Method for removing sulphur and nitrogen in inorganic waste water synchronously
A technology for the removal of inorganic wastewater, which is applied in the direction of anaerobic digestion and treatment, can solve the problems of high energy consumption, high operating costs, secondary pollution, etc., and achieve high treatment efficiency, small floor space, and low sludge yield Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
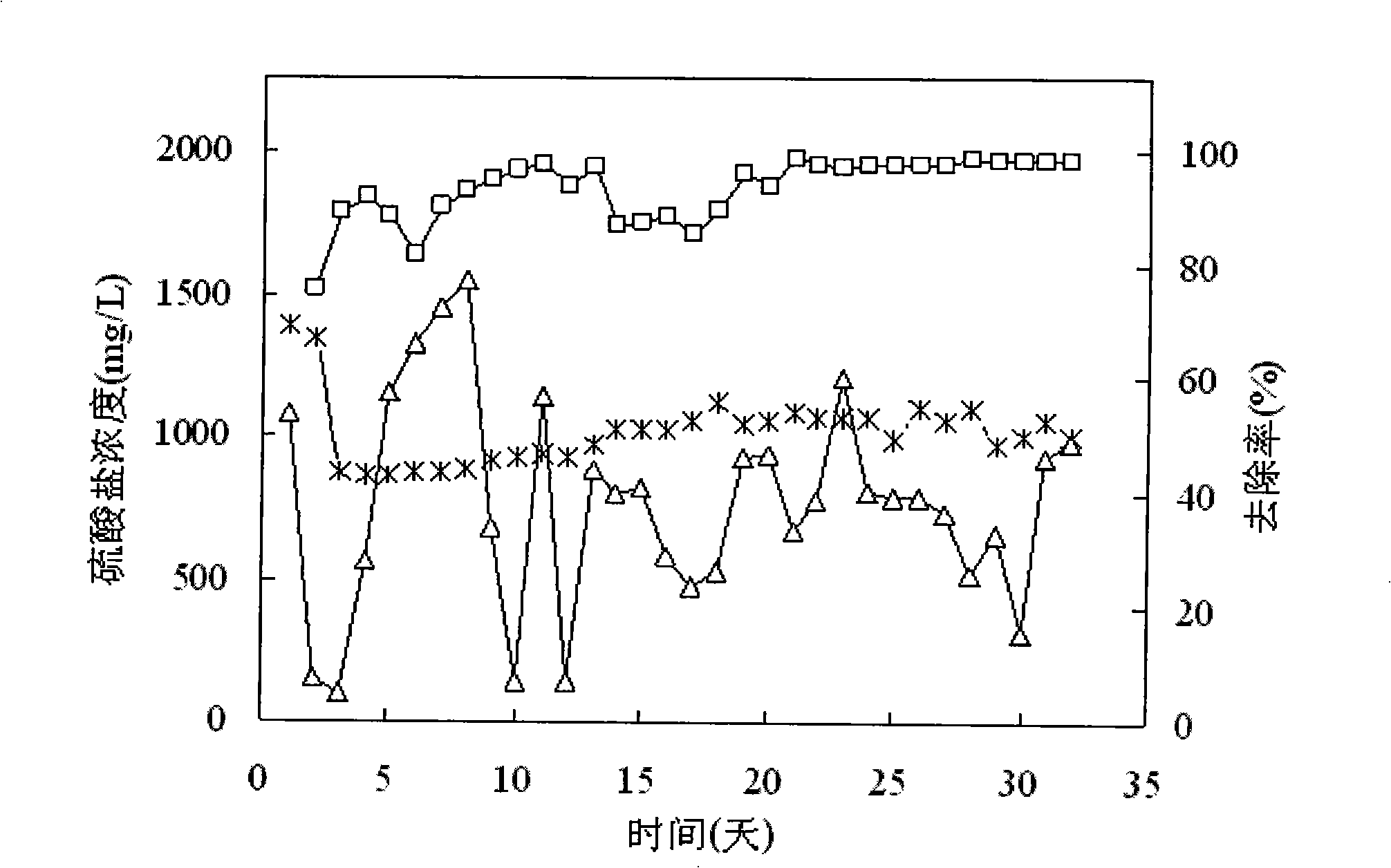
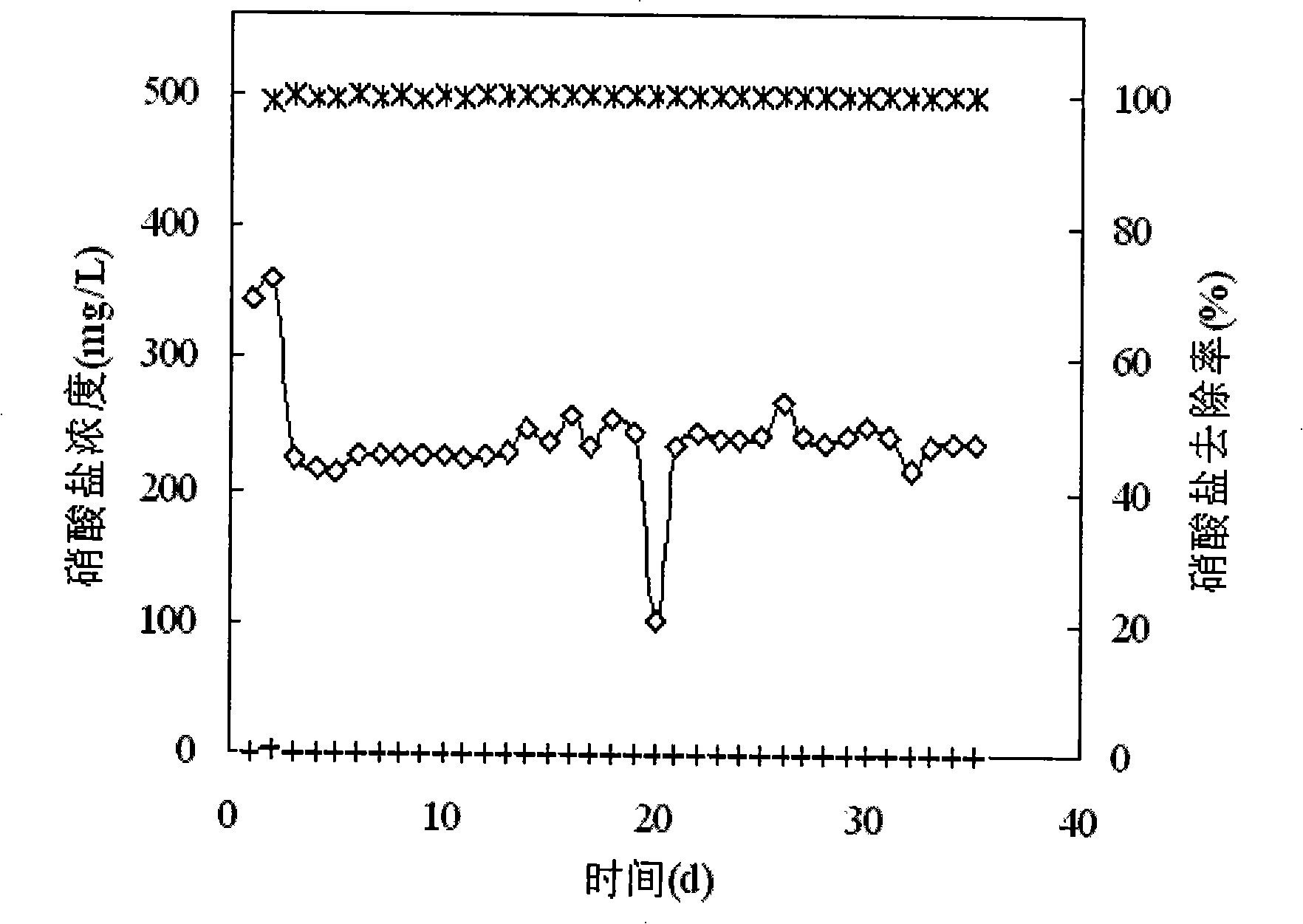
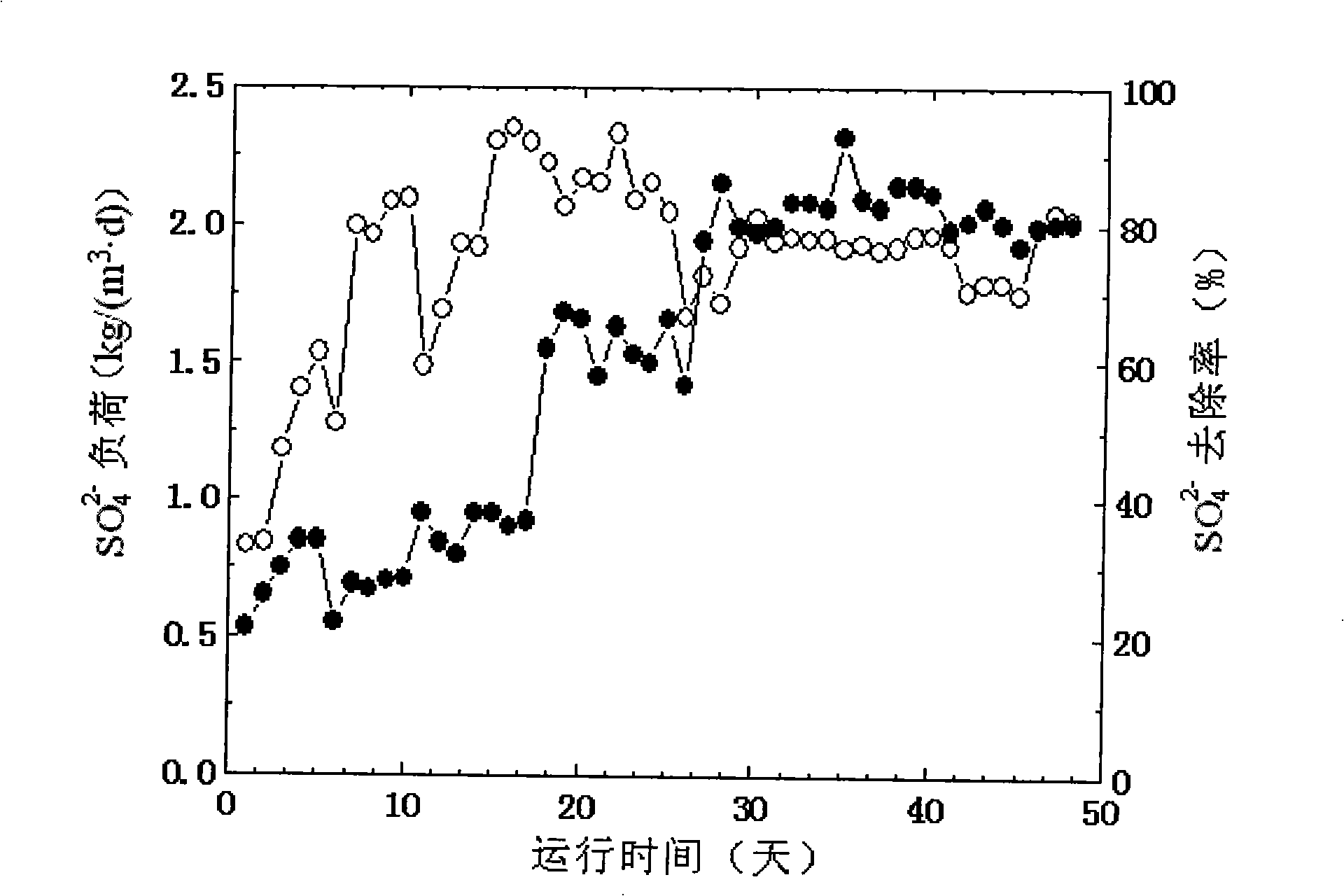
[0011] Specific embodiment one: the method for synchronously removing sulfur and nitrogen in the inorganic waste water in the present embodiment is carried out according to the following steps: one, in the sealed reactor, add anaerobic activated sludge and filler, pass into nutrient solution then Perform bio-filming on the filler, keep the pH value of the culture solution at 7.5-8.3, replace the nutrient solution every 12-24 hours, and complete the bio-filming when the sulfate removal rate reaches 80%; 2. Pass the inorganic waste water into reactor, while adding an organic carbon source to the influent to make COD and SO 4 2- The mass concentration ratio is 1.7~2.1:1, the sulfate in the inorganic wastewater in the biofilm is converted into sulfide, the sulfide diffuses on the surface of the biofilm to be oxidized into elemental sulfur, and the nitrate is denitrified into nitrogen, the process operation Conditions: the reaction temperature is 25°C to 35°C, the pH value is 7.5 ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0017] Embodiment 2: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 in that: the filler is corncob particles, and the particle diameter of the corncob particles is 3-5 mm. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
[0018] Compared with other types of fillers, corncob fillers have a rough surface and a large specific surface area, which is suitable for microbial attachment, and the price of corncob fillers is low, reducing operating costs.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0019] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the reactor in Step 1 is an anaerobic film-attached expanded bed reactor. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com