Method for placenta mesenchyma stem cell separation and in vitro amplify cultivation
A technology for mesenchymal stem cells and in vitro expansion, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, animal cells, tissue culture, etc., can solve the problem of unclear specific marker molecules of placental mesenchymal stem cells, low subculture and expansion ability, It is difficult to form mesenchymal stem cell lines and other problems, and achieve the effect of being conducive to clinical safe transplantation application, improving expansion ability, and obvious expansion advantages
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] A specific method that the method of the present invention takes is: get placental maternal side decidua, cut into pieces fetal decidua side placental tissue, collect cells after 0.1% type IV collagenase digestion, use cell culture medium (containing DMEM, 10% fetal bovine serum, 2mML-glutamine) for adherent culture.
[0022] 1. After the cells are layered in the culture flask, discard the culture medium and suspended cells. Adherent spindle cells were digested with Tryspin-EDTA and harvested. Harvested cells were washed once with PBS and suspended in PBS. Then, according to the instructions provided by MACS, CD34 was sorted from the suspension cells with the adsorption CD14 monoclonal antibody-magnetic bead separation system (MACS, Miltenyi Biotech Inc., Shanghai). - cell. collected CD34 - After the cells were cultured on the wall again, the cells were harvested, washed once with PBS, and then CD34 was sorted using the adsorption CD105 monoclonal antibody-magnetic ...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Separation and purification efficiency
[0026] The proportions of different labeled cell surface antigens in cells obtained by different separation and purification techniques were measured by flow cytometry, as shown in Table 1.
[0027] Table 1 The proportion (%) of different labeled cell surface antigens in cells obtained by different separation and purification techniques
[0028]
[0029] CD34 in primary placental maternal decidua cells + , CD45 + , CD105 + and CD29 + The average cells were 7.22%, 11.65%, 47.14% and 34.62%, indicating that the primary adherent spindle cells were dominated by mesenchymal cells. After 2 passages of adherent culture, CD34 + Cells and CD45+ cells decreased, while CD90+ and CD105 cells increased, but also contained a small amount of CD34 + cells and CD45+ cells. After CD14 monoclonal antibody and CD105 monoclonal antibody-magnetic bead system sorting, the obtained cells are basically CD34 - CD45 - CD105 + CD29 + cell. Ac...
Embodiment 3
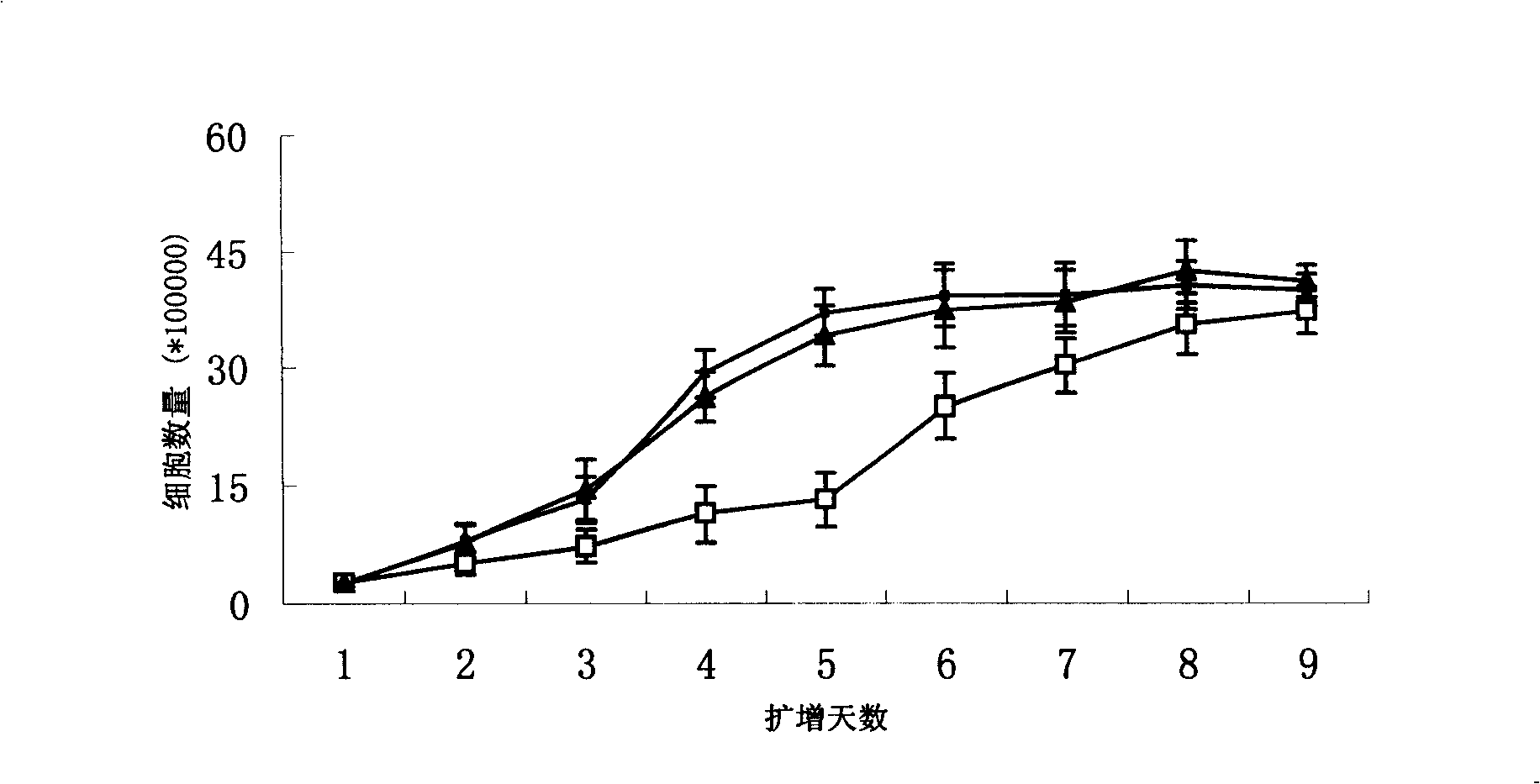
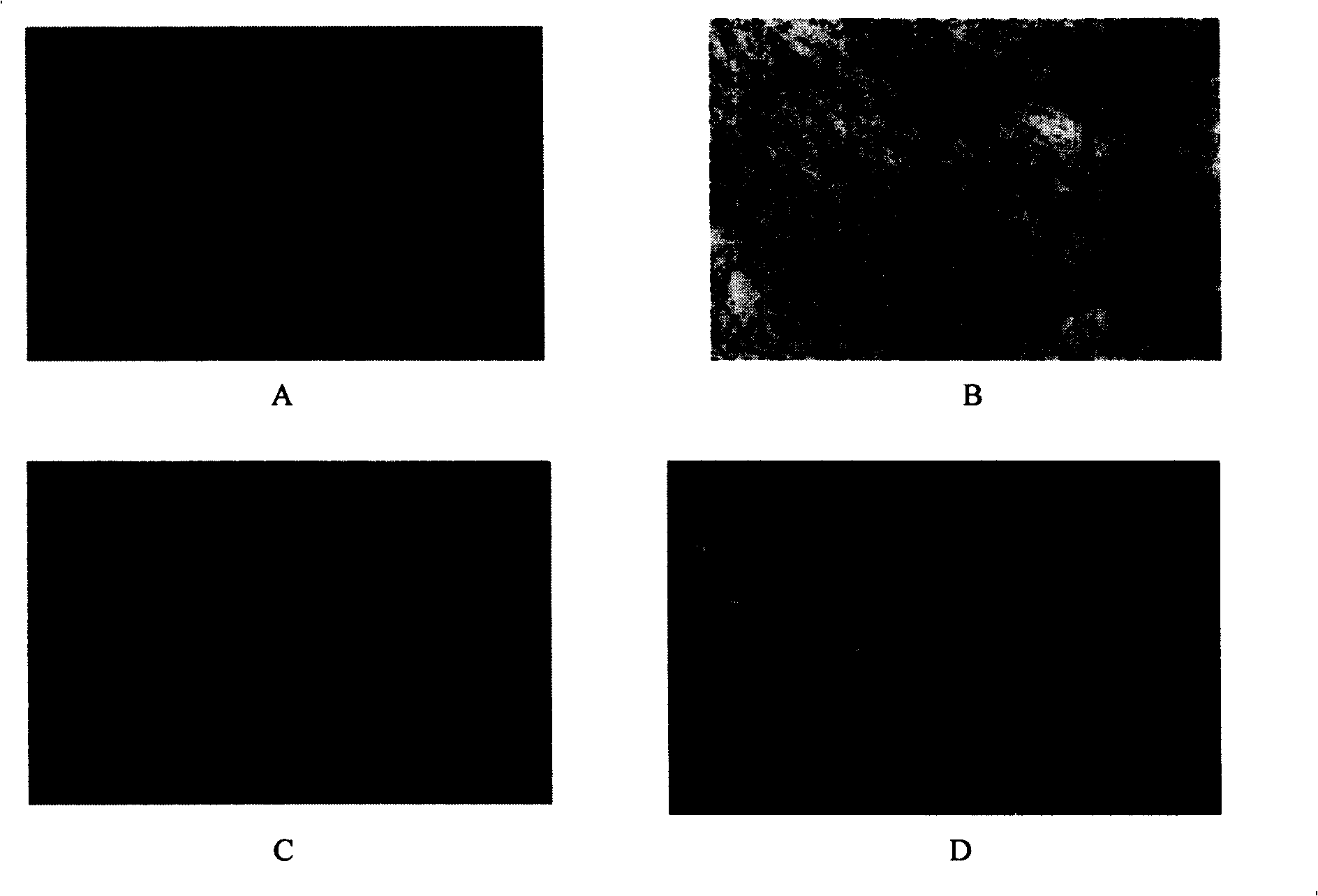
[0031] Cell morphology obtained by different sorting methods
[0032] see figure 1 24 hours after inoculation, long spindle-shaped cells could be seen in placental tissue cells digested with type IV collagenase and arranged radially or concentrically. A large number of colonies appeared 4 days after inoculation and gradually layered on the bottom of the culture flask. It takes 14-16 days for cell expansion to form a monolayer in Teflen-25 flasks. figure 1 A shows that the cells are spindle-shaped under an inverted microscope, 10×10 magnifications. After the cells were subcultured twice, the cells showed remarkable fibrous cells, and a cell monolayer was formed after 8-9 days after cell inoculation ( figure 1 B). Placental mesenchymal stem cells (CD34 - CD105 +) under a new serum-free culture system (ginsenoside polysaccharide / DMEM-LG / 10% FBS) to carry out the first-generation expansion culture, and form a cell monolayer in a Teflen-25 culture flask after 5-6 days. figur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com