Method for sustained-releasing polypeptide with biological activity and application thereof
A bioactive peptide, sustained release technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of loss of activity, peptide or protein drugs cannot be released, etc., to achieve the effect of ensuring activity, strong pharmacokinetic properties, and prolonging half-life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Example 1 Phage display method for screening human serum albumin-binding peptides
[0049] In this example, the Ph.D.-12 phage library of New England Biolabs was used to screen human serum albumin-binding peptides.
[0050] The Ph.D.-12 phage library of New England Biolabs is designed based on the M13 phage and contains a random combination of linear sequences of 12 peptides. There are at least 10 peptide species in this library 9 , and their titer is 10 12 pfu / ml.
[0051] Phage display library screening for human serum albumin-binding peptides underwent a total of four rounds of screening:
[0052] Human serum albumin (Sigma-Aldrich, St-Louis, USA) was dissolved in 0.1mol / L NaHCO 3 Buffer solution (pH 8.6) to prepare 100 μg / ml human serum albumin solution (pH 8.6).
[0053] First round of screening:
[0054] 1. Take 1.5ml of human serum albumin solution (100μg / ml, pH 8.6) and add it to a sterile polystyrene petri dish (60×15mm), then place the plate in a humid con...
Embodiment 2
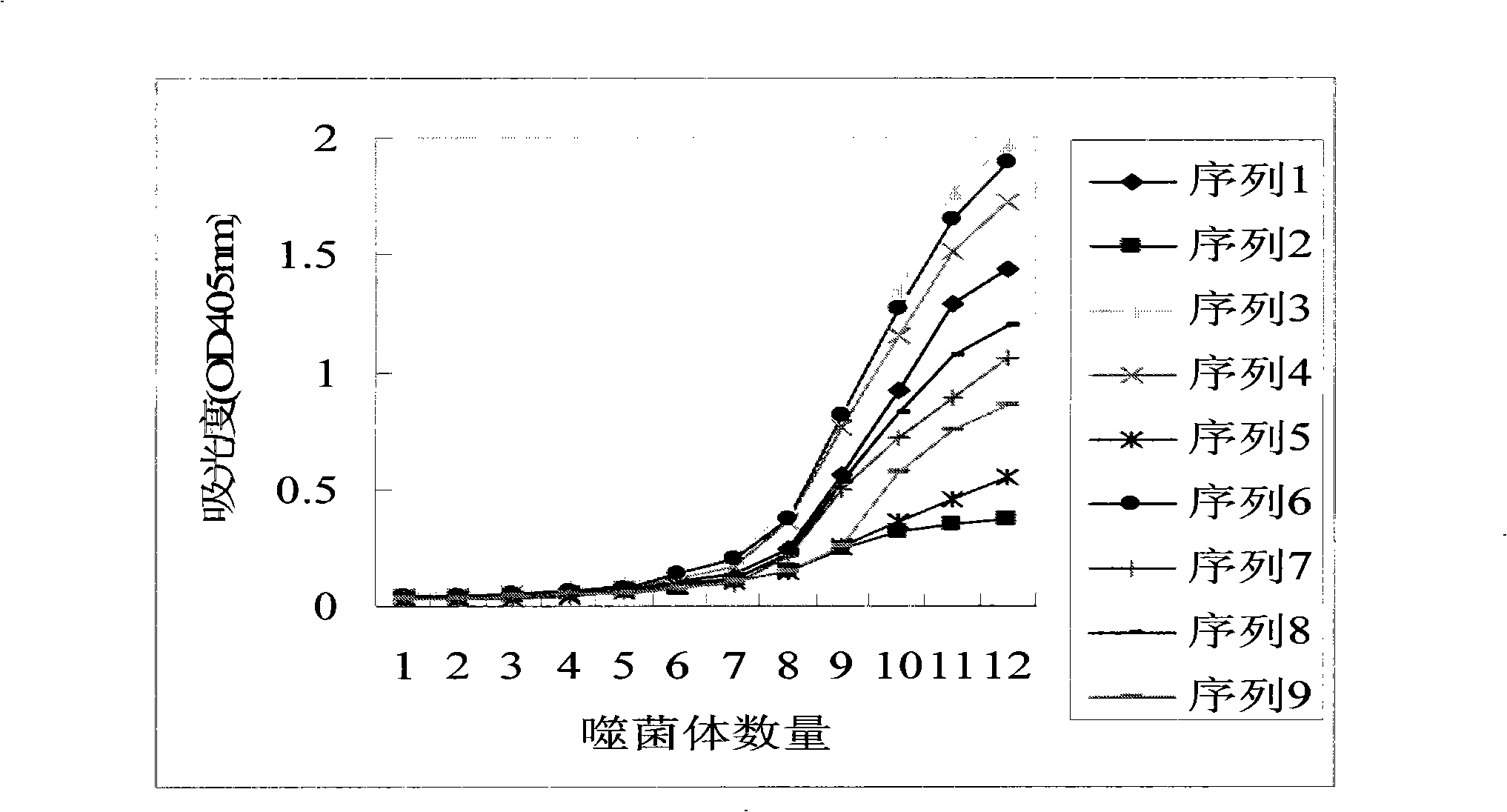
[0068] Embodiment 2 Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method measures the affinity of screened phage and human serum albumin
[0069] The phage plaques respectively containing the 9 amino acid sequences shown in Table 1 obtained in Example 1 were subjected to monoclonal screening and pure culture respectively to obtain phage monoclonals containing the above-mentioned 9 peptide chains respectively, which were used in the test of this embodiment .
[0070] With 0.1mol / L NaHCO 3 Dilute the human serum albumin solution to 100 μg / ml, cover a row of ELISA multiwell plate wells with the solution, add 200 μL of the solution to each well, and place it in a sealed humid environment at 4°C overnight. Another multi-well plate was used for serial dilution of phage. Both plates were treated with 1% casein solution (dissolved in 0.1mol / L NaHCO 3 )cover. Each group of phage monoclonals was serially diluted four-fold, so that the first well contained about 10 12 phage particles, t...
Embodiment 3
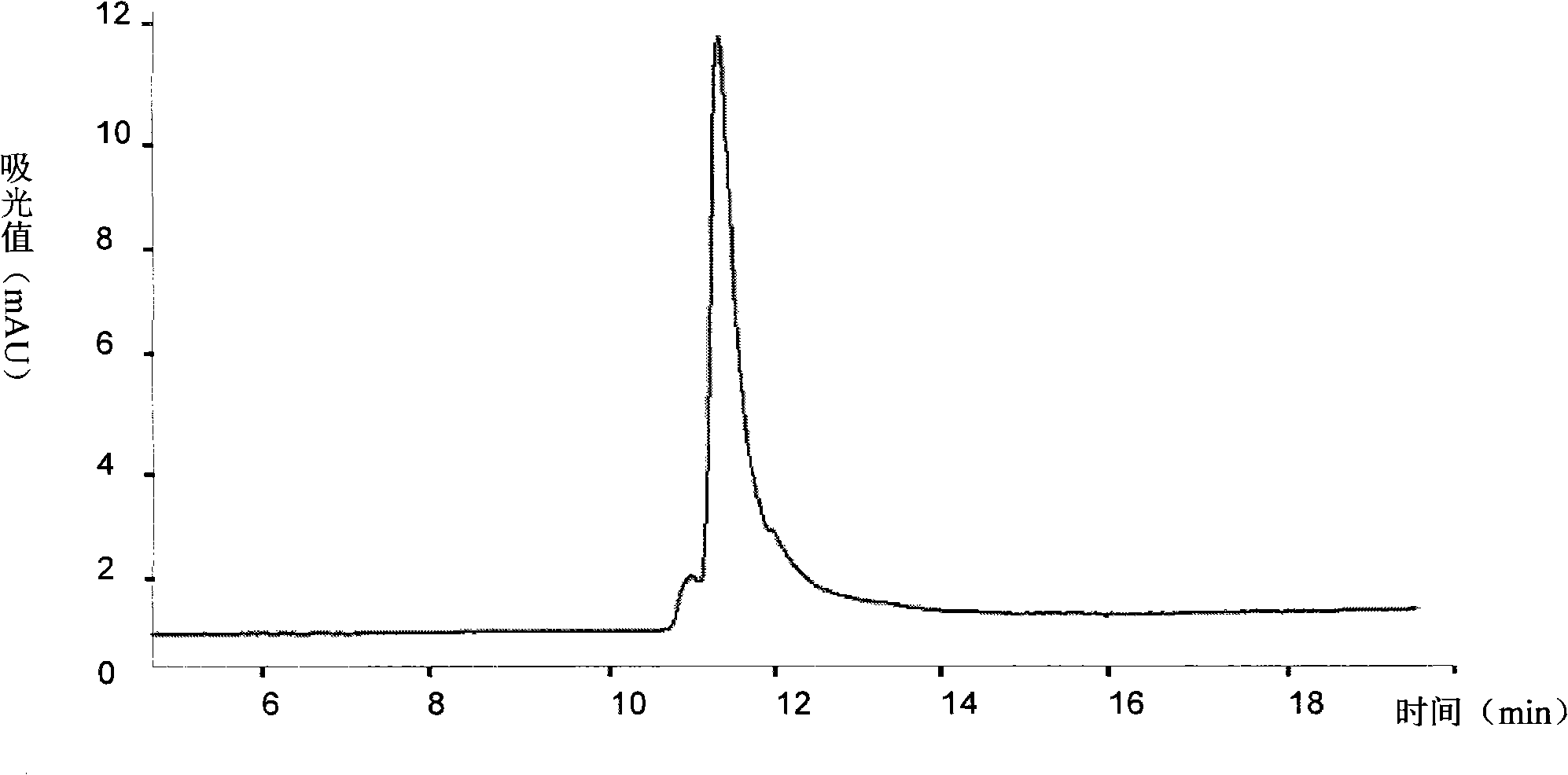
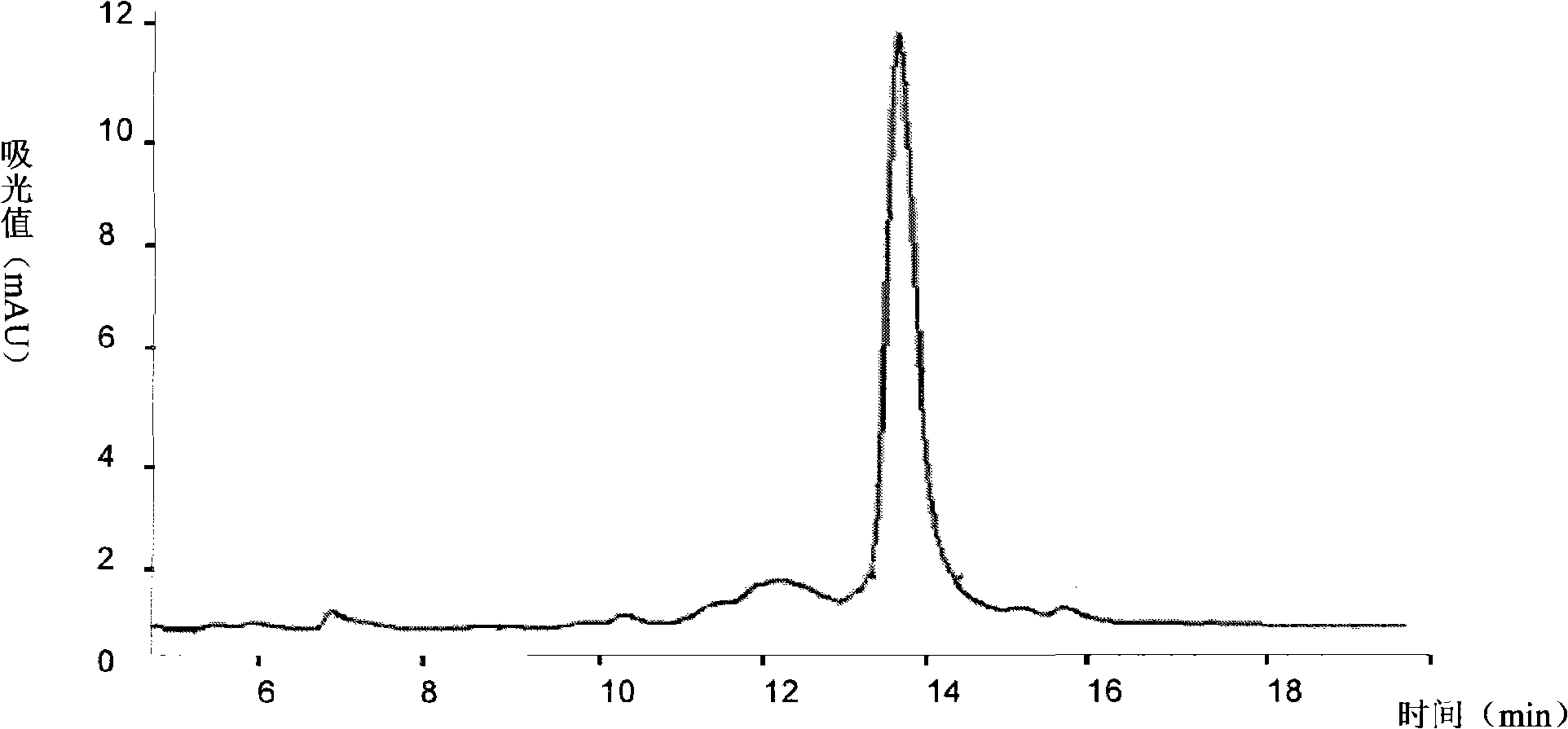
[0078] Example 3 Preparation of anti-type 2 diabetes ABP-LK-GLP fusion peptide using recombinant DNA technology
[0079] In this example, human glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) is taken as an example to design a new therapeutic peptide for treating type 2 diabetes.
[0080] About 90% of diabetic patients suffer from type 2 diabetes, also known as non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). People with type 2 diabetes are usually able to produce insulin, but the insulin produced cannot be used effectively by the cells of the body. This is mainly because the insulin produced in response to elevated levels of blood sugar is not sufficient for the cells to absorb glucose effectively, thereby failing to achieve the purpose of lowering blood sugar levels.
[0081] Since human glucagon-like peptide 1 was discovered in 1984, it has been proven clinically effective in lowering blood sugar concentrations in all stages of diabetes. More importantly, little risk of hypoglycemia was ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Titer | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com