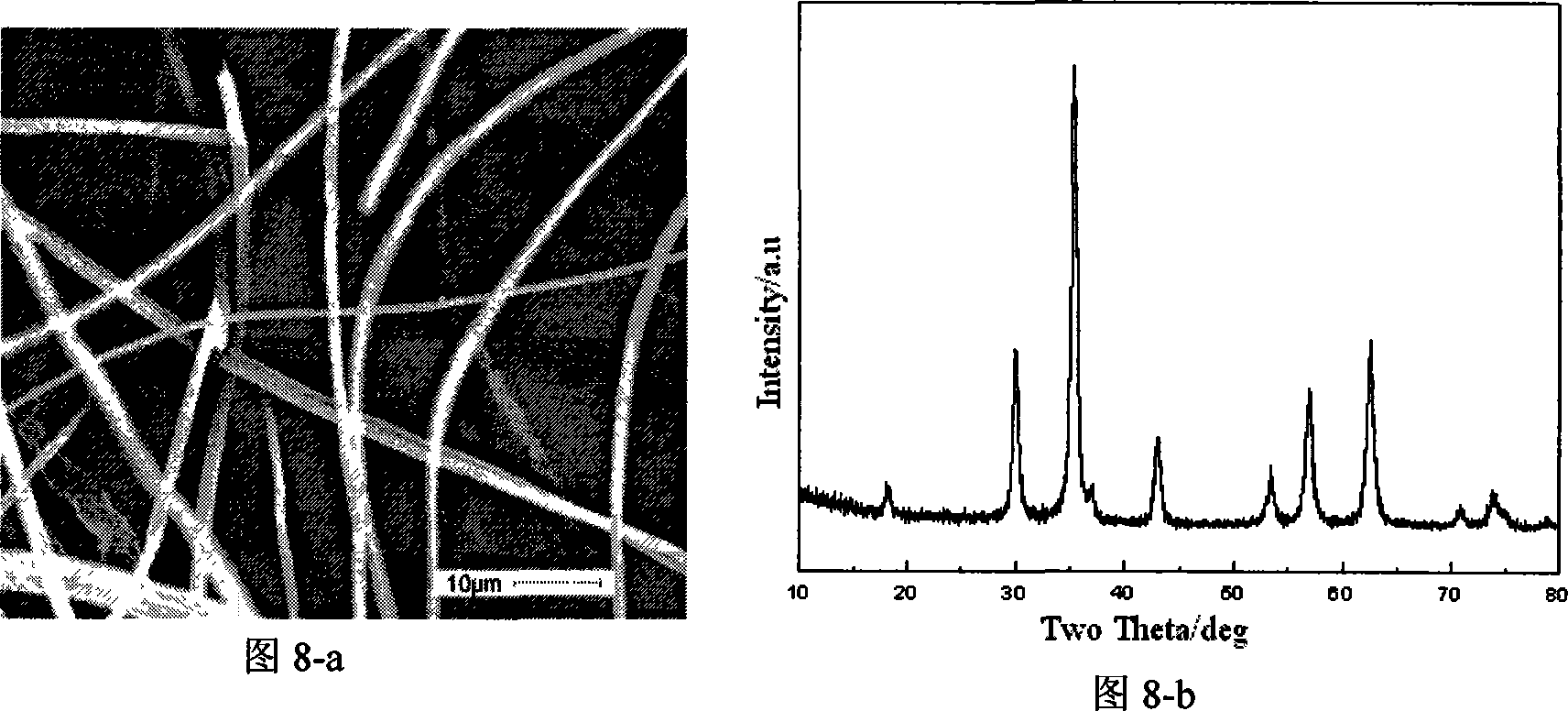
Mn-Zn ferrite fibre and preparing process thereof
A technology of ferrite and fiber, which is applied in the field of Mn-Zn series ferrite ceramic fiber and its preparation, can solve the problem of less ferrite ceramic fiber, achieve low cost, simple process, easy process parameters and microstructure Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Embodiment 1 (spinel type Mn 0.4 Zn 0.6 Fe 2 o 4 ferrite fiber):
[0032] Step 1: get 1.33g manganese nitrate (Mn(NO 3 ) 2 ), 3.31g zinc nitrate (Zn(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O), 15.00g iron nitrate (Fe(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 O), 15.61g citric acid (CA:C 6 h 8 o 7 ·H 2 O) mix in 120ml deionized water, Mn 2+ The molar concentration of Zn is 0.08mol / L, Zn 2+ The molar concentration of Fe is 0.08mol / L, Fe 3+ The molar concentration is 0.31mol / L, and the raw material molar ratio is: CA:Fe 3+ : Zn 2+ :Mn 2+ =4:2:0.6:0.4, and then magnetically stirred for 12 hours.
[0033] Step 2: Then put the precursor solution into a rotary evaporator, dehydrate under reduced pressure at 50°C, and the pressure is less than 0.1Mpa, for about 30 minutes, to obtain a gel-like colloidal substance.
[0034] Step 3: Put the gel obtained in step 2 into an oven, dry it at 50°C, and place it in the oven for about 1 hour, then pull the gel into gel cellulose filaments, place the cellulose filaments...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2 (spinel type Mn 0.6 Zn 0.4 Fe 2 0 4 ferrite fiber):
[0037] Step 1: get 2.73g manganese acetate (Mn(CH 3 COO) 2 4H 2 O), 2.21g zinc nitrate (Zn(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O), 15.00g iron nitrate (Fe(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 O), 19.51g citric acid (CA:C 6 h 8 o 7 ·H 2 O) mix in 200ml deionized water, Mn 2+ The molar concentration of Zn is 0.06mol / L, Zn 2+ The molar concentration of Fe is 0.04mol / L, Fe 3+ The molar concentration is 0.19mol / L, and the molar ratio of raw materials is: CA:Fe 3+ : Zn 2+ :Mn 2+ =5:2:0.4:0.6, and then magnetically stirred for 20 hours.
[0038] Step 2: Then put the precursor solution into a rotary evaporator, dehydrate under reduced pressure at 60°C, the pressure is less than 0.1Mpa, for about 30 minutes, and obtain a gel-like colloidal substance.
[0039] Step 3: Put the gel obtained in step 2 into an oven, dry it at 60°C, and place it in the oven for about 1 hour, then pull the gel into gel cellulose filaments, place the cellulos...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Embodiment 3 (spinel type Mn 0.8 Zn 0.2 Fe 2 o 4 ferrite fiber):
[0042] Step 1: get 3.64g manganese acetate (Mn(CH 3 COO) 2 4H 2 O), 1.11g zinc nitrate (Zn(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O), 15.00g iron nitrate (Fe(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 O), 21.46g citric acid (CA:C 6 h 8 o 7 ·H 2 O) mix in 250ml deionized water, Mn 2+ The molar concentration of Zn is 0.06mol / L, Zn 2+ The molar concentration of Fe is 0.02mol / L, Fe 3+ The molar concentration is 0.15mol / L, and the raw material molar ratio is: CA:Fe 3+ : Zn 2+ :Mn 2+ =5.5:2:0.2:0.8, and then magnetically stirred for 28 hours.
[0043] Step 2: Then put the precursor solution into a rotary evaporator, depressurize at 70°C, the pressure is less than 0.1Mpa, and dehydrate for about 30 minutes to obtain a gel-like colloidal substance.
[0044] Step 3: Put the gel obtained in step 2 into an oven, dry it at 65°C, and place it in the oven for about 1 hour, then pull the gel into gel cellulose filaments, place the cellulose filament...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com