In situ detoxication alcohol fermentation method of ligno-cellulose hydrolysate using single strain
A lignocellulose and ethanol fermentation technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, fermentation, etc., can solve the problems such as the complexity of the ethanol fermentation process and increase the cost, and achieve the effect of low production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
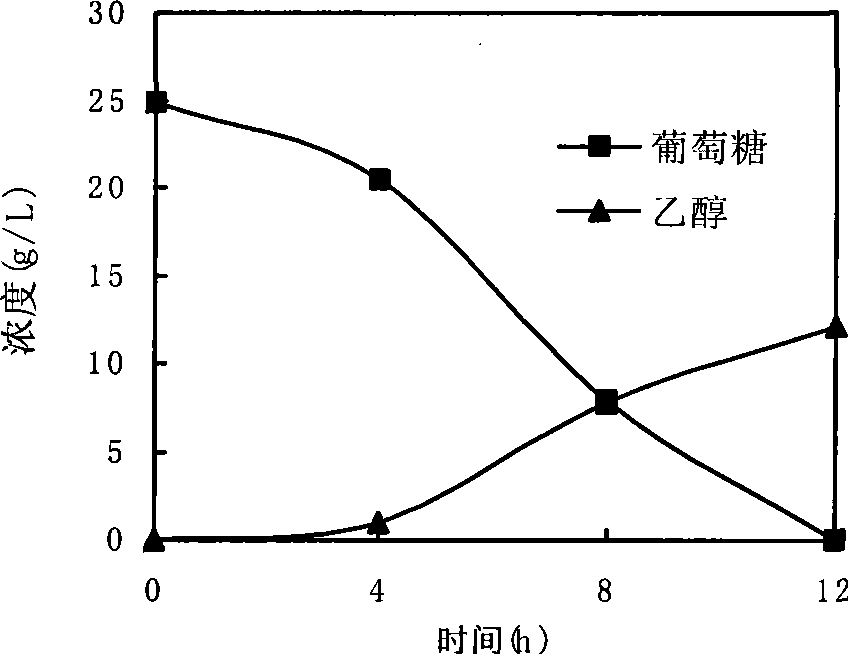
[0023] The separation and identification of embodiment 1 Y7
[0024] 1 Screening process
[0025] It was isolated from the sewage sludge of the alcohol factory in our laboratory. It was enriched and cultured in the YPD liquid medium added with furfural and hydroxymethylfurfural, and then spread on a solid plate containing xylose to isolate a single colony. After a large number of screenings, it was found that one of the strains had a strong metabolism, could efficiently utilize glucose and xylose in the hydrolyzate, and could tolerate high concentrations of inhibitors. It was named Y7 and was finally preserved on a slant.
[0026] 2 Morphological characteristics
[0027] The colonies are smooth, spherical and small, and reproduce by binary fission without false filaments.
[0028] 3 culture characteristics
[0029] After being cultured in the liquid medium for a period of time, the bacterial solution was turbid without flocculation.
[0030] 4 metabolic characteristics
...
Embodiment 2
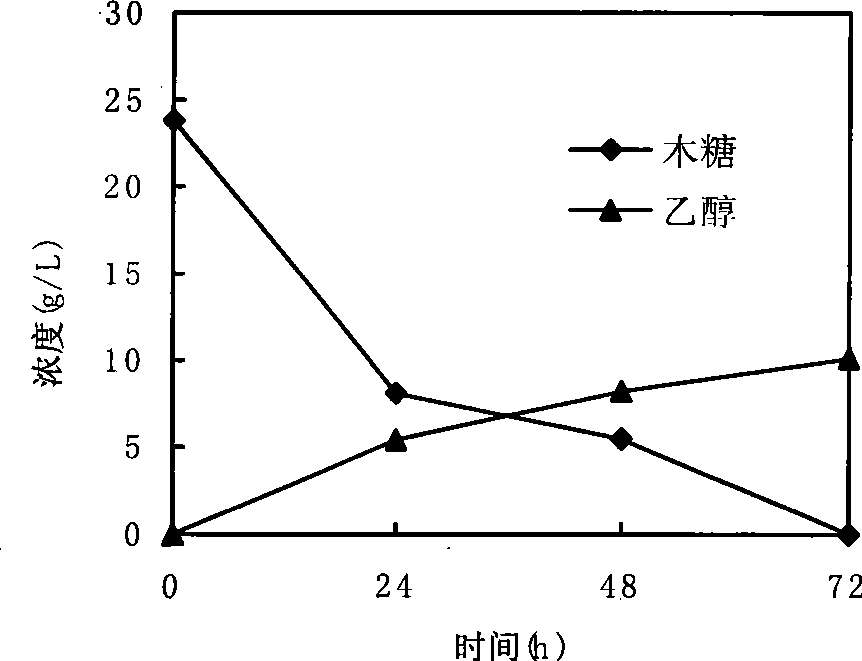
[0032] Example 2 Identification of Y7 on the in-situ detoxification ethanol fermentation of lignocellulose dilute acid hydrolyzate
[0033] 1 Materials and methods
[0034] 1.1 Strains
[0035] Strain Pichia.Stipitis Y7
[0036] 1.2 Medium (g / L)
[0037] YPD medium: glucose 20, yeast extract 10, peptone 20, pH 5.0-5.5.
[0038] Fermentation medium: yeast extract 10, peptone 20. In addition, glucose and xylose were added according to different needs (concentration is subject to actual measurement) pH 5.0-5.5.
[0039] 1.3 Dilute acid hydrolyzate of lignocellulose (g / L)
[0040] The dilute acid hydrolyzate of lignocellulose used in this study was provided by East China University of Science and Technology, in which glucose was 44.678, xylose was 24.35, furfural was 1.37, 5-HMF0.47, acetic acid was 10, Ca(OH) 2 Adjust the pH of the hydrolyzate to 5.0.
[0041] 1.4 Culture of strains
[0042] The strain Y7 was inoculated in 100ml of YPD medium and cultured at 30°C and 150r...
Embodiment 3
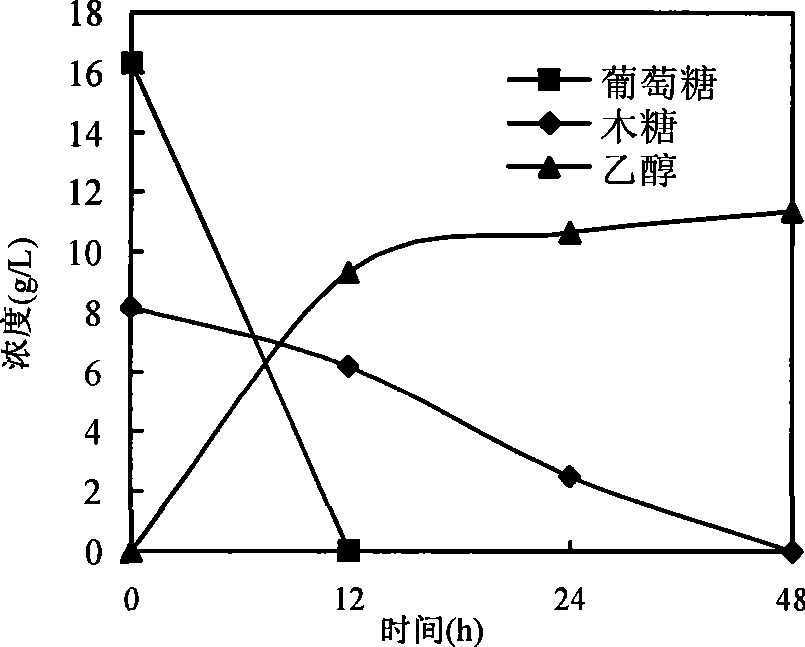
[0068] Example 3 In situ detoxification ethanol fermentation of lignocellulose dilute acid hydrolyzate by Y7
[0069] 1 seed solution preparation
[0070] Add 100mL YPD liquid medium (glucose 20g / L, peptone 20g / L, yeast extract 10g / L) into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, put it into a sterilizing pot at 115°C for 25 minutes for sterilization. Pick a ring of single colony into the Erlenmeyer flask, 150rpm, shaker at 30°C for 12 hours.
[0071] 2 Treatment of hydrolyzate
[0072] Add peptone (20g / L), yeast extract (10g / L), Ca(OH) to the hydrolyzate 2 Adjust the pH to 5.0, put it into a sterilizing pot at 115°C for 25 minutes to sterilize.
[0073] 3 Fermentation of lignocellulose dilute acid hydrolyzate
[0074] Take 10mL Y7 seed solution (the number of viable bacteria is 8×10 8 pcs / ml~9×10 8 Each / ml) was added to the Erlenmeyer flask equipped with hydrolyzate, 150rpm, shaker and cultured at 30°C.
[0075] 4 analysis method
[0076] 4.1 Determination of sugar concentration
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com