Method of producing fungal culture
A technology for filamentous fungi and products, applied in the field of producing filamentous fungi culture products, can solve problems such as insufficient saccharification ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment Embodiment 1
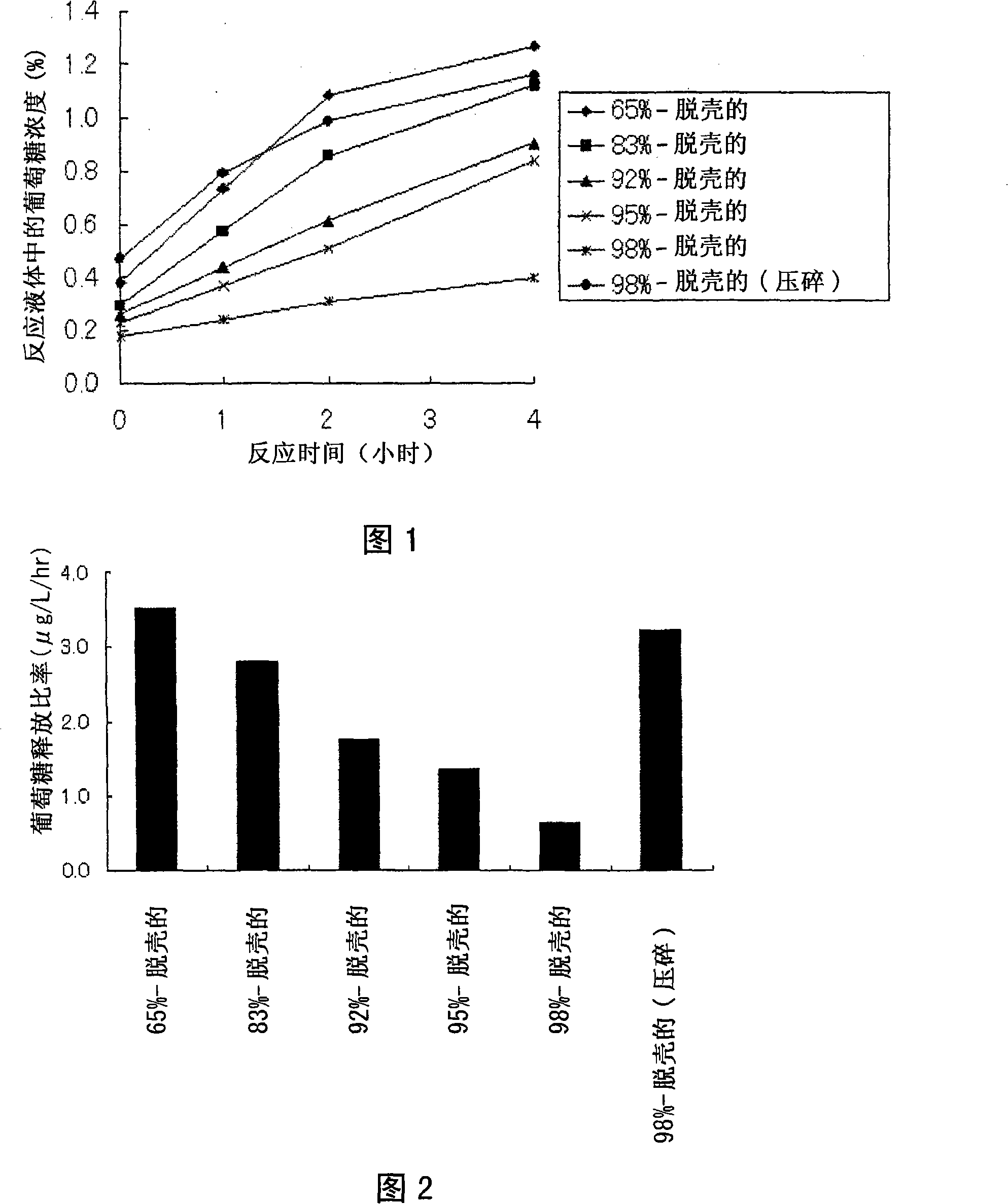
[0130] Measuring the release rate of glucose from barley with different hulling ratios
[0131] Barley (Stirling, produced in Australia) having different husk ratios from 65% to 98% was reacted with an enzyme derived from an Aspergillus culture product, and the release rate of glucose from the barley was measured.
[0132] Specifically, 2 g were weighed separately as 65%-hulled barley, 83%-hulled barley, 92%-hulled barley, 95%-hulled barley, 98%-hulled barley and 98%-hulled barley Crushed products of barley, and each weighed material and 50 ml of water were placed in a 200-ml Erlenmeyer flask. This was sterilized with an autoclave at 121° C. for 15 minutes to prepare a “barley substrate solution”.
[0133] Subsequently, an Aspergillus culture product produced by using barley (Stirling, produced in Australia) as a culture raw material was subjected to solid-liquid separation by filtration with filter paper to obtain an "Aspergillus culture supernatant".
[0134] The method fo...
Embodiment 1
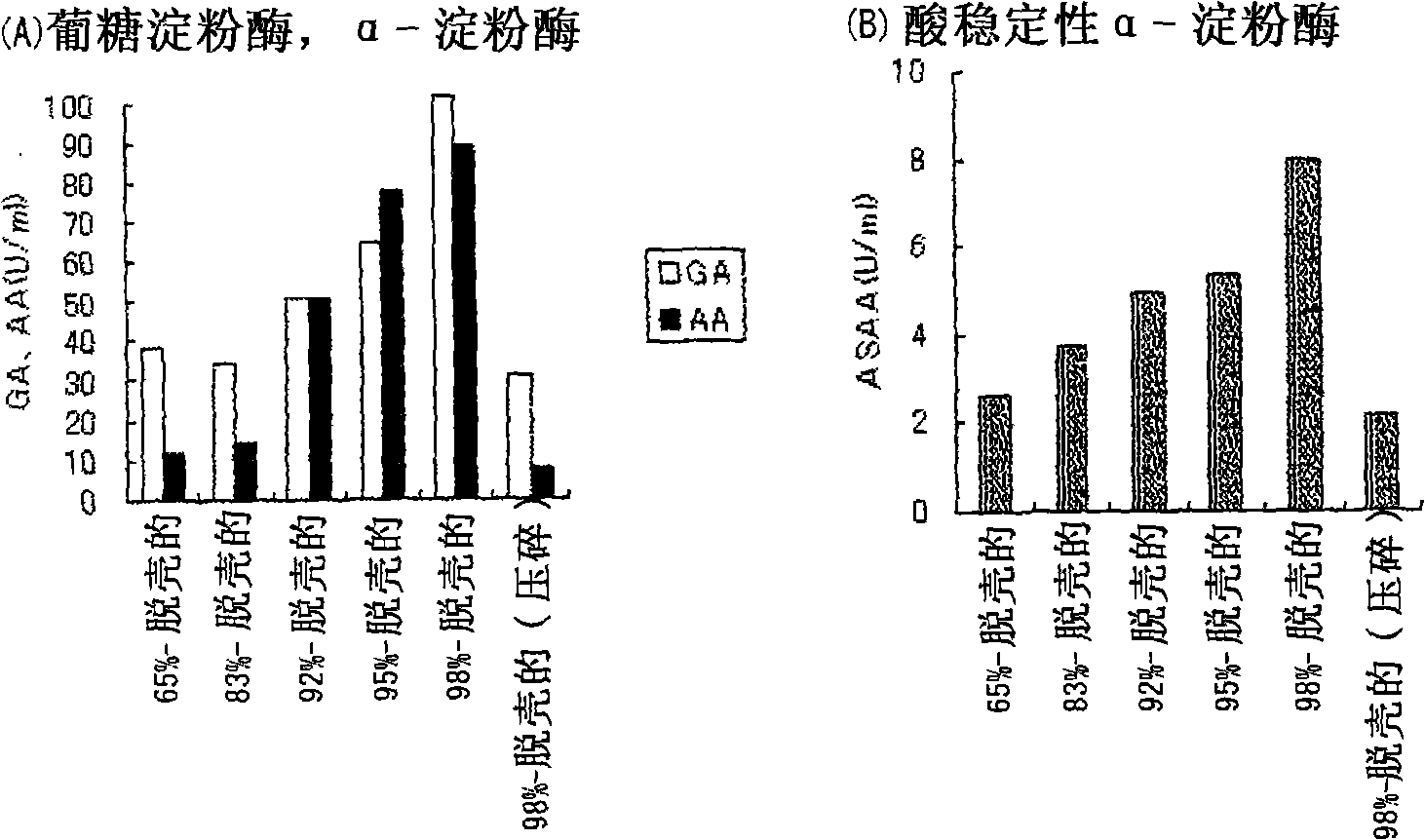
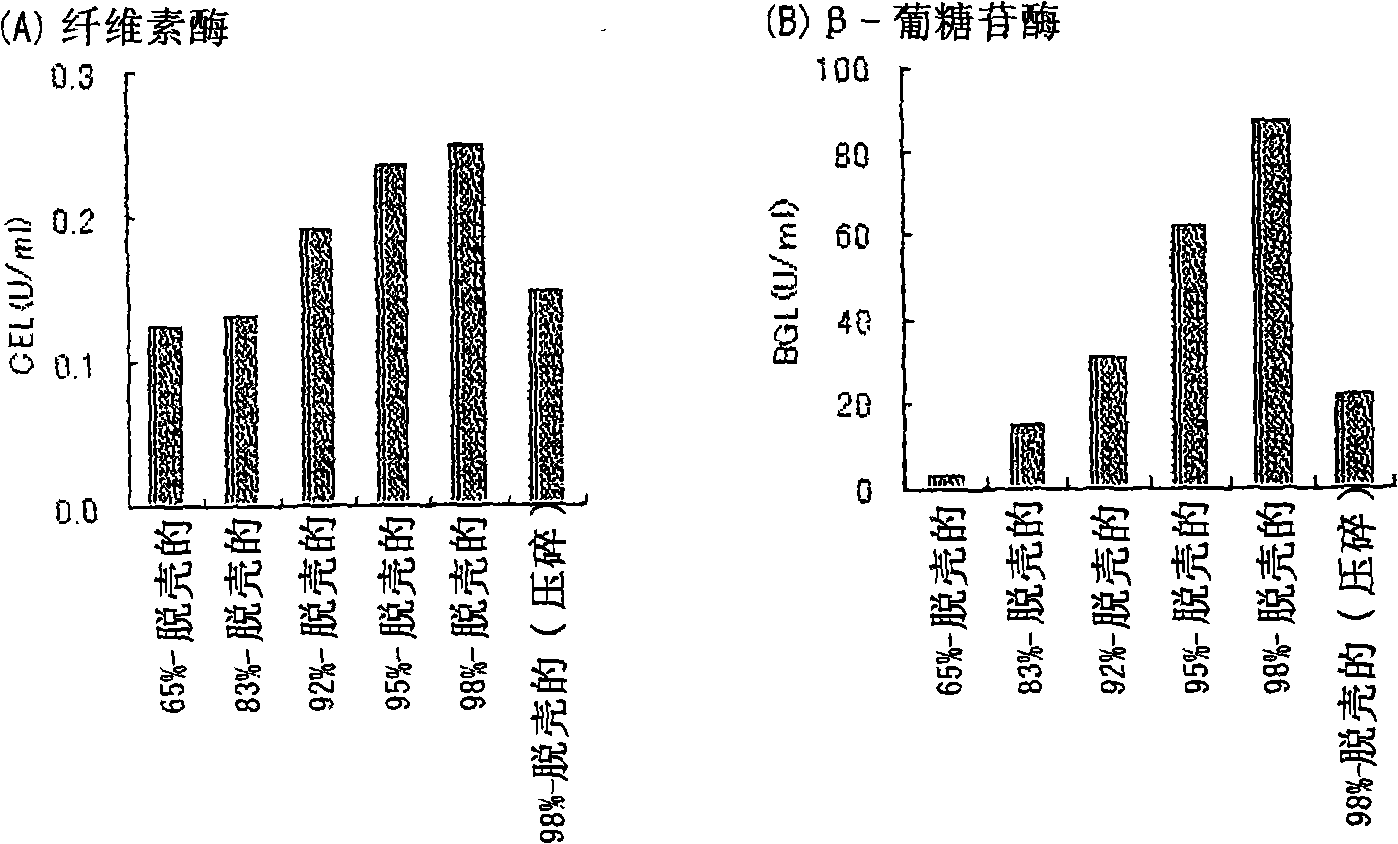
[0147] Production of white koji culture products using barley with different husking ratios
[0148] By the method described below, using different degrees of hulled barley (Stirling, produced in Australia), the Aspergillus basilica culture product was produced, and the enzyme activity therein was measured.
[0149] 1. Pre-culture method
[0150] 8 g of 65%-hulled barley and 100 ml of water were placed in a 500-ml Erlenmeyer flask with baffles, and it was sterilized with an autoclave at 121° C. for 15 minutes to obtain a preculture medium. After cooling, Aspergillus kawachii NBRC4308 was treated with 1×10 6 / ml was inoculated in the pre-culture medium, and cultured with shaking at 37° C. and 100 rpm for 24 hours to obtain a pre-culture liquid.
[0151] 2. Main culture method
[0152]2g of any one of 65%-hulled barley, 83%-hulled barley, 92%-hulled barley, 95%-hulled barley and 98%-hulled barley, 0.2g potassium nitrate, 0.3g diphosphate Potassium hydrogen and 100 ml of wate...
Embodiment 2
[0162] Production of Aspergillus niger cultures using barley with different husking ratios
[0163] By using different degrees of hulled barley (Stirling, produced in Australia), Aspergillus niger culture products were produced by the method described below, and the enzyme activities therein were measured.
[0164] 1. Pre-culture method
[0165] 8 g of 65%-hulled barley and 100 ml of water were placed in a 500-ml Erlenmeyer flask with baffles, and it was sterilized with an autoclave at 121° C. for 15 minutes to obtain a preculture medium. After cooling, Aspergillus niger (Aspergillus awamori NBRC4388) was treated with 1×10 6 / ml was inoculated in the pre-culture medium, and cultured with shaking at 37° C. and 100 rpm for 24 hours to obtain a pre-culture liquid.
[0166] 2. Main culture method
[0167] 2g of any one of 65%-hulled barley, 83%-hulled barley, 92%-hulled barley, 95%-hulled barley and 98%-hulled barley, 0.2g potassium nitrate, 0.3g diphosphate Potassium hydrogen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com