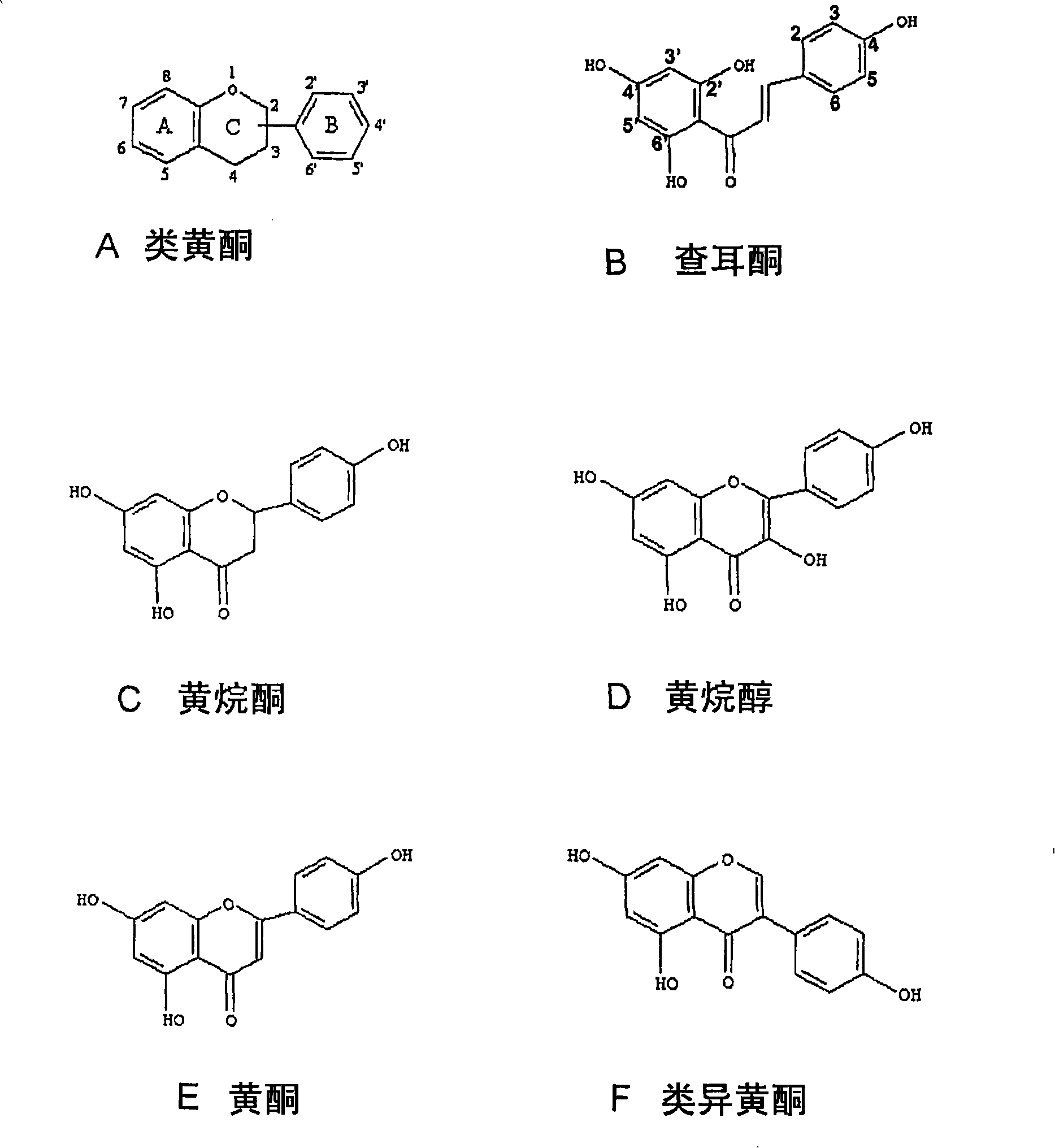
Enzymatic demethylation of flavonoids
A flavonoid and alkoxy technology, applied in the field of enzymatic demethylation of flavonoids, can solve the problem of no prenylated phytoestrogens and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
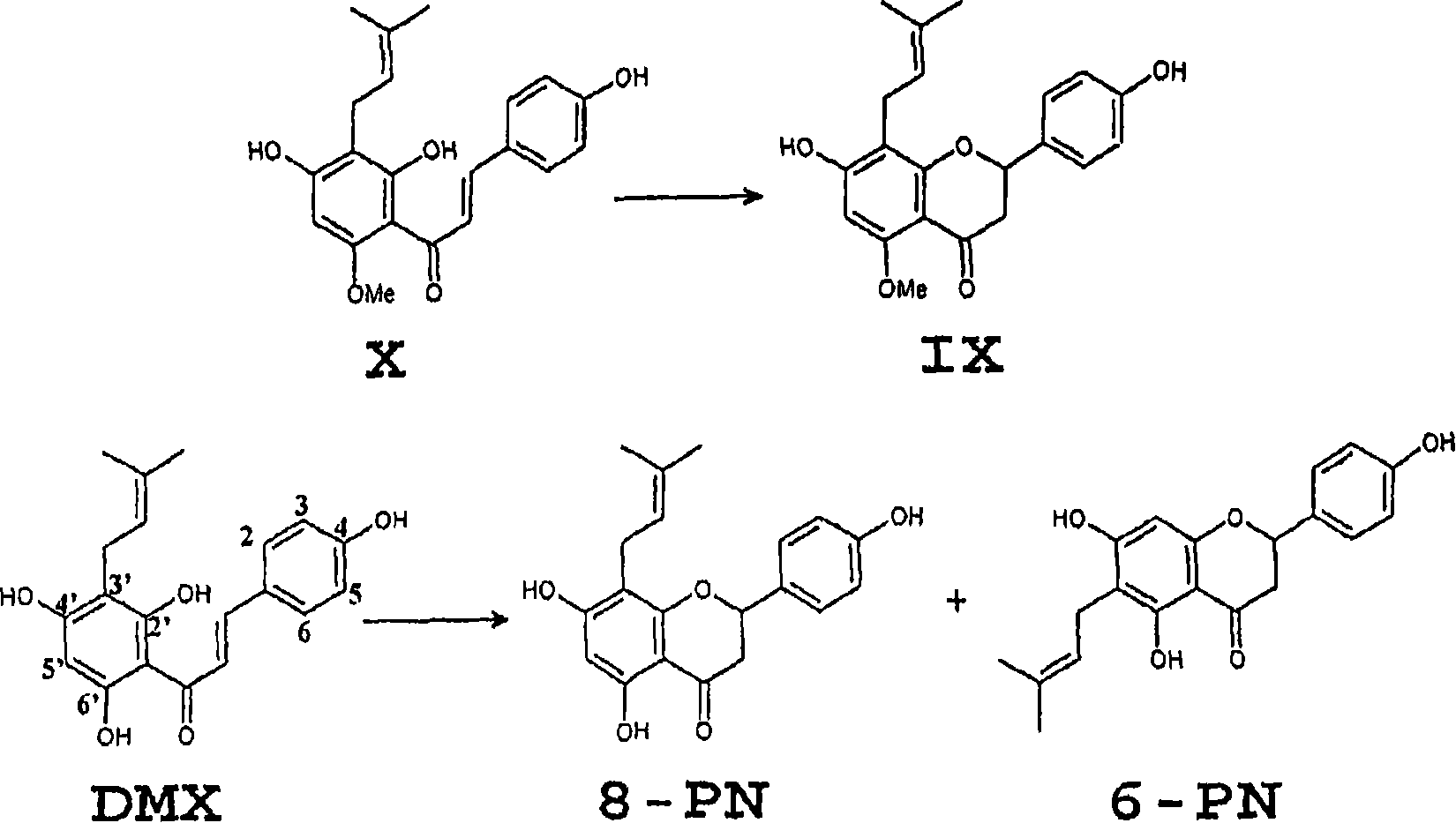
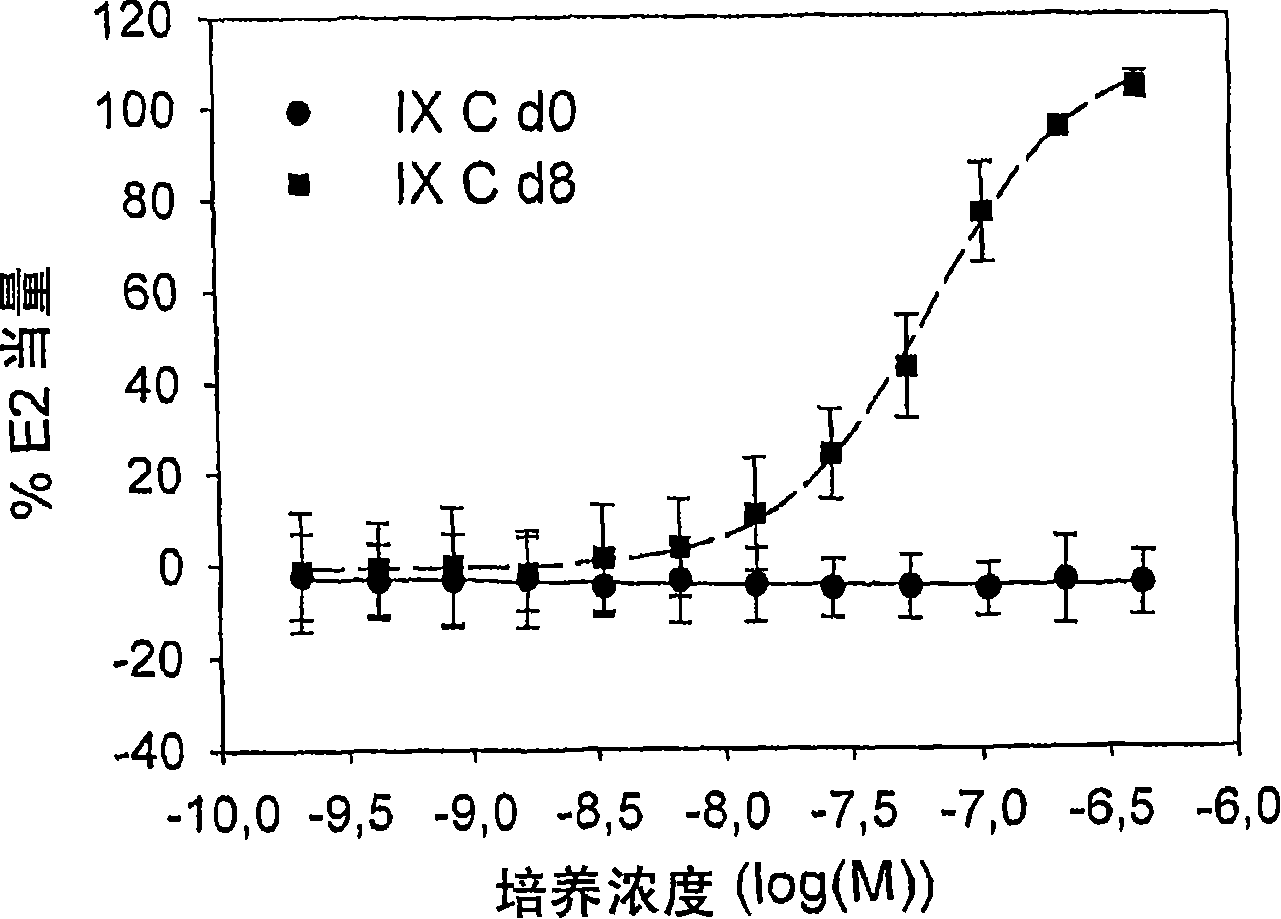
[0095] Example 1: Demethylation of isoxanthohumol (IX) using human fecal cultures.
[0096] Fecal samples were obtained from 12 healthy human subjects, aged between 20 and 35 years, indicated by A to L. None of the subjects had a history of gastrointestinal disease and had not taken antibiotics in the 3 months prior to sampling. A 20% (w / v) fecal slurry was prepared from fresh fecal samples by homogenizing the feces with phosphate buffered saline (0.1 M, pH 7) containing 1 g / l reducing agent sodium thioglycolate. Particulate matter was removed by centrifugation (1 min, 500xg). This supernatant is hereinafter referred to as "culture".
[0097] By culturing fecal cultures (10% (v / v)) under anaerobic conditions in Brain Heart Infusion medium (containing 0.5 g / l cysteine hydrochloride) containing 25 mg / l isoxanthohumol, culture On day 8, the cultures from faecal samples A, B, C and D (hereinafter referred to as cultures A-D) were tested for their ability to degrade or conve...
Embodiment 2
[0106] Example 2. Use of microorganisms to produce compounds with 8-prenylnaringenin-type estrogen-like properties use of things
[0107] This example describes the ability of two known enteric anaerobes to convert IX to 8-PN.
[0108] Eubacterium limosum ATCC 8486 and Peptostreptococcus productus ATCC 27340 were obtained from the German Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures (DSMZ, Braunschweig, Germany). E. limosum was co-cultured with 25 mg / l IX and 8-PN for 13 days in Brain Heart Infusion medium (containing 0.5 g / l cysteine hydrochloride) under anaerobic conditions (Table 2). This strain is capable of converting IX to 8-PN. This strain did not further degrade 8-PN because all 8-PN added as a substrate could be recovered after 13 days of culture. These features markedly differ from the metabolic pathways observed in liver microsomes, where 8-PN is extensively further metabolized [Nikolic et al. (2005) J. of Mass Spectrom. 40, 289-299; Nikolic et al. (2004) ...
Embodiment 3
[0118] Example 3 Application of microorganisms capable of converting methylated prenyl flavonoids in fermentation.
[0119] A fed-batch fermentation experiment was designed to convert methylated prenylflavonoids under fermentative conditions using a Eubacterium limosum strain selected as described above. Fermentation in Braun Biostat M was carried out in a fermenter (2 L container), and 1.5 L of Brain Heart Infusion medium (containing 0.5 g / l cysteine hydrochloride) was added thereto. Subsequently, the fermenter was autoclaved at 121 °C for 30 min. Before inoculation, the fermenter was flushed with a nitrogen flushing system for 1 h to create an anaerobic environment. Thereafter, in the fermenter, a 2-day-old E. limosum culture was introduced into the culture solution, and 25 mg / L of IX was added. Fermentations were carried out at 37°C for 2 weeks without pH control. From the first day, add 200ml of anaerobic Brain Heart Infusion medium (containing 0.5g / l cysteine h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com