Fine purification and energy-saving dewatering process for phosphogypsum
A technology of phosphogypsum and process water, applied in the field of gypsum production, can solve the problems of reducing the relative content of solid impurities, increasing investment, management costs, affecting product quality, etc., to improve purity, reduce drying costs, economic and social Significant effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
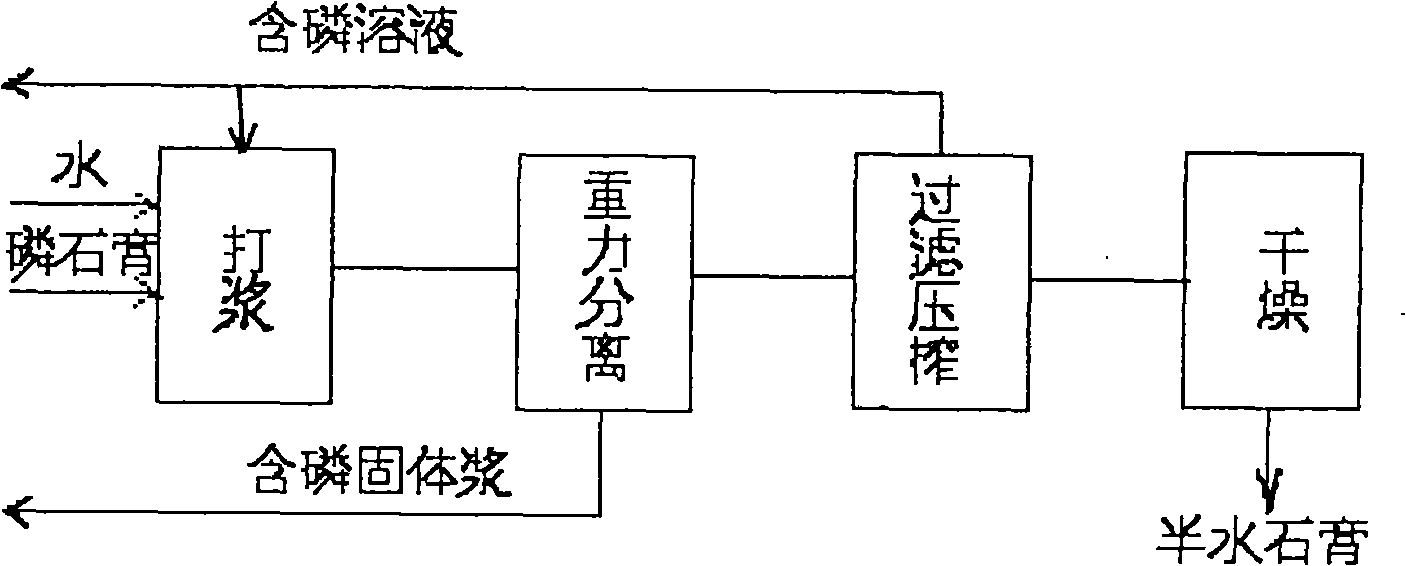
[0017] Take 15 kilograms of ordinary process water in a 30 liter stirring tank, add 5 kilograms of phosphogypsum (see Table 1 for its composition), and stir for 30 minutes; then stand still for 5 minutes, release 95% of the upper layer of slurry into 0.1m 2 Press filter in the filter press, squeeze it with a diaphragm for one minute, and dry it with 6.0 bar compressed air for 2 minutes to obtain 3.8 kg of gypsum (see Table 1 for its composition).
[0018] Table 1. Composition of phosphogypsum before and after purification and dehydration
[0019] Element
Embodiment 2
[0021] The phosphogypsum is input at an hourly rate of 3600 kg, with a liquid-solid ratio of 4.0, continuously and evenly adding water and part of the filtrate separated and returned by pressure filtration, into the continuous stirring and beating tank, and the material residence time is 30 minutes; pumped into the series cyclone In the separator, the heavy phase ratio is maintained at 0.04, and the heavy phase is pumped back to the phosphoric acid production extraction system, and the light phase enters the press filter press for filtration and squeezing, and the pressurized filtration pressure is 0.20Mpa; a part of the filtrate is returned to the phosphoric acid production filtration system to maintain production The water in the system is balanced, and part of it is returned to the phosphogypsum beating tank together with water to maintain the liquid-solid ratio; the filter cake on the filter press is dried with 0.25Mpa compressed air, and then sent to the dryer for drying; t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com