Patents
Literature
33 results about "Mycology culture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
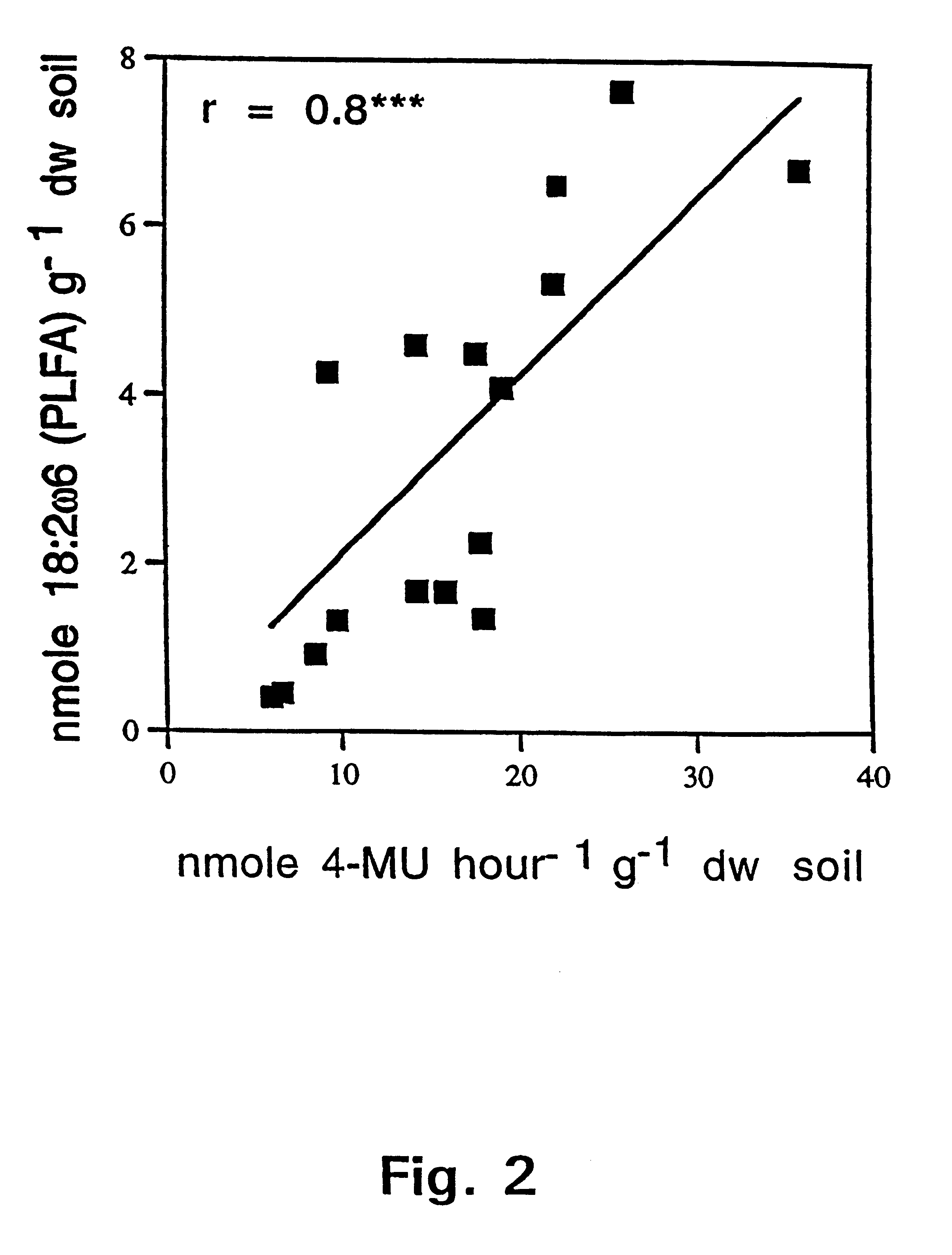
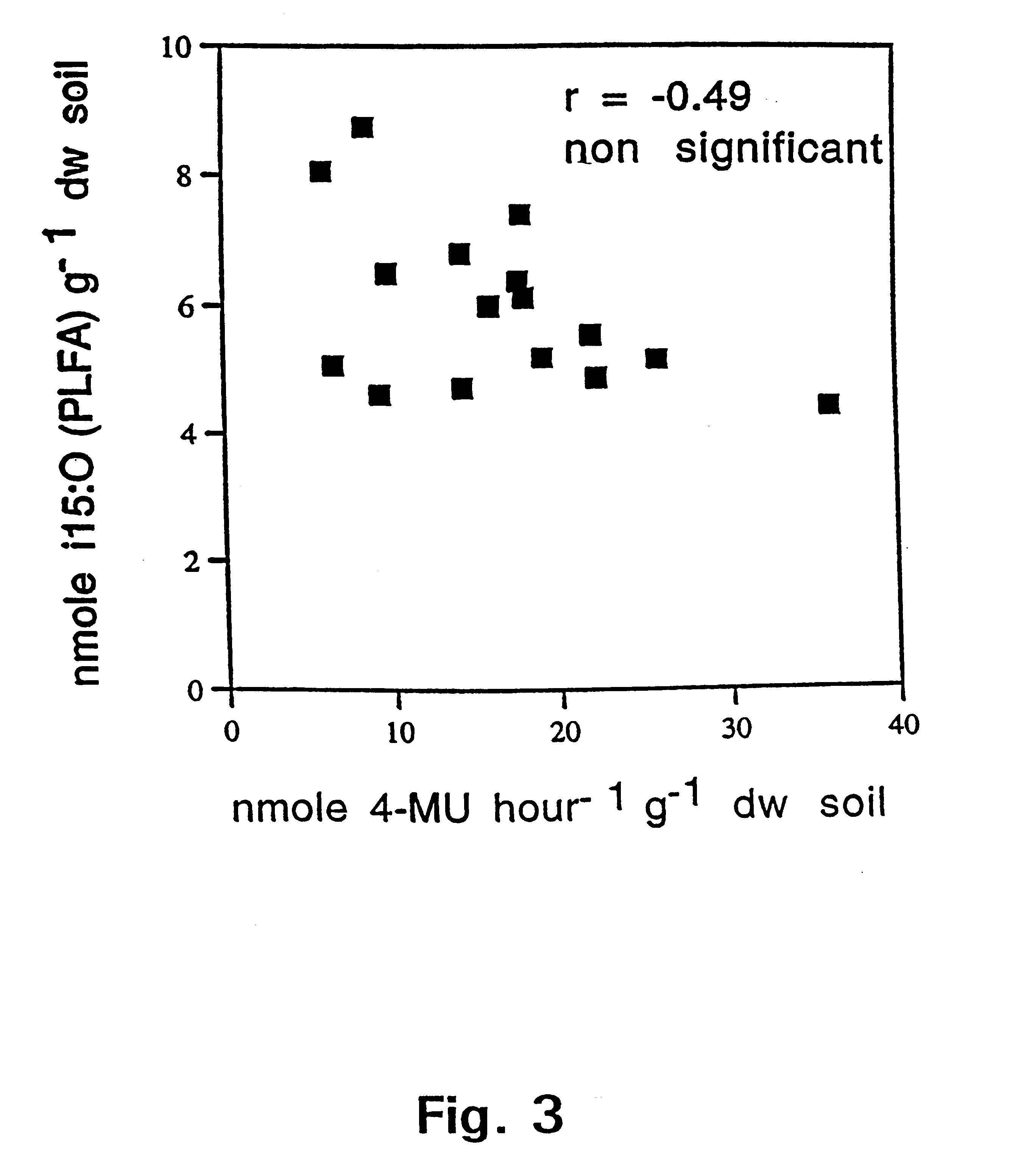
The Mycology Culture Collection Repository was established in 2007. The collection has approximately 5500 fungi comprising 204 genera and 392 species. The majority of fungi in the collection are of human origin, with a few of environmental and of animal origin.
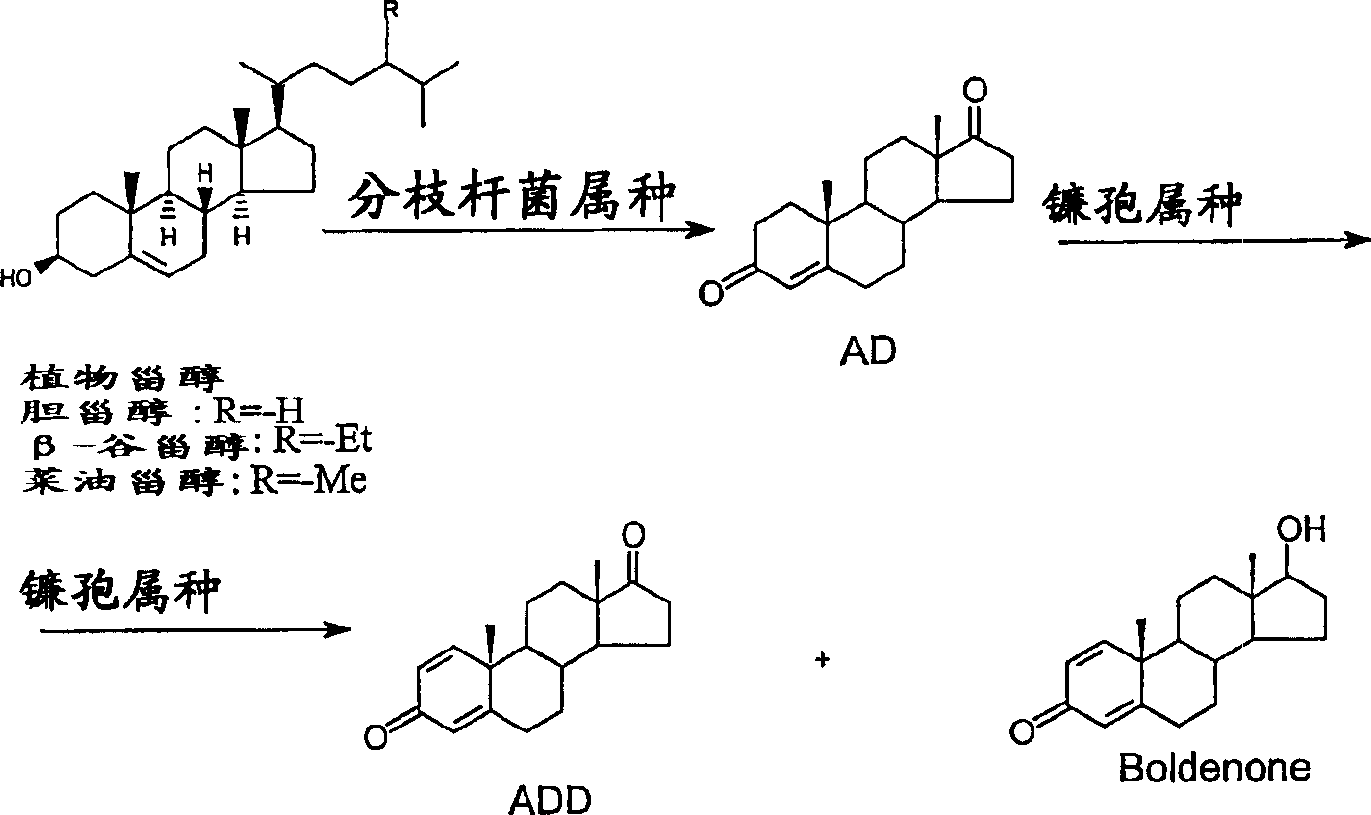
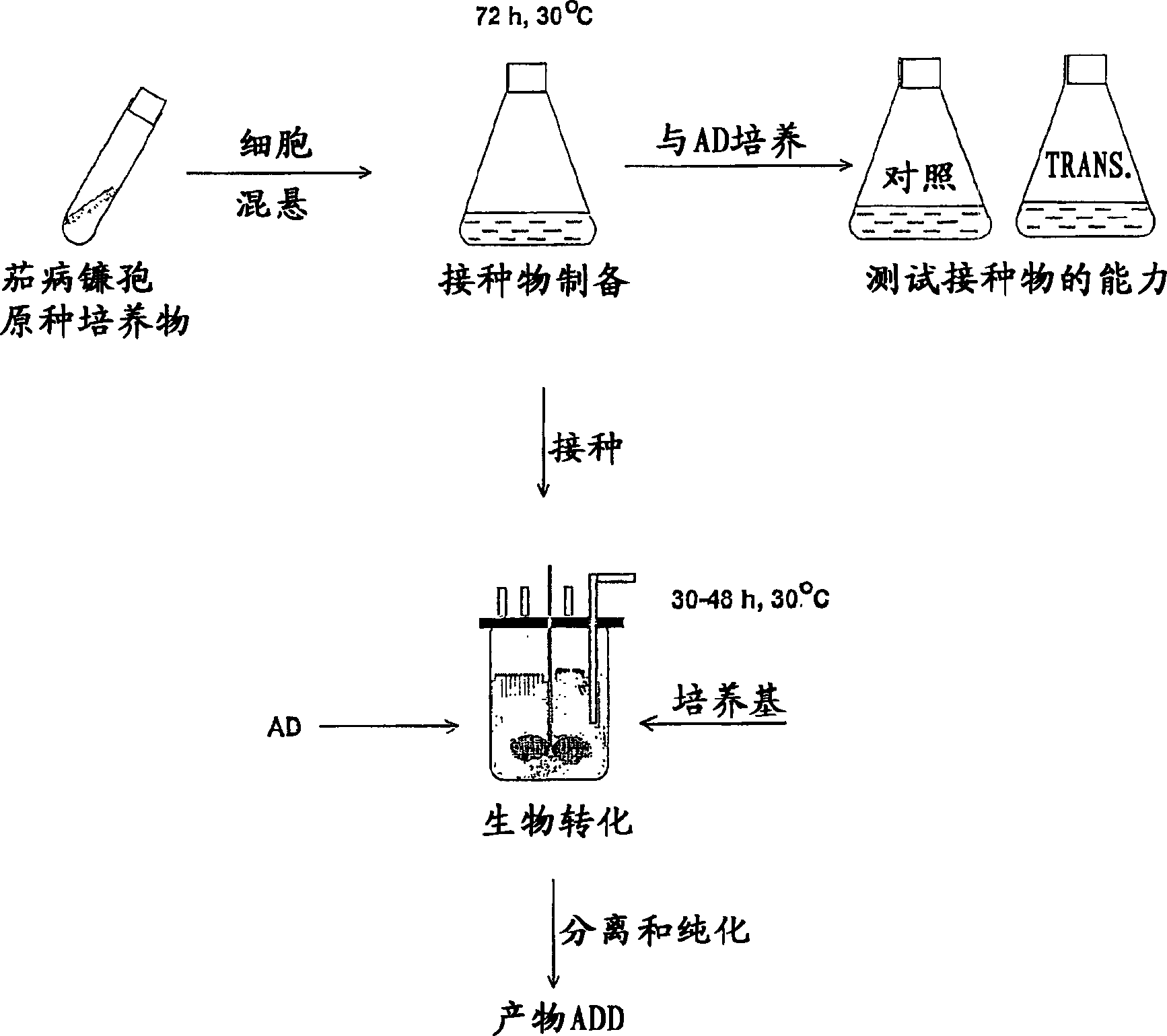
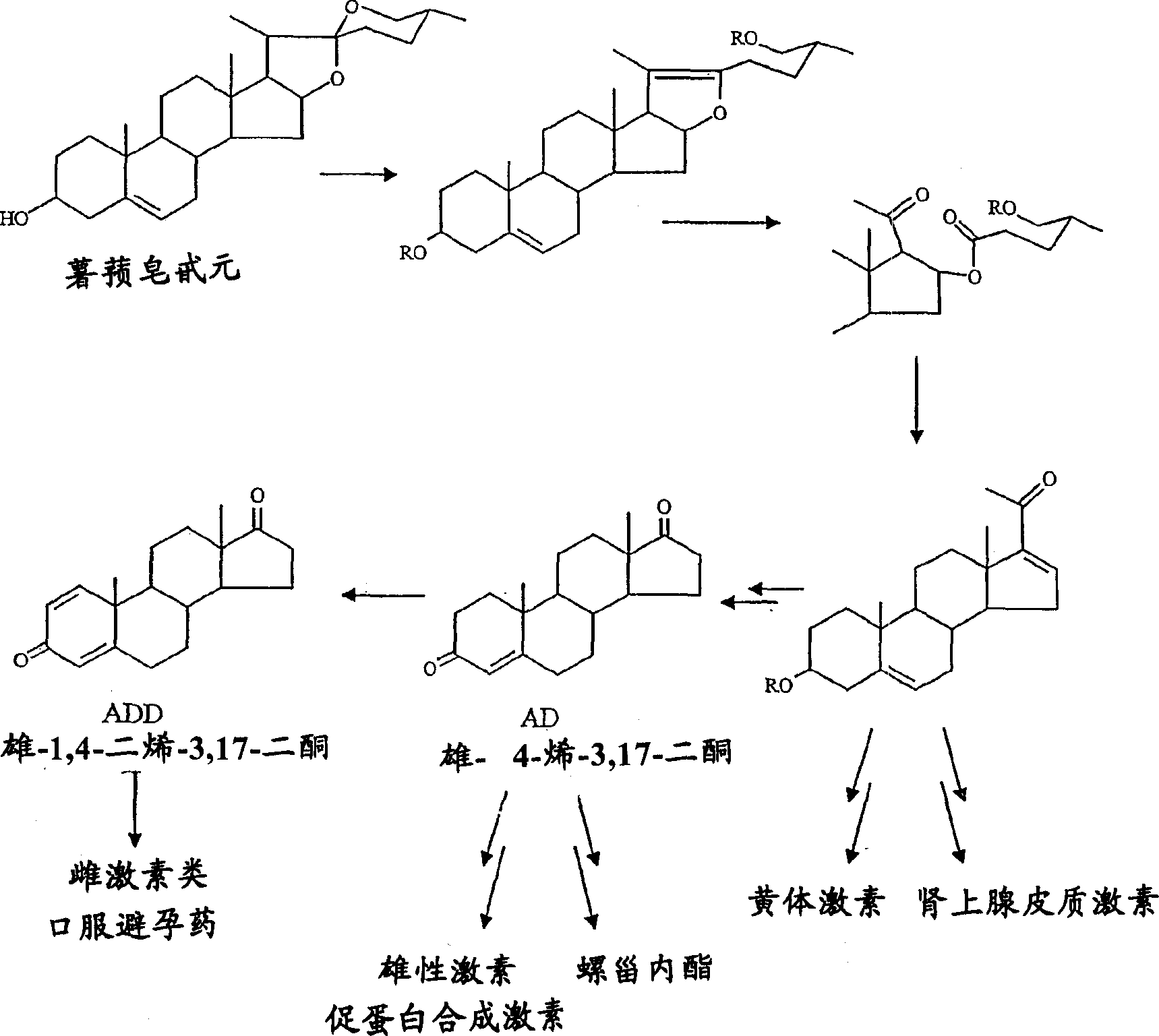
Process for fermentation of phytosterols to androstadienedione
A process of fermenting a phytosterol composition to produce androstenedione (androst-4-ene-3,17-dione) and subsequently androstadienedione (and rosta-1,4-diene,3,17-dione) comprises propagating a microbial culture of the genus Mycobacterium in a first nutrient medium, placing the microbial culture and the phytosterol composition in a bioreactor for a sufficient time to transform the composition substantially to androstenedione (the "AD solution"), propagating a fungal culture of the genus Fusarium in a second nutrient medium, and then injecting one or more of 1) Fusarium sp, or 2) the fungal culture medium into the bioreactor for a sufficient time to transform the AD solution to androstadienedione.
Owner:NV ORGANON
Methods of culturing fungi and producing cellulases and chitin
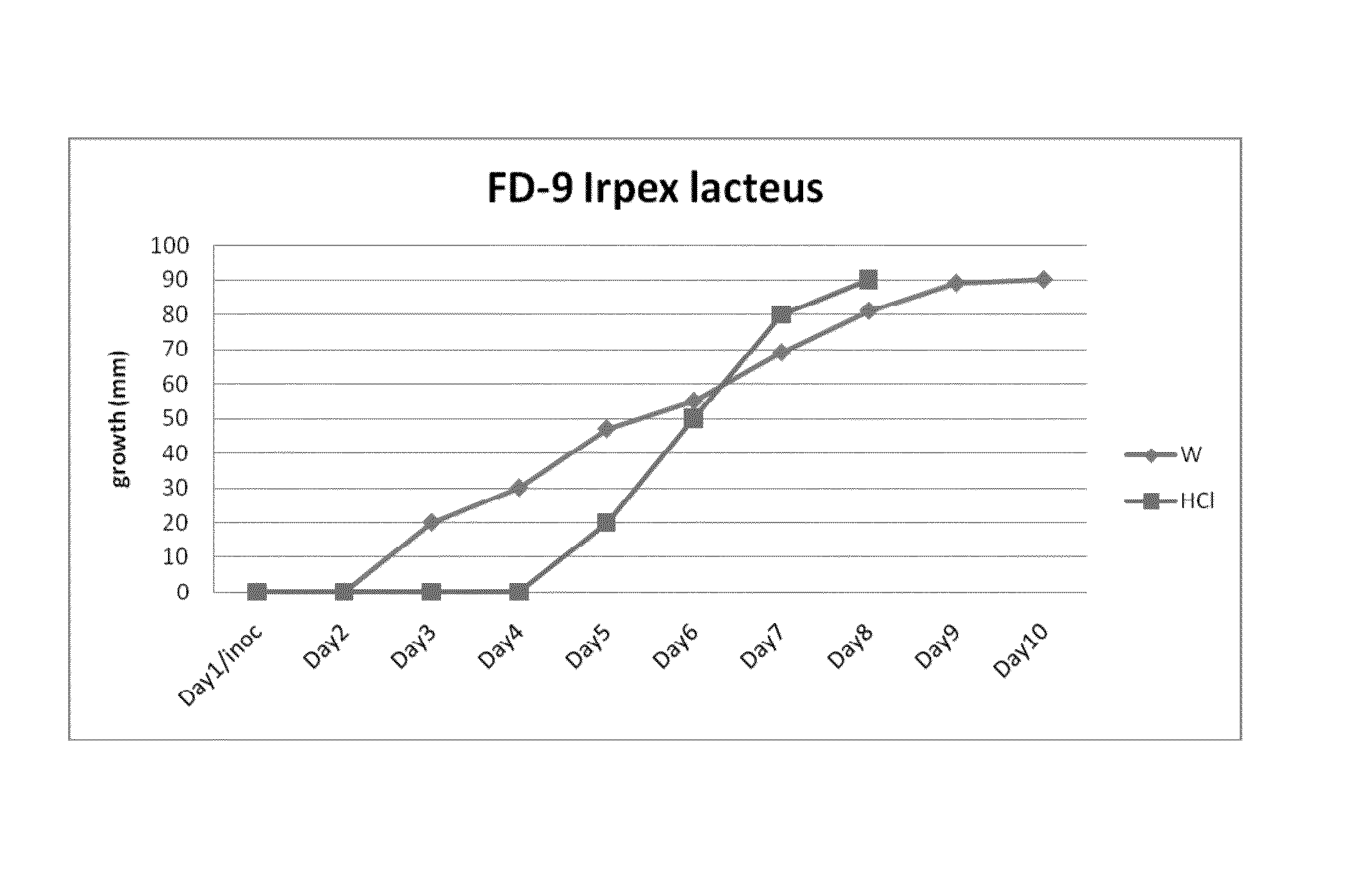
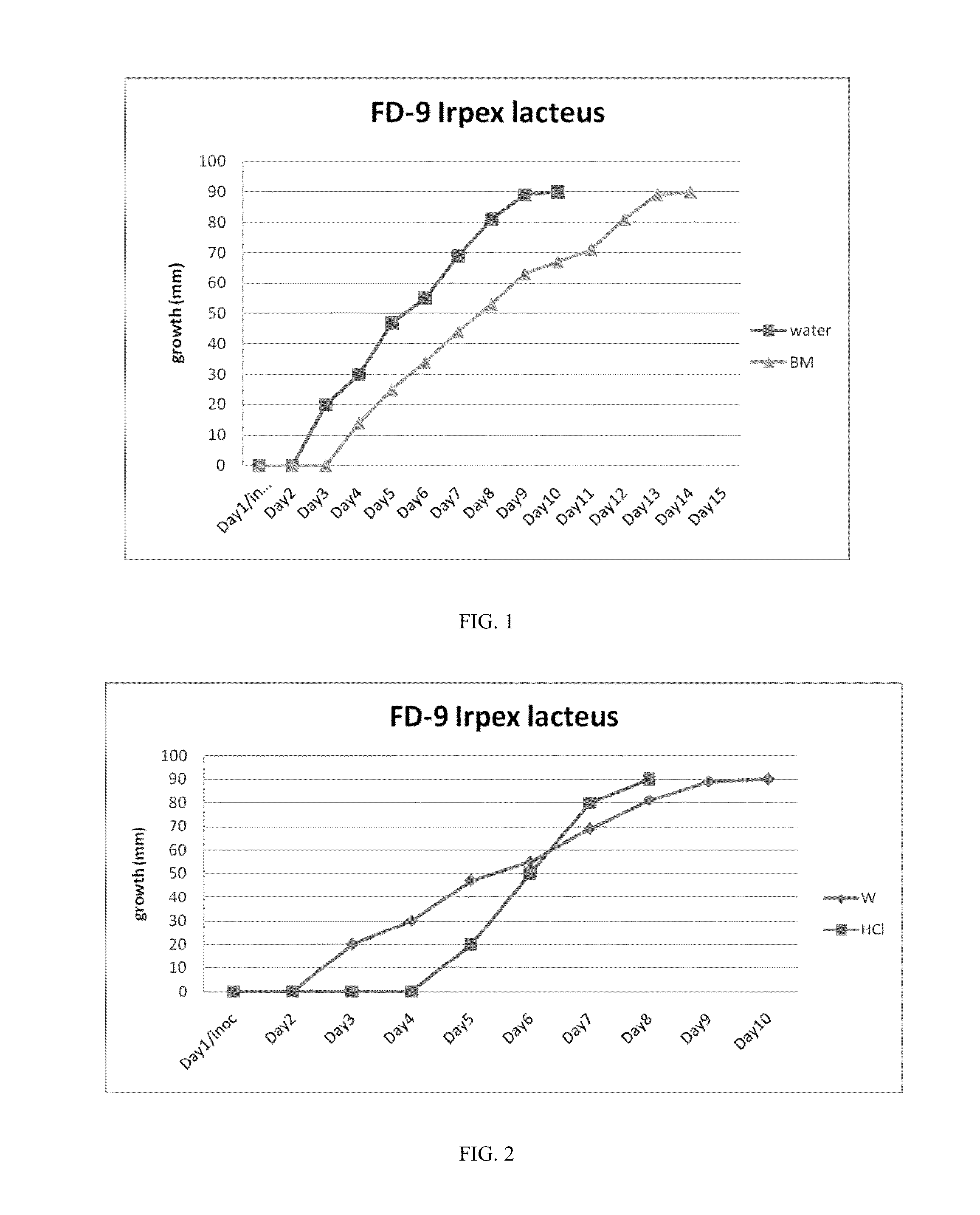
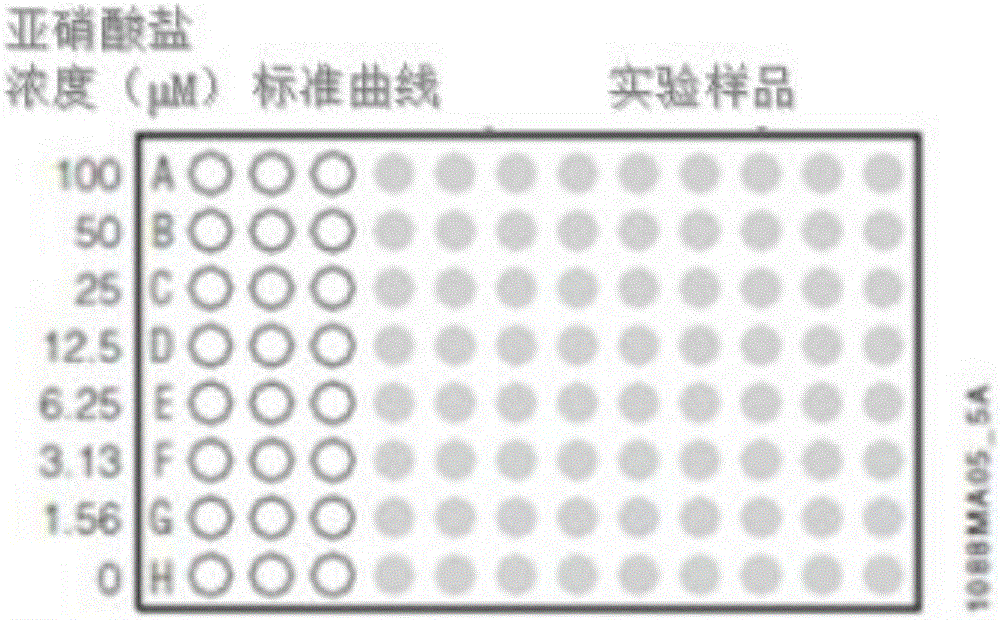
The fungus Irpex lacteus is efficiently cultured on a solid substrate with a high content of crystalline cellulose. The fungal culture can be used to produce cellulases that are useful in conversion of cellulose to sugars. The fungal culture can also be used to produce chitin, which is itself valuable and can also be converted to chitosan. Use of the fungal culture for co-production of cellulases and chitin is also described.
Owner:ECLIPSE BIOPROD +1
Fungus culture extract and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106497797ANo toxicityStrong inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsFungiDiseaseDipeptide
The invention is suitable for the field of biopharmaceutics, and provides a fungus culture extract and a preparation method and application thereof. The extract is a cyclic dipeptide compound which can be separated from a deep sea fungus fermentation culture of which the number is CCTCC M 2015628. The cyclic dipeptide compound has the high activity of inhibiting generation of nitric oxide (NO), has no toxicity on cells and can be applied to preparation of medicine for treating an Alzheimer disease.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Carbohydrate compositions from basidiomycete fungi as biocidal agents active against pathogens
InactiveCN101389764AShows pH-dependent growth rateShows temperature-dependent growth rateAntibacterial agentsBiocideBiotechnologyAnti fungal
The invention provides biologically active compositions comprising oligosaccharides, and which are produced by growing a fungal culture, and are at least partially purified for use. The compositions of the invention have antibacterial, antifungal and nematicidal activity, and are thus useful to reduce the impact of such pathogens on growing plants, to reduce the occurrence of such pathogens on surfaces and in substances, and to treat infections caused by such pathogens in animals and humans. The invention also provides methods for producing such compositions from certain fungal cultures.
Owner:ABR
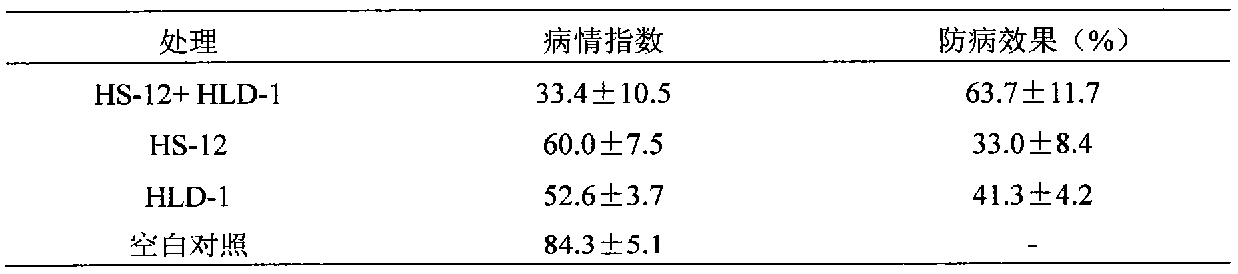
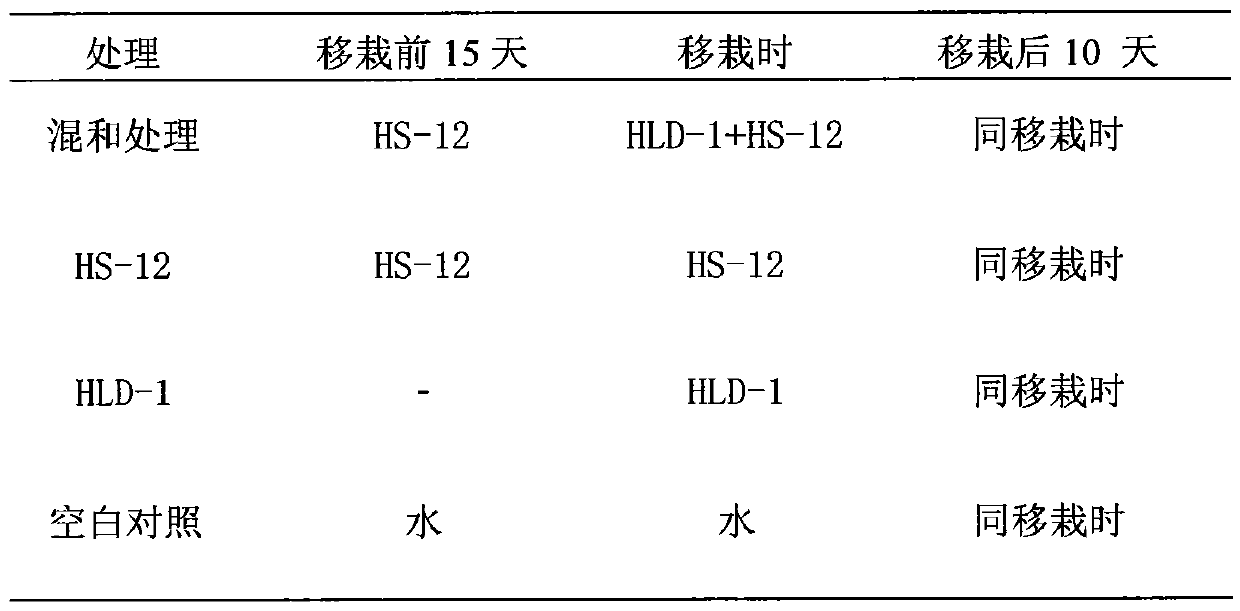
Biocontrol fungi mixing bacterial agent for preventing and controlling plant meloidogyne diseases, and applications thereof
The present invention relates to a fungi mixing bacterial agent for preventing and controlling plant meloidogyne diseases, and applications thereof, wherein two fungi cultures such as Purpureocillium lilacinum CGMCC No.9344 and Clonostachys rosea CGMCC No.1037 are cultured to prepare the fungi mixing bacterial agent. According to the present invention, the fungi mixing bacterial agent can be mixed with seedling breeding mediums, organic fertilizers and organic-inorganic compound fertilizers or be used separately so as to perform soil treatment or hole application before or after transplantation, or root-irrigation, and is used for preventing and controlling plant meloidogyne diseases.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Electroionic cellular agitation apparatus for influencing the metabolic cellular functions and method therefore
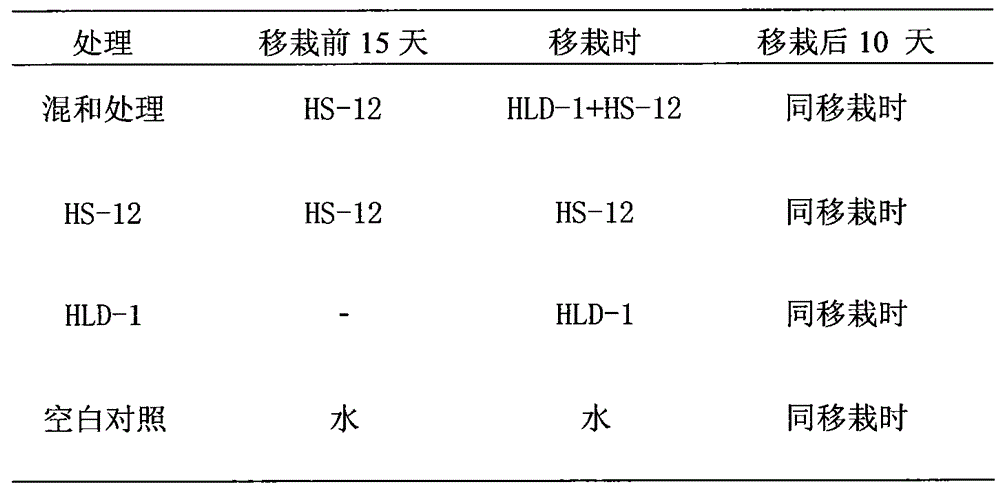
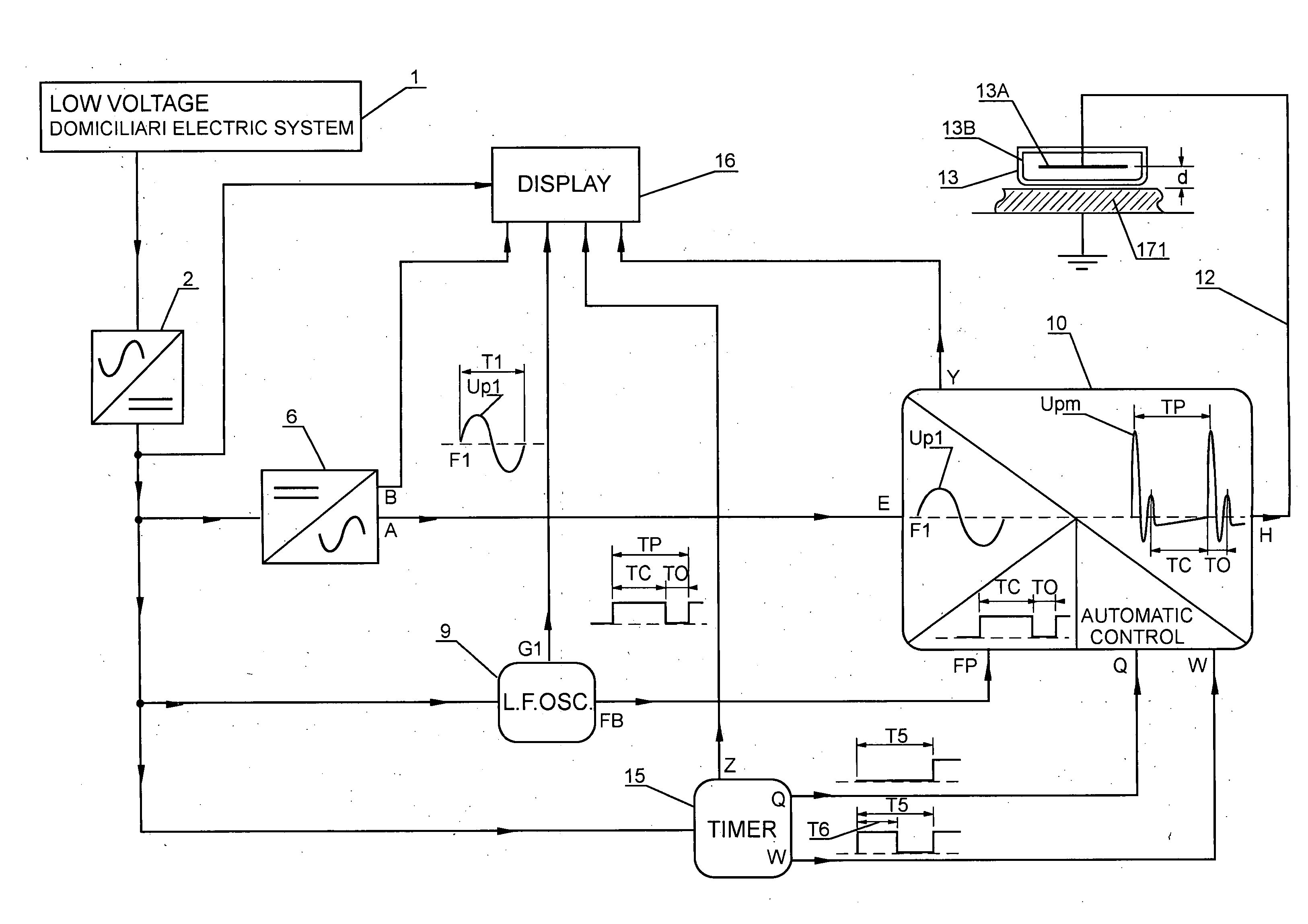
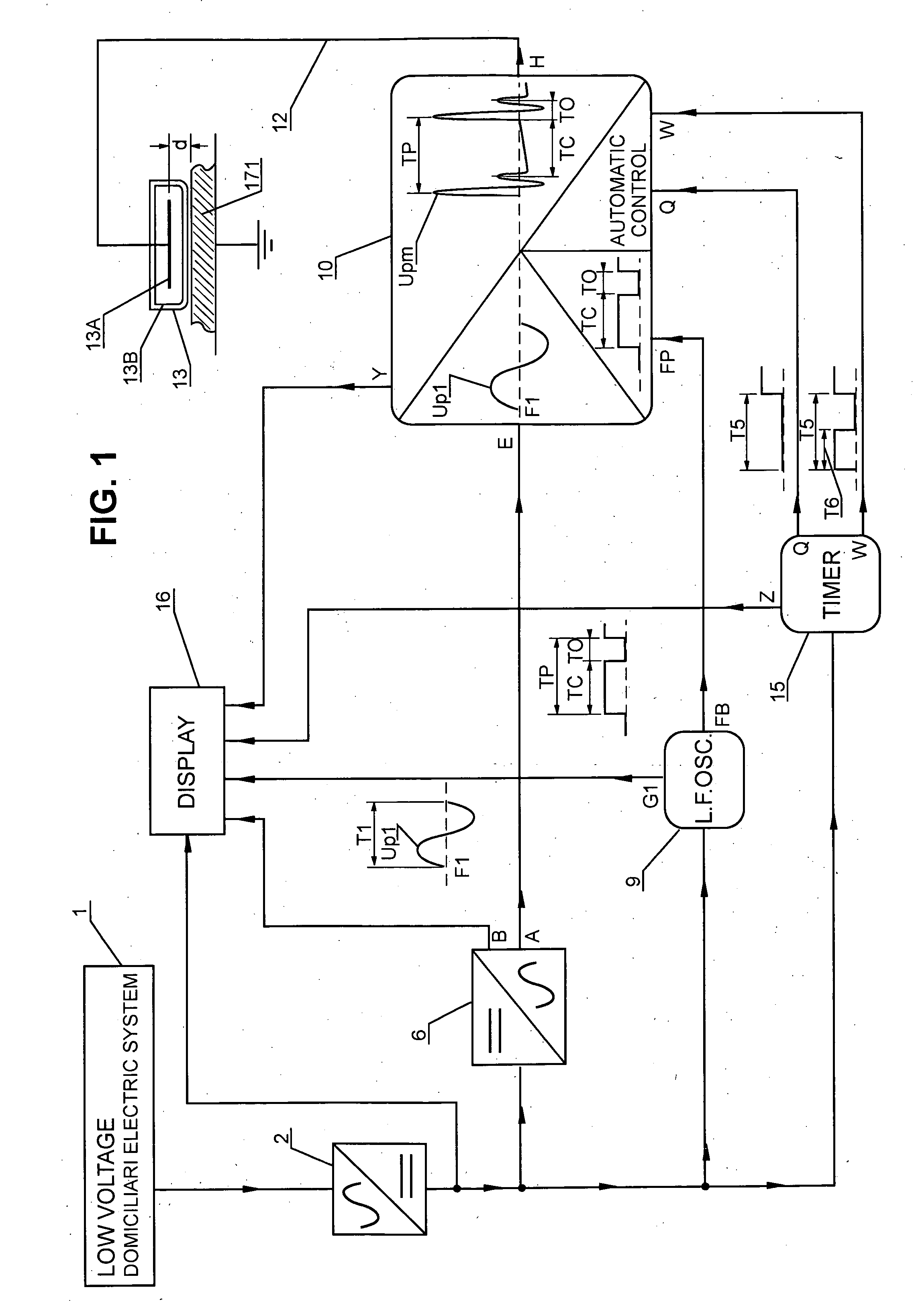
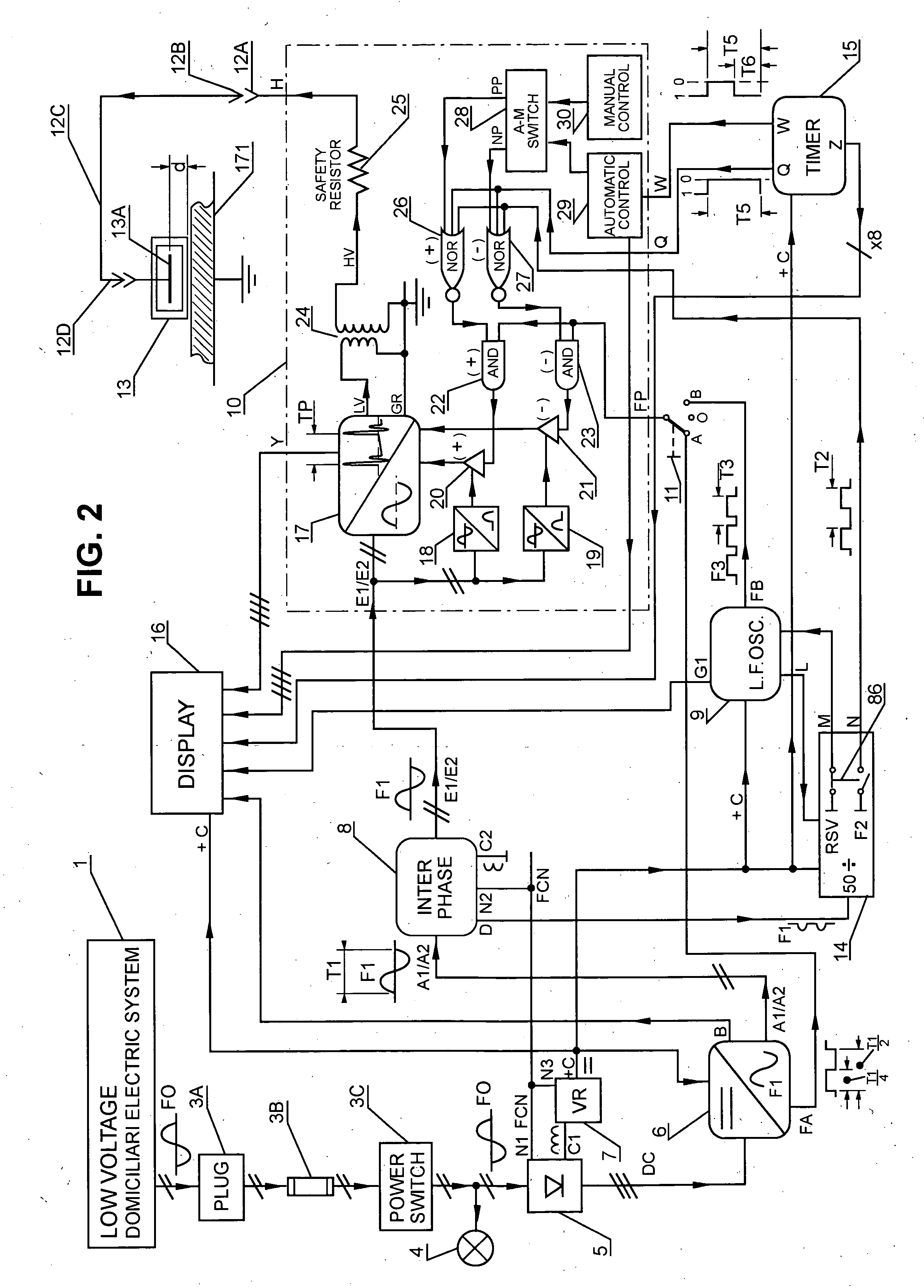
InactiveUS20060121590A1Increasing growth of biologicalSatisfied with the resultEnergy modified materialsElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentCapacitanceLiving systems
An electroionic cellular agitation apparatus for the biophysical stimulation of the cellular metabolism of live systems uses a generator emitting high-voltage pulses at time intervals typically comprised between 1 ms and 100 ms, corresponding to a pulse-frequency pf between 1,000 and 10 pulses / second, respectively, and which by means of a capacitive application device generates an electrical flow penetrating the soft and osseous tissues and originating short duration electrical impulsive forces on the ions situated within and outside the cells thus causing an ionic agitation influencing the metabolic characteristics to increase the development of bacterial and fungal cultures, soft and osseous live tissues, and also for the treatment of a variety of ailments, thus attaining an anticipated healing and the reduction of rehabilitation times. The range for the voltage and pulse frequency values are selected such that the RMS value of the electrical current density has a power level that does not cause any significant heating on said tissues.
Owner:SPEERLI RODOLFO C
Method for improving content of salidroside and tyrosol in rhodiola rosea tissue culture seedling
InactiveCN104212725AIncrease contentEasy to operateFungiMicroorganism based processesSalidrosideRHODIOLA ROSEA ROOT
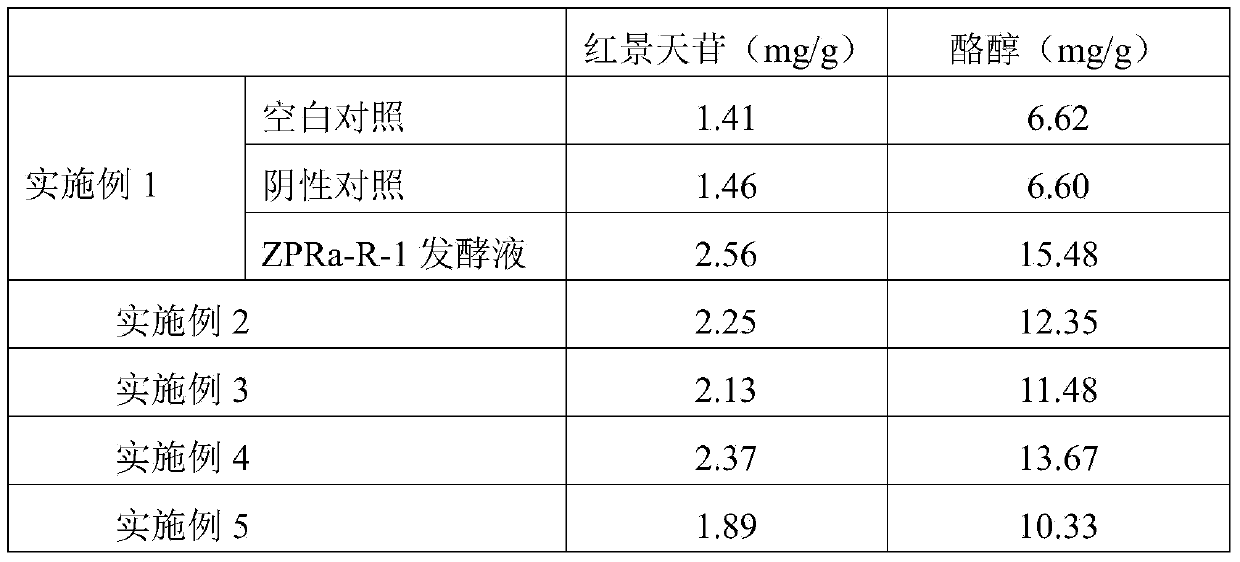
The invention provides a method for improving content of salidroside and tyrosol in a rhodiola rosea tissue culture seedling and particularly relates to a method for improving content of salidroside and tyrosol by means of co-culturing phialocephala fortinii with the preservation number of CGMCC No. 9347 and the rhodiola rosea tissue culture seedling. The method comprises the following steps: fungal culture and culture preparation; and co-culture of the fungal culture and the rhodiola rosea tissue culture seedling, wherein the culture conditions are as follows: illumination for 12-16 hours, temperature at 25-28 DEG C and humidity at 70-75%; non-illumination for 12-8 hours, temperature at 18-23 DEG C and humidity at 75-80%; and alternate culture for 10-30 days to obtain the rhodiola rosea tissue culture seedling with high content of salidroside and tyrosol. The highest content of salidroside can reach 2.56mg / g and the highest content of tyrosol can reach 5.48mg / g. The method is simple to operate and low in cost, and is an effective method for improving the content of salidroside and tyrosol in the rhodiola rosea tissue culture seedling under a low altitude condition.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Methods for lowering gluten content using fungal cultures
The present invention provides a method for the preparation of a gluten-containing grain having lowered levels of gluten. The method includes providing a prepared gluten-containing grain which may be optionally sterilized or pasteurized. The prepared gluten-containing grain is then inoculated with a prepared fungal component and incubated. In one embodiment the prepared fungal component myceliates the prepared gluten-containing grain while incubated and during this process hydrolyzes gluten in the prepared gluten-containing grain. The present invention also includes a gluten-containing grain having lowered levels of gluten which has been prepared by the methods of the invention.
Owner:MYCOTECH
Process for producing protein hydrolyzate
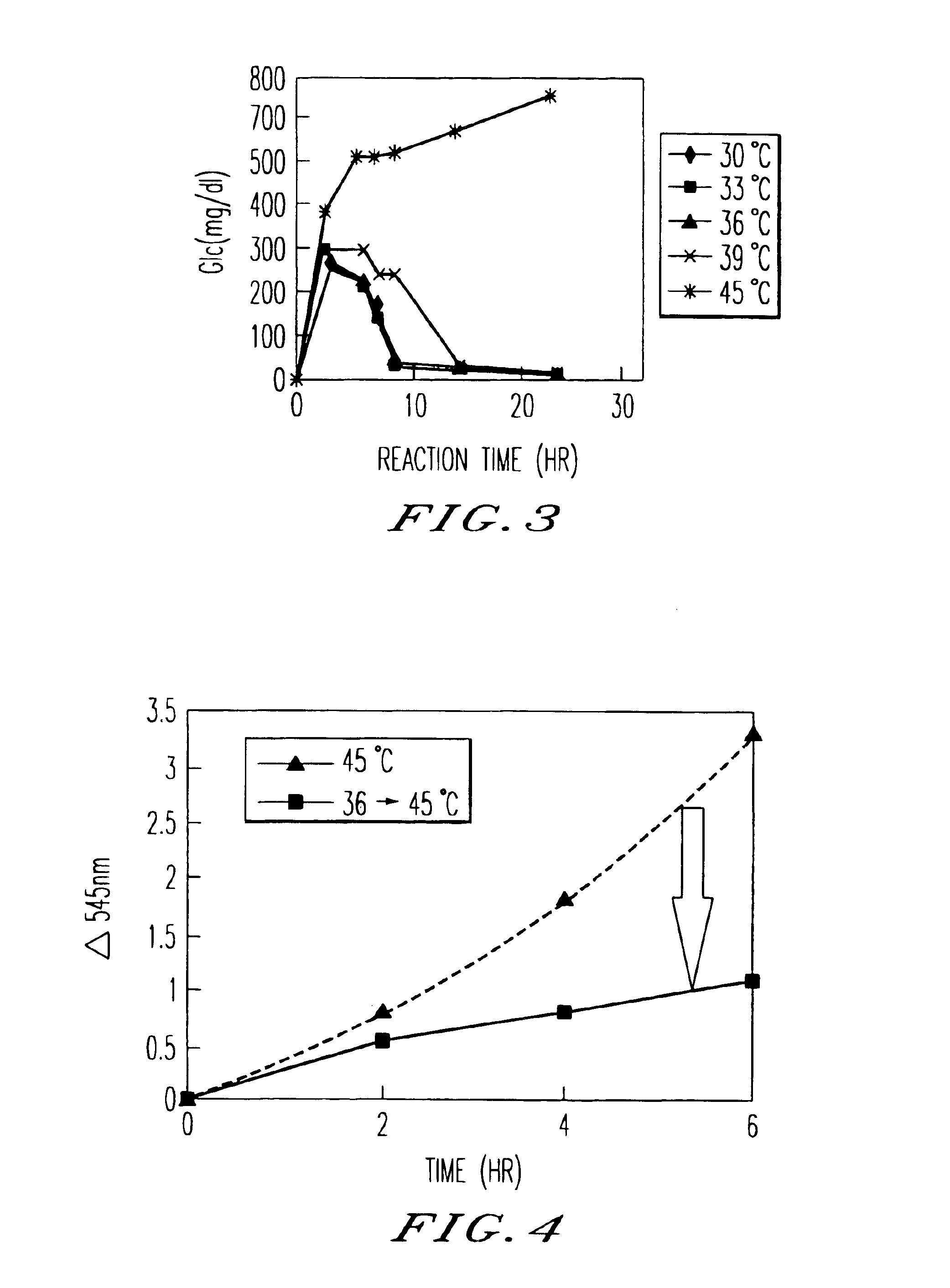
The present invention relates to a method which can prevent browning of hydrolyzed protein obtained by enzymatic hydrolysis of vegetable protein material.A vegetable protein material containing saccharides is mixed with the fungal culture and is subjected to enzymatic hydrolysis in a liquid reaction system. The reaction is conducted first at a temperature ranging from 15° C. to 39° C. with aeration and agitation, and then, after stopping the aeration, the reaction is conducted and completed at a temperature ranging from 40° C. to 60° C.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Extract of sea fungal culture and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101386818AStrong relaxant activityBacteriostaticFungiNervous disorderAdemetionineEthyl acetate
The invention discloses an extract for marine fungi culture, a preparation method thereof and application thereof. The extract is an oily matter prepared by the following steps: after seed culture and fermentation culture of marine fungi CCTCC M 208095, collection of culture fermentation broth, extraction of the fermentation broth by ethyl acetate and concentration and drying of the residual matter. The extract has the advantages of resisting pathogenic bacteria and oral cancer cells KB and inhibiting acetylcholinesterase, topoisomerase I, and a drug-resistant strain KBv200 of the extract, and can be used for preparing antibacterial and antineoplastic medicines for treating senile dementia.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
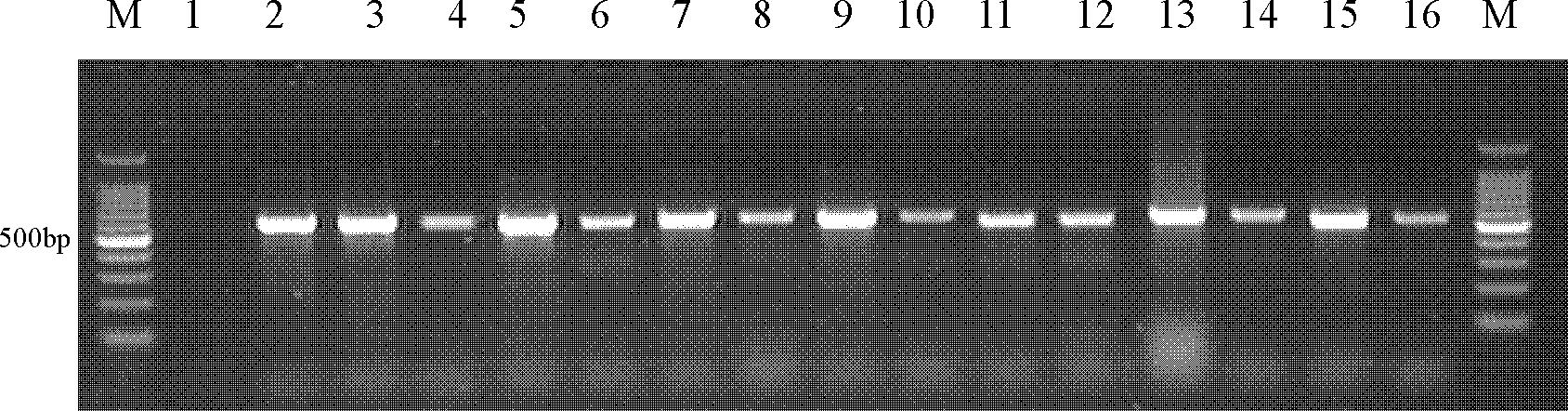
Fungus colony polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method and pathogenic fungus identification method
ActiveCN101851684AIncrease positive rateShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementFungal geneGenomic DNA
The invention relates to a fungus colony PCR method and a pathogenic fungus identification method. The fungus colony PCR method aims to achieve the high positive rate of amplification, and the pathogenic fungus identification method aims to achieve short detection time and reliable results. The fungus colony PCR method comprises the following steps of: inoculating fungus cultures onto a culture medium for culture; taking fungus colonies which begin to appear on the culture medium as experimentally available colonies; and preparing a DNA template for colony PCR amplification. The pathogenic fungus identification method comprises the following steps of: inoculating clinical sample cultures or pathogenic fungus cultures onto the culture medium for culture; taking the colonies which begin to appear on the culture medium as the experimentally available colonies; preparing the DNA template for the PCR amplification; and detecting amplification products. The fungus colony PCR method and the pathogenic fungus identification method have the advantages of improving the positive rate of the fungus colony PCR amplification, solving the problems of complex steps, wall-breakage difficulty, longtime and the like in fungus genomic DNA extraction, performing colony identification at the very beginning of the growth of pathogenic fungi, and achieving reliable results and identification time remarkably shorter than conventional fungus phenotype identification time.
Owner:CHUGOKU IGAKU KAGAKUIN HIFUBIYOU KENKYUSHO
Method of treating drains using fungus cultures
A method of treating drain systems containing organic matter and providing a pesticide for killing insects is provided. Introducing a bacterial culture into a drain system that is operable to metabolize organic matter will reduce the quantity of the organic matter in the drain system. Introducing a biocidal amount of fungus culture such as, Metarhizium, into the drain system allows for exposure of the fungus to insects which feed on the organic matter in the drain system. The insects, once infected, will spread the fungus to other insects. The fungus, provided in suitable quantities, will kill the insects. The insect is infected through contact or ingestion. The drain system can be a residential or commercial drain system. The fungus can be intended to kill insects that are cockroaches or other soft-bodied insects. The bacterial cultures can be separately sprayed into the drain or dispersed together into the drain with the fungus. The bacterial cultures and the fungi are maintained separately and then mixed for the treating of the drain. The cultures are maintained together prior to introducing them into the drain. The cultures can be dispersed as a spray, a powder, a liquid, or a foam.
Owner:OSPREY BIOTECHNICS
Method of selectively determining a fungal biomass
InactiveUS6372446B1High sensitivityAvoid selectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisChitinaseChitin synthase
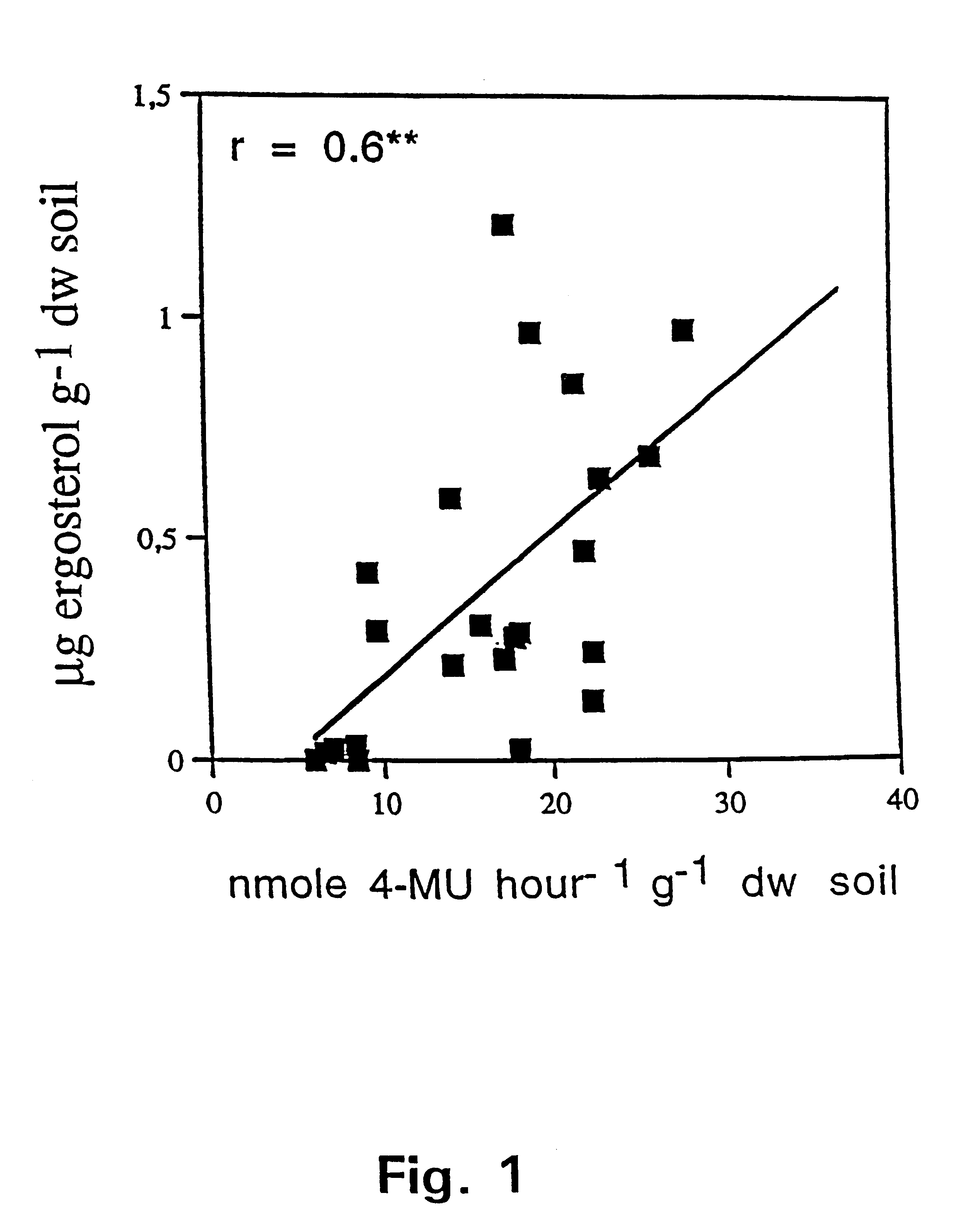
A method for selectively determining a fungal biomass by detection of a fungal enzymatic activity that is present in substantially all fungal species, such as enzymes involved in chitin metabolism (chitinase, chitin synthase, chitosanase, N-acetyl-glucosaminidase and beta-N-acetylhexosamidase). The invention can be used for detecting a fungal biomass in environmental samples, food products, plant material, building materials, industrial fungal cultures or sample from a human being or animal including blood samples. In particular, 4-methylumbelliferyl-N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminide is used as substrate for beta-N-acetylhexosamidase (EC 3.2.1.52). This enzyme activity correlates with the amount of fungal biomass present in a sample.
Owner:MYCOMETER
Liquid preparation capable of degrading petroleum pollutants
InactiveCN105385645APromote degradationStrong complementarityFungiBacteriaPhanerochaeteBacterial strain
The invention discloses a liquid preparation capable of degrading petroleum pollutants. The liquid preparation consists of a fungus liquid cultural substance, a bacterial liquid cultural substance and a degradation accelerant, wherein the mixing ratio of the fungus liquid cultural substance and the bacterial liquid cultural substance is 1: (0.1 to 10); the fungus liquid cultural substance is a single plant liquid cultural substance of cunninghamella echinulata or white-rot fungus phanerochaete chrysosporium, or a mixture of the two fungus liquid cultural substances, the content of fungi in the fungus cultural substances is 10 to 80mg dry weight / ml; the bacterial liquid cultural substance is a liquid cultural substance of a bacterial strain with the capability of petroleum hydrocarbon degradation, and the bacterial content is 106 to 1012 pieces / ml; the degradation accelerant is barbaloin, and the concentration in the liquid preparation is 0.2 to 0.6mg / ml. The degradation accelerant provided by the invention can obviously improve the degradation ability of fungi and bacteria to the petroleum pollutants.
Owner:叶君芝
Method for observing and identifying filamentous fungi
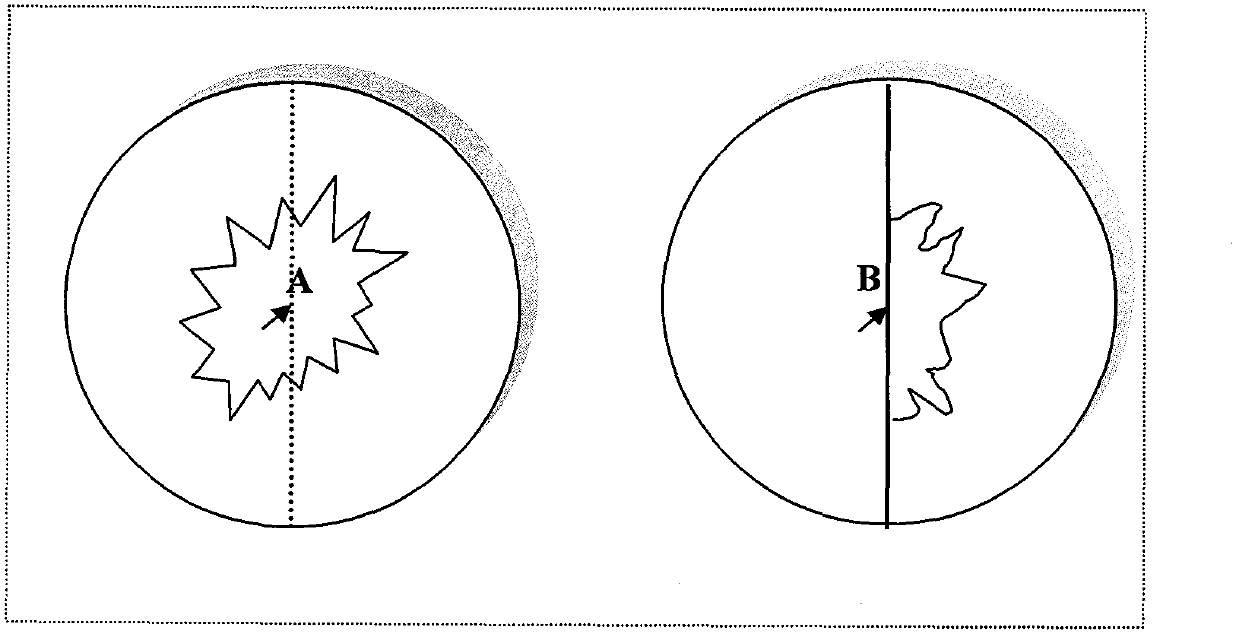
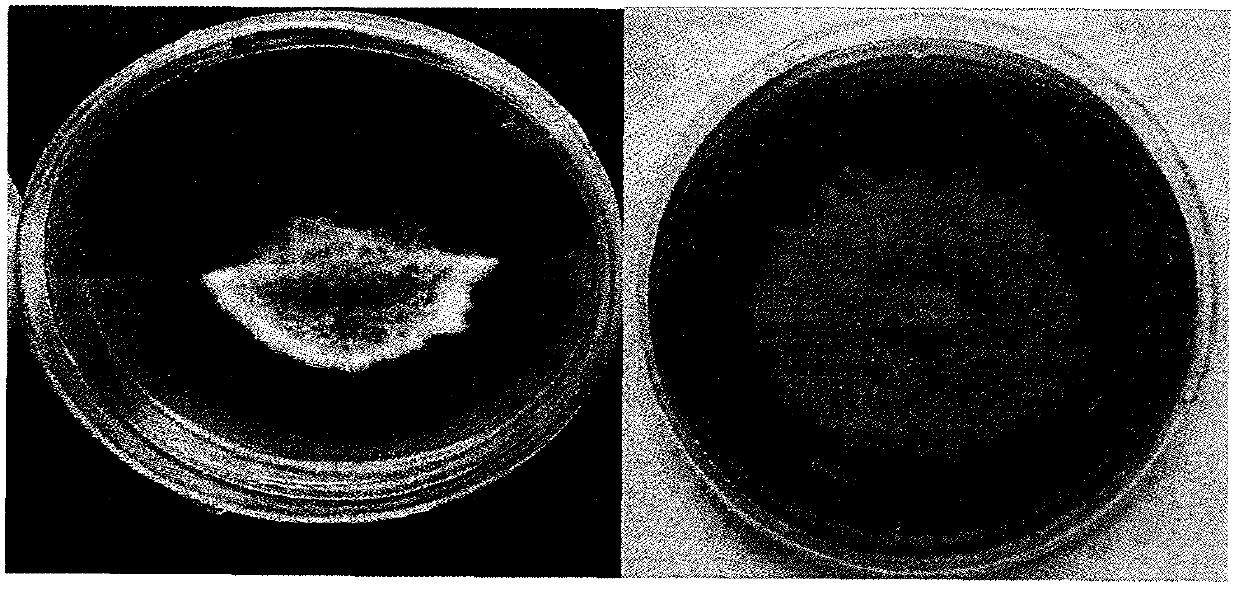
Disclosed is a method for observing and identifying filamentous fungi. The method includes the steps of adding a potato dextrose agar (PDA) culture medium into a culture dish first, cutting the PDA culture medium by using an operating knife along the diameter of the culture medium and perpendicular to the bottom of the culture dish after the PDA culture medium condenses, removing half of the culture medium, selecting to-be-identified fungus culture and inoculating the to-be-identified fungus culture to the middle of the connection portion of the culture medium and the bottom of the culture dish, covering the culture dish with a culture dish lid, carrying out marking after sealing the culture dish through a parafilm, and culturing the culture medium in dark at the temperature of 28 DEG C. After culturing is finished, the fungi grow into half of a normal bacterial colony in half of the culture dish with the culture medium, and bacterial colony characteristics can be observed; and hyphae grow sparsely in the other half of the culture dish without the culture medium, and the hyphae can be micro-observed when the culture dish is inversely placed. The method for observing and identifying the filamentous fungi has the advantages that flaking is not needed, fungus individual form observation and colony form observation are combined, operation is simple, convenience and quickness are achieved, the hyphae and the bacterial colony, in a naturally-growing state, of strain can be observed in real time at the same time, accuracy of identifying work for the filamentous fungi can be guaranteed, cost is saved, and workload is reduced.
Owner:FARMING & CULTIVATION RES INST OF HEILONGJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +2
Method and device for the control of formation and propagation of bacterial cultures, viral, fungal cultures, mildew, and micro organisms etc. on the condenser coil in larger refrigeration systems
InactiveCN103096942AEasy to spreadEliminate odorSafety devices for heat exchange apparatusEvaporators/condensersUnit operationEngineering
There is specified a method and a device for combating of formation of and propagation of bacteria cultures and microorganisms etc. on the condenser surfaces (28) in refrigeration plants / units (4). The method is peculiar in that the cooling air and the condenser surfaces during operation is continuously illuminated with UV light in combination with a filter (12) treated with titanium oxide. The method is further supplemented with that the cooling air and the condenser in a period immediately subsequent to operation stop of the refrigeration plant / unit is radiated by with electromagnetic radiation generated by a high frequency generator (24). Performed tests with the device arranged in the refrigeration plant / unit (4) in a cooling container has shown that bacteria cultures and microorganisms etc. on the condenser surfaces (28) in refrigeration plants / units after relative short time is eliminated to an unprecedented minimum, subsequent to setting a device according to the invention in operation near by the condenser of the refrigeration plant / unit.
Owner:AIRVENTION
Methods for lowering gluten content using fungal cultures
The present invention provides a method for the preparation of a gluten-containing grain having lowered levels of gluten. The method includes providing a prepared gluten-containing grain which may be optionally sterilized or pasteurized. The prepared gluten-containing grain is then inoculated with a prepared fungal component and incubated. In one embodiment the prepared fungal component myceliates the prepared gluten-containing grain while incubated and during this process hydrolyzes gluten in the prepared gluten-containing grain. The present invention also includes a gluten-containing grain having lowered levels of gluten which has been prepared by the methods of the invention.
Owner:MYCOTECH
A Method of Obtaining Useful Material from Plant Biomass Waste
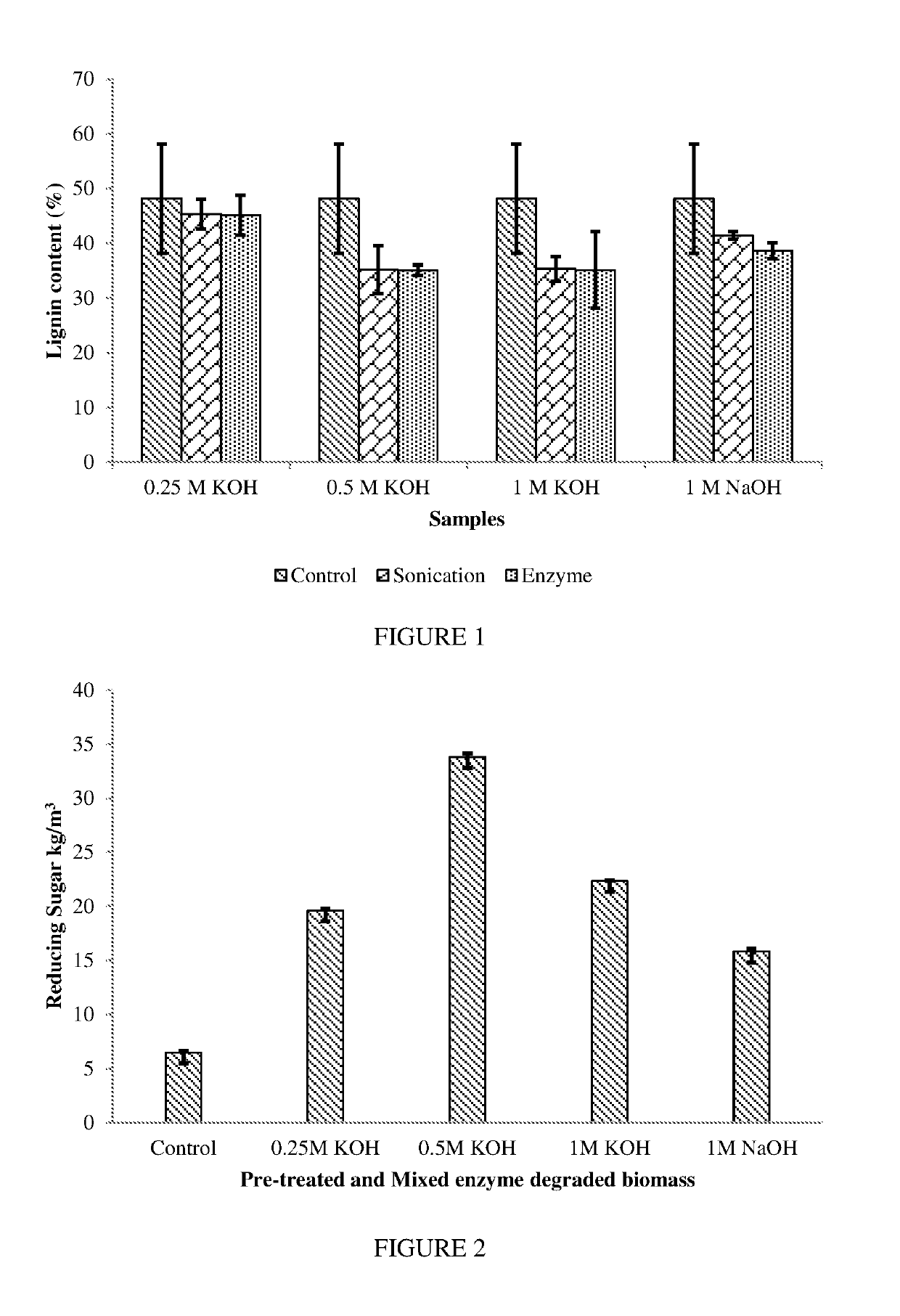
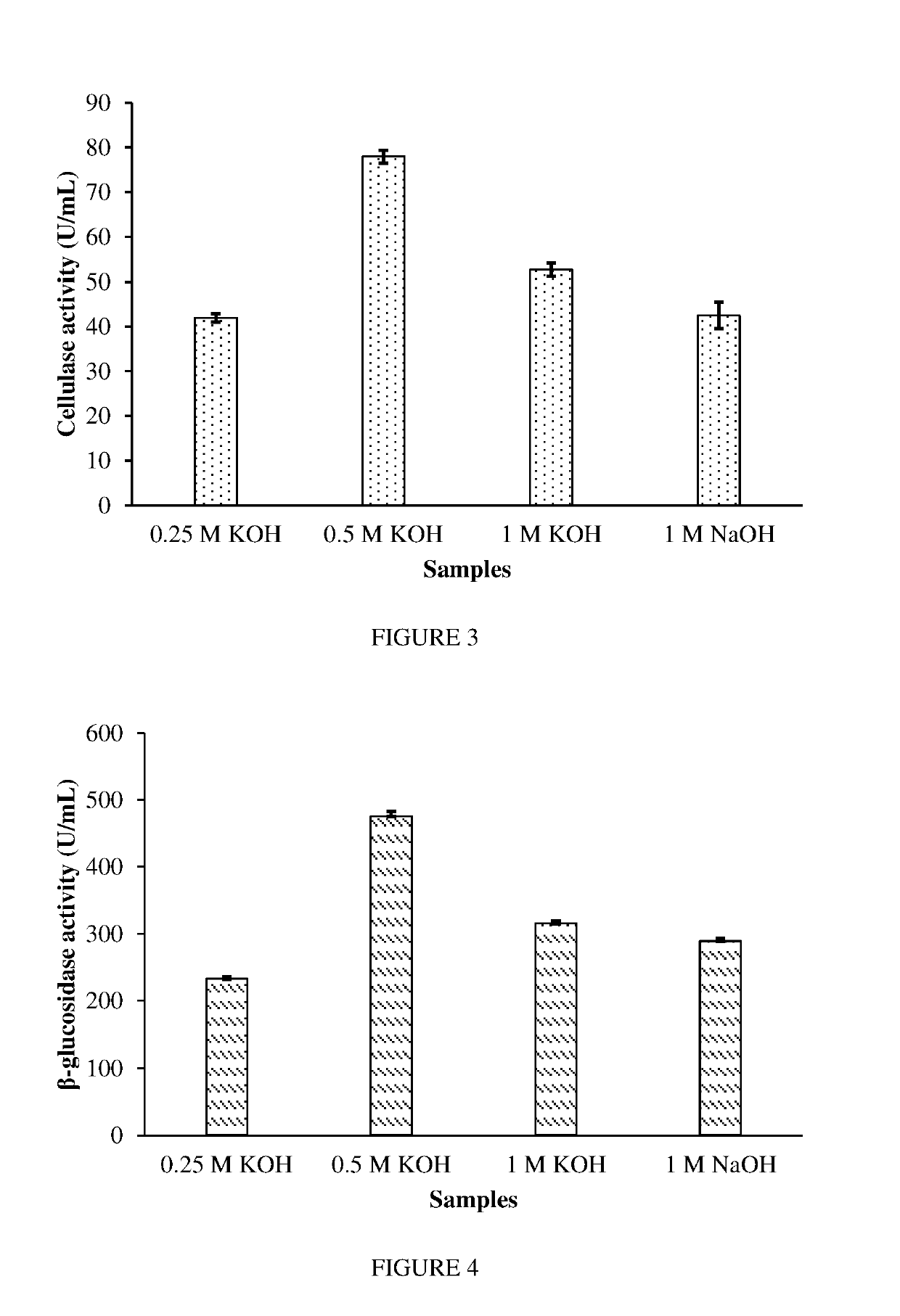
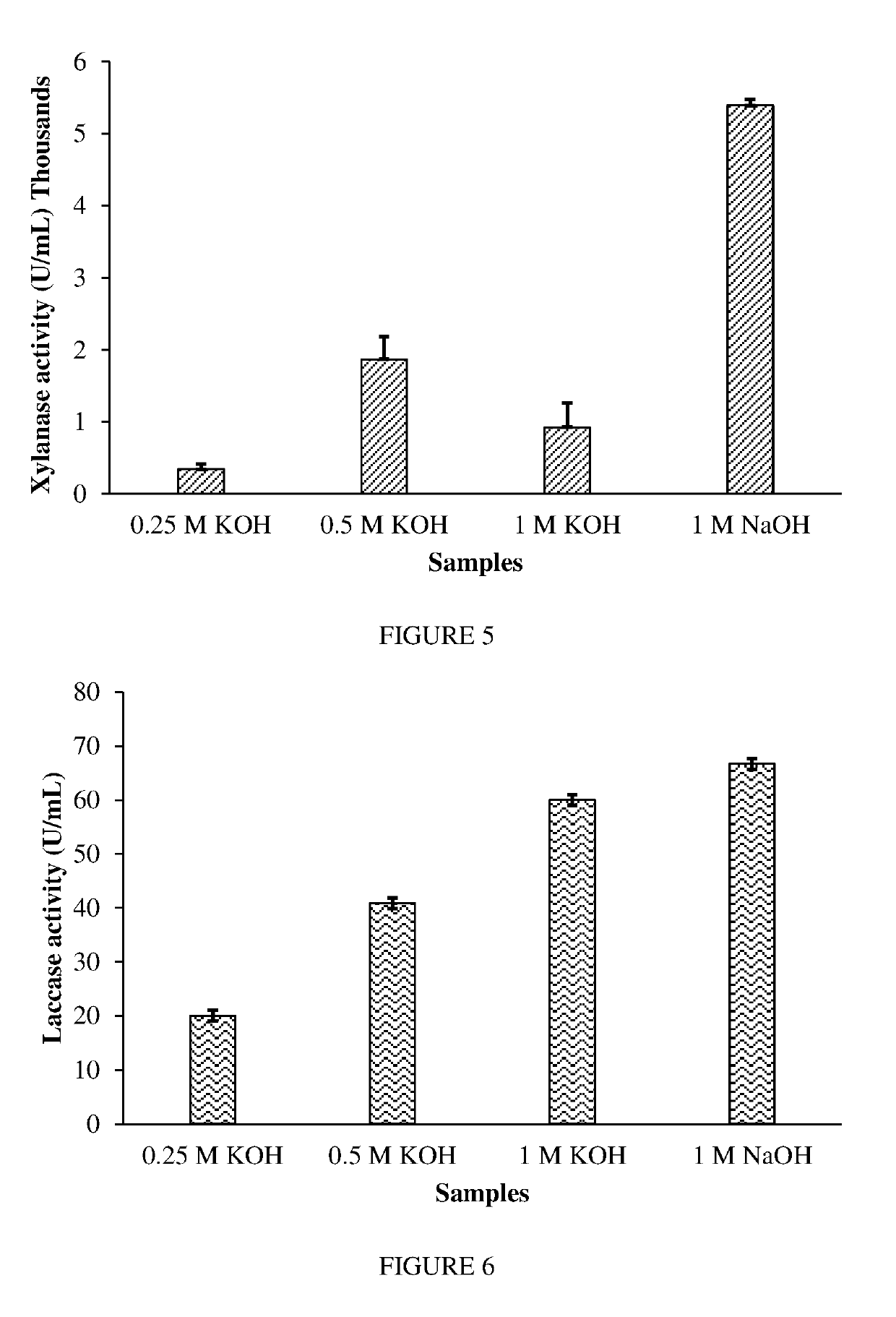
A method of obtaining useful material from plant biomass waste. The method uses sonication and / or microwave irradiation followed by sequential incubation with mixed fungal cultures. In particular, the method involves obtaining useful material from plant biomass waste comprising the steps of: a) subjecting the biomass waste to microwave irradiation and / or sonication; b) incubating the biomass waste from step a) with one or more enzymes extracted from Basidiomycete fungi; and c) incubating the biomass waste from step b) with one or more enzymes extracted from Ascomycete fungi.
Owner:VIRIDI INNOVATIONS PTY LTD
Extract of sea fungal culture and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101386818BBacteriostaticSignificant effect and effectFungiNervous disorderBiotechnologyEthyl acetate
The invention discloses an extract for marine fungi culture, a preparation method thereof and application thereof. The extract is an oily matter prepared by the following steps: after seed culture and fermentation culture of marine fungi CCTCC M 208095, collection of culture fermentation broth, extraction of the fermentation broth by ethyl acetate and concentration and drying of the residual matter. The extract has the advantages of resisting pathogenic bacteria and oral cancer cells KB and inhibiting acetylcholinesterase, topoisomerase I, and a drug-resistant strain KBv200 of the extract, and can be used for preparing antibacterial and antineoplastic medicines for treating senile dementia.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
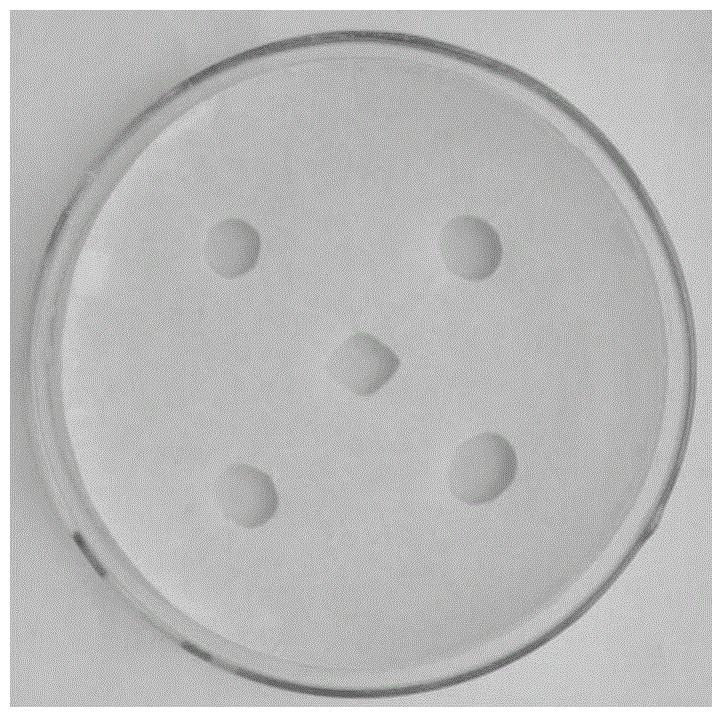
Manufacturing method of dry preserved specimen of hyphomycetes culture
ActiveCN104830697AEvenly distributedReduce moisture contentFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementDrying timeCulture mediums
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a dry preserved specimen of hyphomycetes culture. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: adding a prepared agar culture medium into a culture dish to manufacture an agar culture plate, paving wet filter paper with a plurality of holes on the surface of the agar culture plate, inoculating hyphomycetes strains on the centers of the filter paper holes, sealing the culture disc, placing the culture disc at a room temperature under the nature lights to obtain hyphomycetes culture; taking out the filter paper, placing the filter paper on another culture disc, fumigating the filter paper in a formaldehyde fumigating barrel for 6 to 8 days, and then naturally drying the filter paper in the air in a place with good ventilation so as to obtain the dry preserved specimen of hyphomycetes culture. The provided method has the advantages of simple operation and mild culture conditions; the spore yield of hyphomycetes is prominently increased, the method is effective for most hyphomycetes, conidia are evenly distributed on the filter paper, the observation on the conidia is convenient, the phenotype of conidia can be observed conveniently, moreover, the drying time of species is greatly shortened, and the efficiency and quality of species manufacturing are both improved.
Owner:WEIFANG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
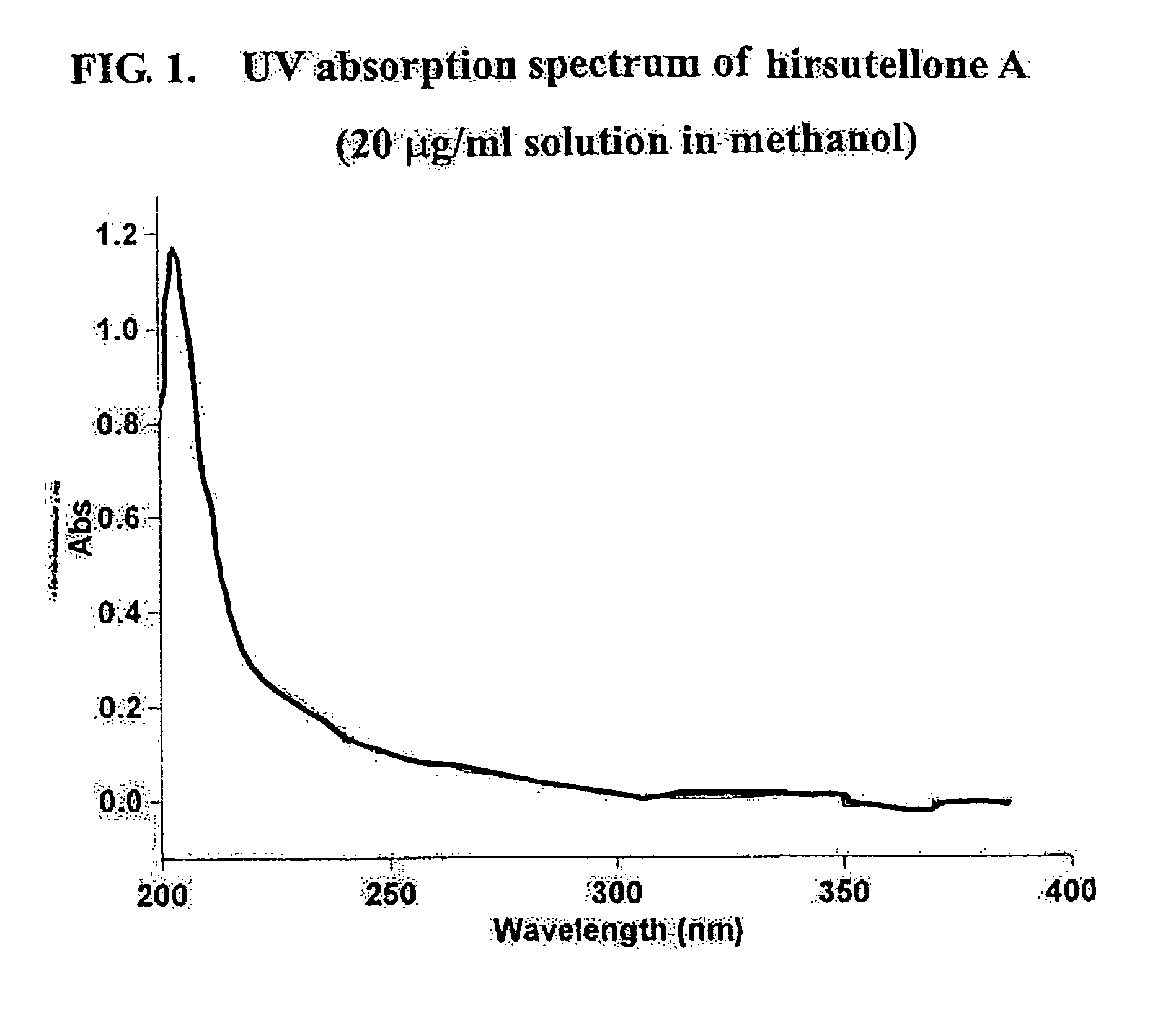
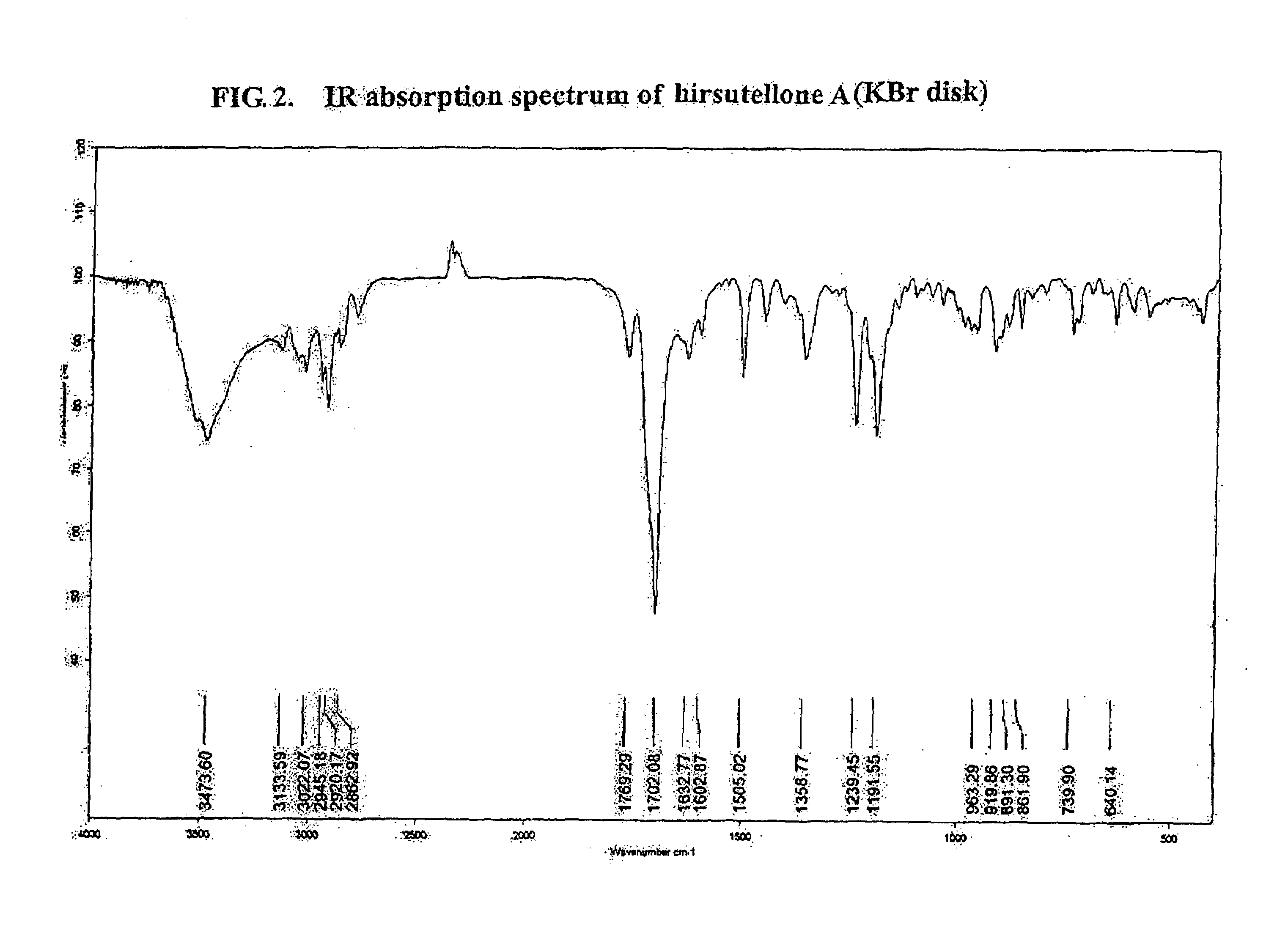
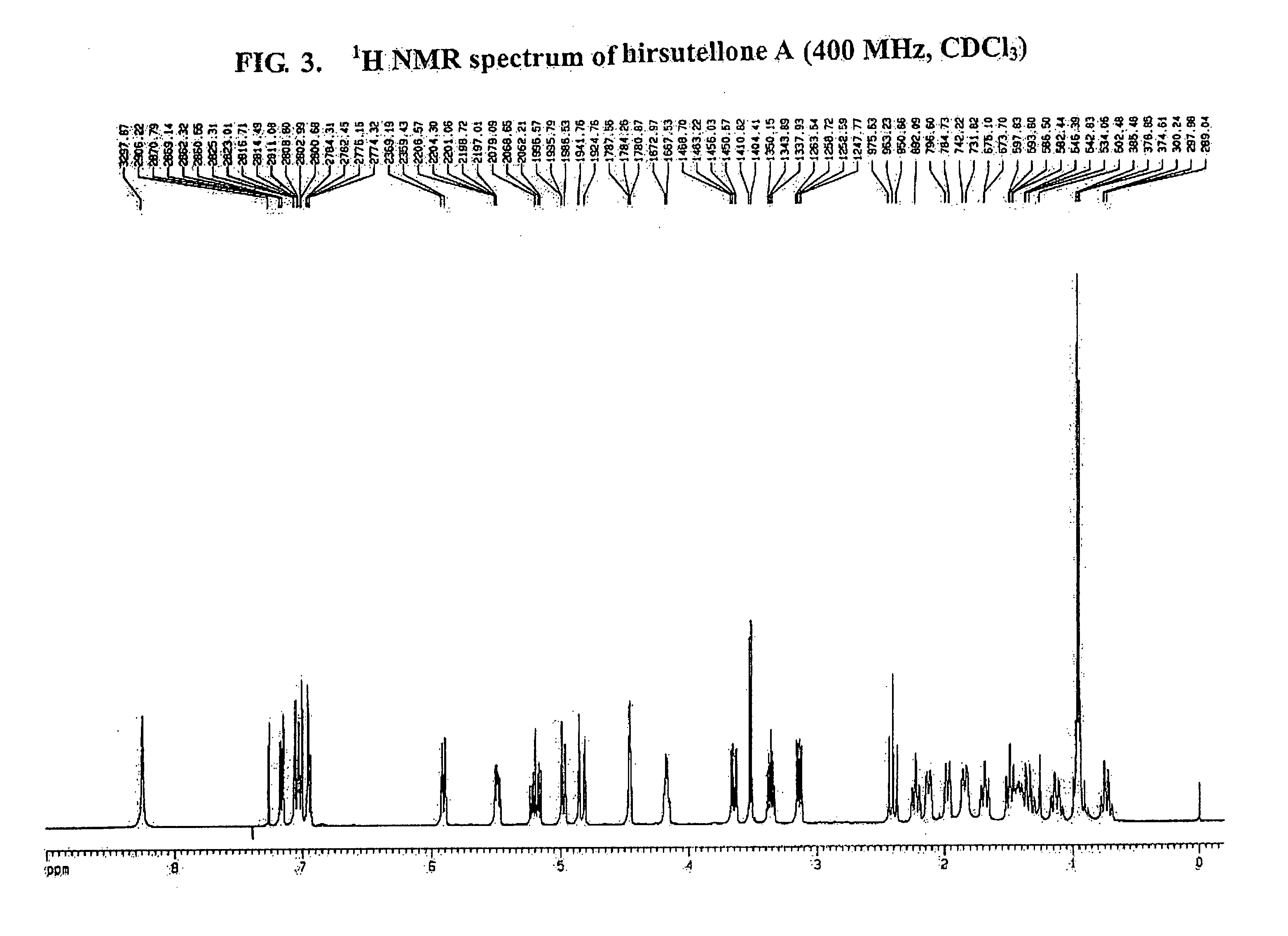
Antituberculosis compounds, Hirsutellones A, B, and C
Three new alkaloids, Hirsutellones A, B, and C, are produced in cultures of fungus such as Hirsutella nivea strain BCC 2594 and Trichoderma sp. strain BCC 7579. The Hirsutellones exhibited potent growth inhibitory activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis (H37Ra strain) with an MIC value of 0.78 μg / ml, while showing weak or no cytotoxicity to mammalian cells. Therefore, Hirsutellones and pharmaceutical compositions containing Hirsutellones may be useful for the treatment of tuberculosis. Also described herein are methods of isolating the Hirsutellones.
Owner:NAT CENT FOR GENETIC ENG & BIOTECH NAT SCI & TECH DEV AGENCY
Method of treating drains using fungus cultures
A method of treating drain systems containing organic matter and providing a biopesticide for killing insects is provided. The method comprises introducing into a drain system a bacterial culture, such as Bacillus sp or Pseudomonas sp, which metabolizes the organic matter, and a biocidal amount of an entomopathogenic fungal culture, such as Metarhizium, which kills the insects such as cockroaches or other soft-bodied insects. The drain system can be a residential or commercial drain system. The bacterial culture and the fugal culture can be maintained separately and then mixed for the treating of the drain, or they can be maintained together prior to introducing them into the drain. The microorganism cultures are dispersed separately or together into the drain. The cultures can be dispersed as a spray, a powder, a liquid, or a foam.
Owner:OSPREY BIOTECHNICS
Method of producing fungal culture
InactiveCN101273120ARegulates enzyme productivityEasy to produceFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyLiquid medium
It is intended to provide a method of producing a fungal culture obtained by culturing a fungus in a liquid medium, which contains as a culture material at least one member selected from among cereals, beans, potatoes, amaranthus and quinua, wherein the speed of releasing a nutrient in the culture material into the culture system is controlled to thereby control the productivity of an enzyme (in particular, a starch digesting enzyme, a vegetable fiber digesting enzyme or a protease) of the fungal culture. Namely, a method of producing a fungal culture characterized by comprising culturing a fungus by using a liquid medium, which contains as a culture material at least one member selected from among cereals, beans, potatoes, amaranthus and quinua, while controlling the speed of releasing a nutrient in the culture material into the culture system to thereby control the enzyme productivity of the fungal culture.
Owner:ASAHI BREWERIES LTD
Methods for the production and use of myceliated amino acid-supplemented food compositions
PendingUS20220095646A1Reduce bitternessReduce flavorDough treatmentProteins working-up by texturisingBiotechnologyAgaricus
Methods, and compositions derived thereof, for preparing a myceliated amino-acid-supplemented high-protein food product having desired digestibility and amino acid content. An aqueous medium comprising a high-protein material is inoculated with a fungal culture to produce a myceliated amino acid-supplemented high-protein food product. The plant protein can include pea, rice and / or chickpea protein. The fungi can include Lentinula spp., Agaricus spp., Pleurotus spp., Boletus spp., or Laetiporus spp. Preferably, the myceliated amino acid-supplemented high-protein food product has reduced bitterness and / or reduced volatile amino-acid-derived aroma compared to high-protein amino acid-supplemented material that is not myceliated. Also disclosed are myceliated amino-acid-supplemented high-protein food products and compositions, such as dairy alternative products, beverages and beverage bases, extruded and extruded / puffed products, meat analogs and extenders, baked goods and baking mixes, texturized plant-based protein products, granola products, bar products, smoothies and juices, and soups and soup bases.
Owner:MYCOTECH
Large-Scale Aerobic Submerged Production of Fungi
Methods are provided for cultivating fungi for scaled-up production of microbe-based products. Specifically, cultures of fungi, such as, e.g., Pisolithus tinctorius, are grown by aerobic submerged fermentation in liquid medium containing a particulate anchoring carrier to increase mycelial biomass.
Owner:LOCUS SOLUTIONS IPCO LLC
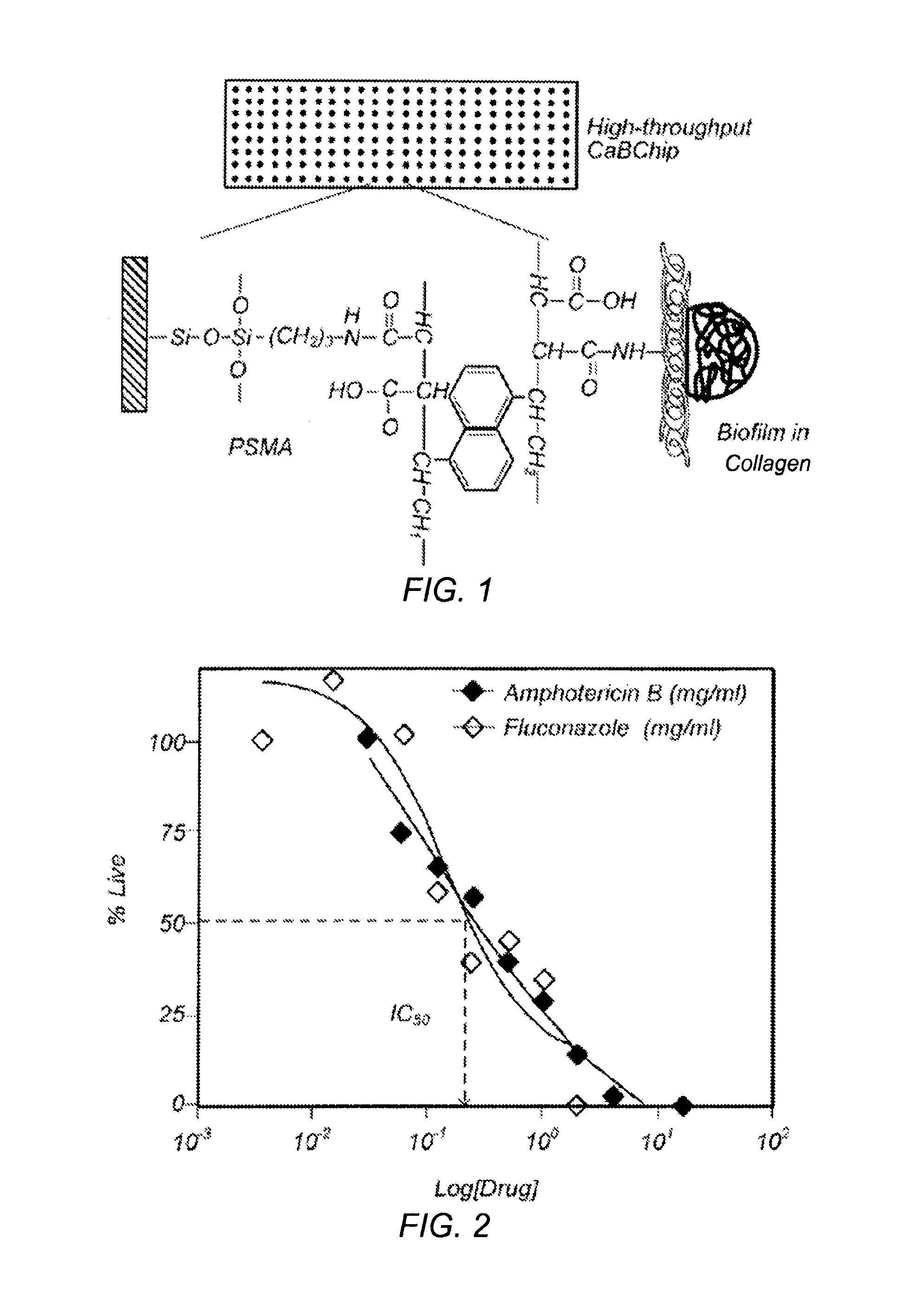
Development of a high-throughput screen for the identification of novel antifungal drug candidates
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Large-scale aerobic submerged production of fungi
Methods are provided for cultivating fungi for scaled-up production of microbe-based products. Specifically, cultures of fungi, such as, e.g., Pisolithus tinctorius, are grown by aerobic submerged fermentation in liquid medium containing a particulate anchoring carrier to increase mycelial biomass.
Owner:LOCUS SOLUTIONS IPCO LLC
Biocontrol fungus mixed bacterial agent for controlling plant root-knot nematode and its application
The present invention relates to a fungi mixing bacterial agent for preventing and controlling plant meloidogyne diseases, and applications thereof, wherein two fungi cultures such as Purpureocillium lilacinum CGMCC No.9344 and Clonostachys rosea CGMCC No.1037 are cultured to prepare the fungi mixing bacterial agent. According to the present invention, the fungi mixing bacterial agent can be mixed with seedling breeding mediums, organic fertilizers and organic-inorganic compound fertilizers or be used separately so as to perform soil treatment or hole application before or after transplantation, or root-irrigation, and is used for preventing and controlling plant meloidogyne diseases.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Fungus colony polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method and pathogenic fungus identification method
ActiveCN101851684BIncrease positive rateShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementFungal geneGenomic DNA
The invention relates to a fungus colony PCR method and a pathogenic fungus identification method. The fungus colony PCR method aims to achieve the high positive rate of amplification, and the pathogenic fungus identification method aims to achieve short detection time and reliable results. The fungus colony PCR method comprises the following steps of: inoculating fungus cultures onto a culture medium for culture; taking fungus colonies which begin to appear on the culture medium as experimentally available colonies; and preparing a DNA template for colony PCR amplification. The pathogenic fungus identification method comprises the following steps of: inoculating clinical sample cultures or pathogenic fungus cultures onto the culture medium for culture; taking the colonies which begin to appear on the culture medium as the experimentally available colonies; preparing the DNA template for the PCR amplification; and detecting amplification products. The fungus colony PCR method and the pathogenic fungus identification method have the advantages of improving the positive rate of the fungus colony PCR amplification, solving the problems of complex steps, wall-breakage difficulty, longtime and the like in fungus genomic DNA extraction, performing colony identification at the very beginning of the growth of pathogenic fungi, and achieving reliable results and identification time remarkably shorter than conventional fungus phenotype identification time.
Owner:CHUGOKU IGAKU KAGAKUIN HIFUBIYOU KENKYUSHO
Exract of sea fungus culture and its preparation method and use
The present invention relates to a kind of ethyl acetate extract effective part oil of the culture endophytic fungus of South China Sea mangrove and its preparation method and this extract is used for preparing and killing cotton bollworm [Heliothis armigera (Hühner)] and fish parasite Pesticide application of Sinergasilus spp.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com