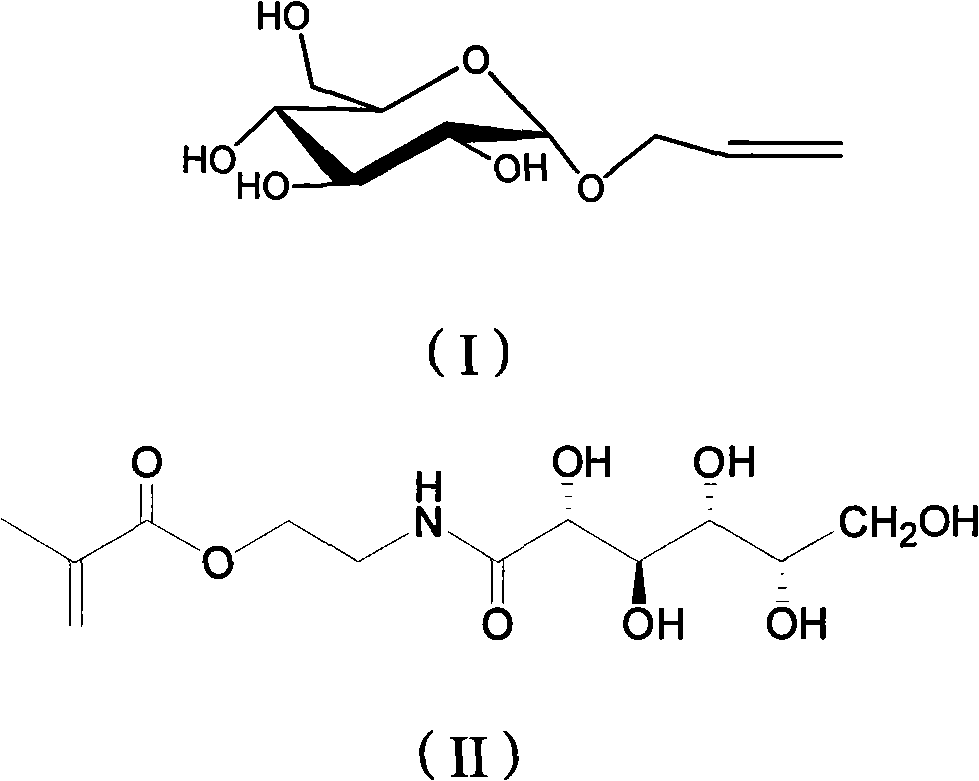
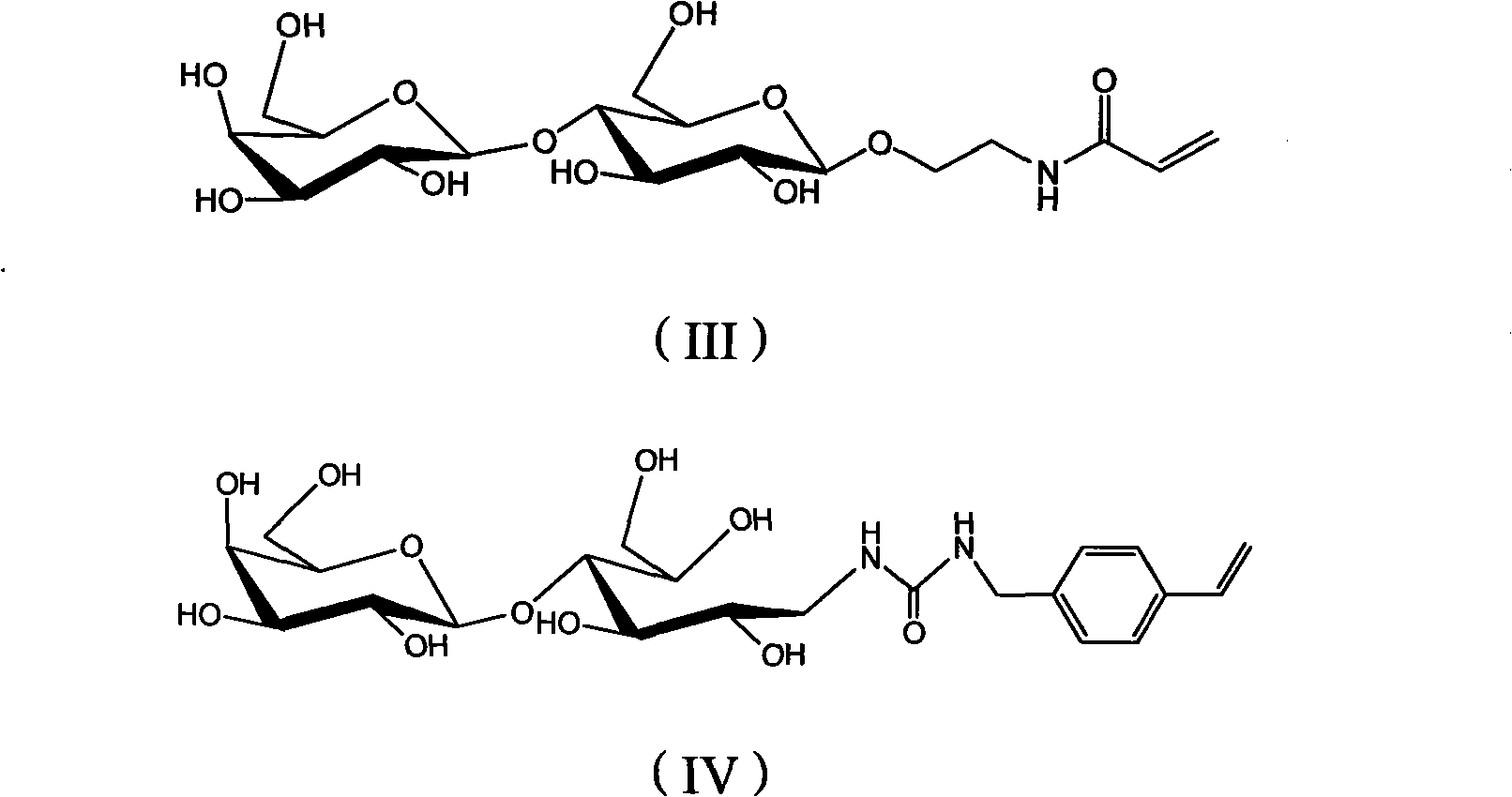
Sugar-containing polymer compound film with blocked pore and preparation thereof
A composite membrane and polymer technology, applied in the field of membrane separation, can solve the problems of no preparation method and practical application, poor mechanical properties of sugar-containing polymers, failure to maintain integrity, etc., achieve good practical value, and solve compatibility problems , good mechanical strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Methanol and water were prepared as a mixed solvent at a volume ratio of 1:4, and 3 grams of AG, 2 milliliters of AA, 0.25 grams of MBA, and 0.005 grams of AIBN were dissolved in a mixed solvent with a volume of 5 milliliters. Soak a PP microporous membrane with a thickness of 50 microns, an average pore diameter of 0.2 microns, a porosity of 85%, and an area of 16 square centimeters in the above solution for 60 minutes, and remove the residual solution on the surface with filter paper after taking it out. Polymerization was thermally initiated at 60° C. for 24 hours, under nitrogen protection during the process. After the polymerization reaction was completed, the membrane was taken out, washed with deionized water and ethanol in turn, and dried. The obtained sugar-containing polymer plugging composite membrane was subjected to isopropanol dehydration pervaporation experiment, and the operating parameters and test results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 2
[0034] Methanol and water were prepared as a mixed solvent at a volume ratio of 4:1, and 0.5 g of GAMA, 4.5 g of AAm, 1 g of MBA, and 0.25 g of AIBN were respectively taken and dissolved in a mixed solvent with a volume of 5 ml. Soak a PE microporous membrane with a thickness of 15 microns, an average pore diameter of 0.2 microns, a porosity of 20%, and an area of 16 square centimeters in the above solution for 30 minutes, and remove the residual solution on the surface with filter paper after taking it out. Polymerization was thermally initiated at 60° C. for 6 hours, under nitrogen protection during the process. After the polymerization reaction was completed, the membrane was taken out, washed with deionized water and ethanol in turn, and dried. The obtained sugar-containing polymer plugging composite membrane was subjected to isopropanol dehydration pervaporation experiment, and the operating parameters and test results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0036] Methanol and water were prepared as a mixed solvent at a volume ratio of 1:1, and 3 grams of AAEL, 2 milliliters of MAA, 0.25 grams of MBA, and 0.005 grams of AIBN were taken respectively and dissolved in a mixed solvent with a volume of 5 milliliters. Soak a PTFE microporous membrane with a thickness of 500 microns, an average pore diameter of 1 micron, a porosity of 60%, and an area of 16 square centimeters in the above solution for 30 minutes, and remove the residual solution on the surface with filter paper after taking it out. Polymerization was thermally initiated at 80° C. for 24 hours, under nitrogen protection during the process. After the polymerization reaction was completed, the membrane was taken out, washed with deionized water and ethanol in turn, and dried. The obtained sugar-containing polymer plugging composite membrane was subjected to ethanol dehydration pervaporation experiment, and the operating parameters and test results are shown in Table 1. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com