Complementary type high capacity adenoviral vector and vaccine and gene therapy producers constructed by the same
A vector system, adenovirus technology, applied in gene therapy, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve the problems of low yield, deletion and recombination, lack of selective growth advantages, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
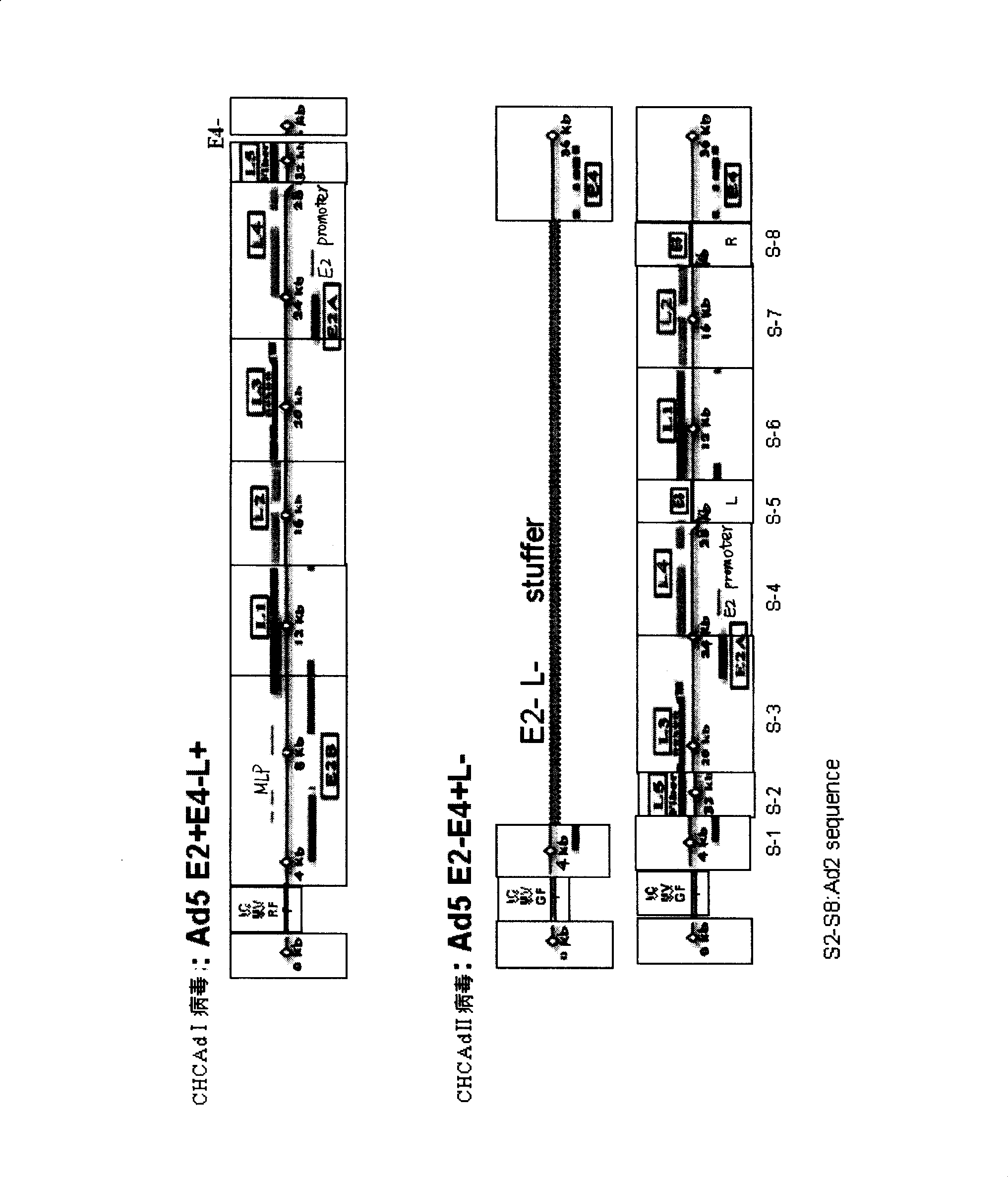
[0057] Construction of complementary high-capacity adenoviral vector I (CHCAd I)
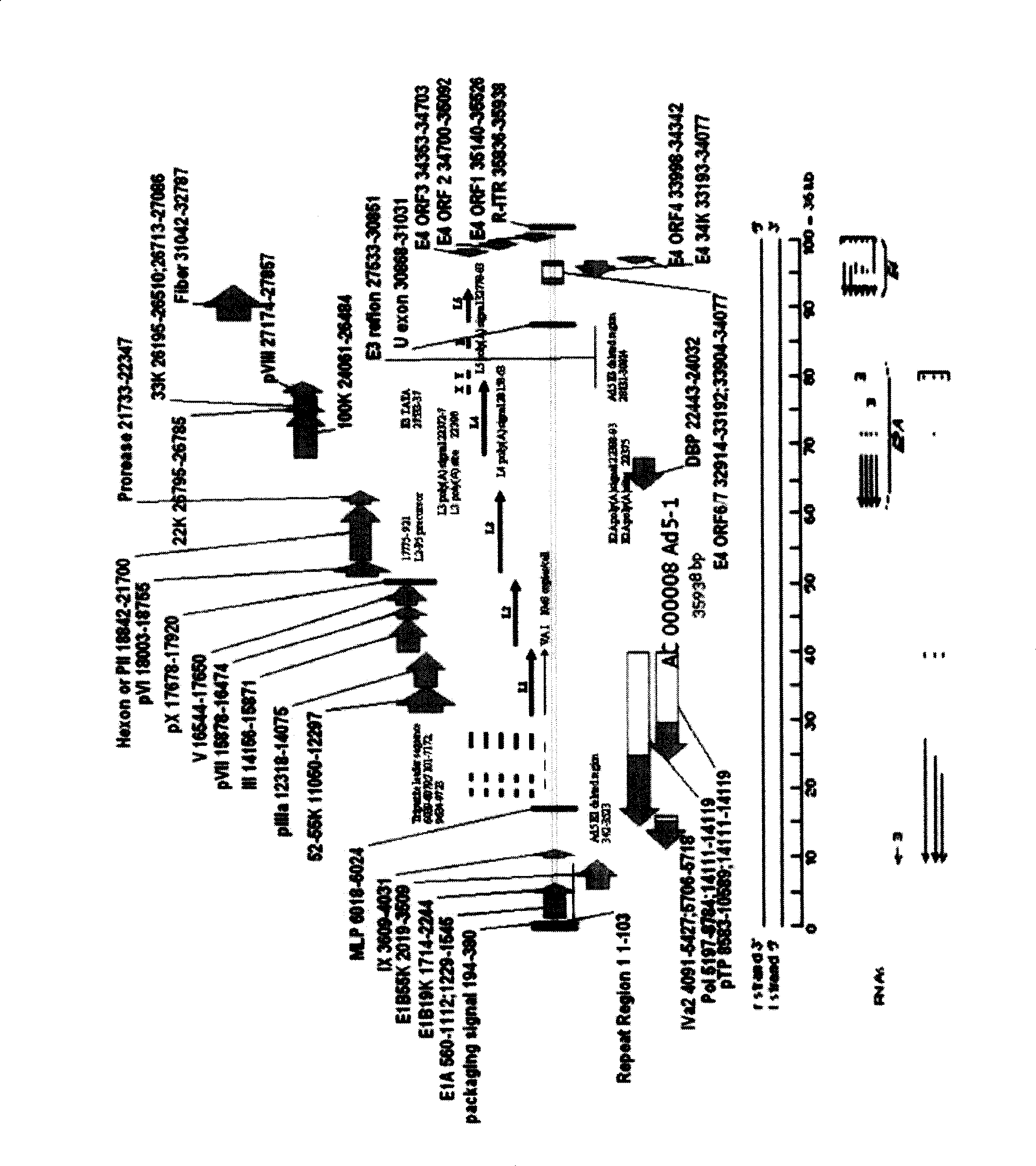
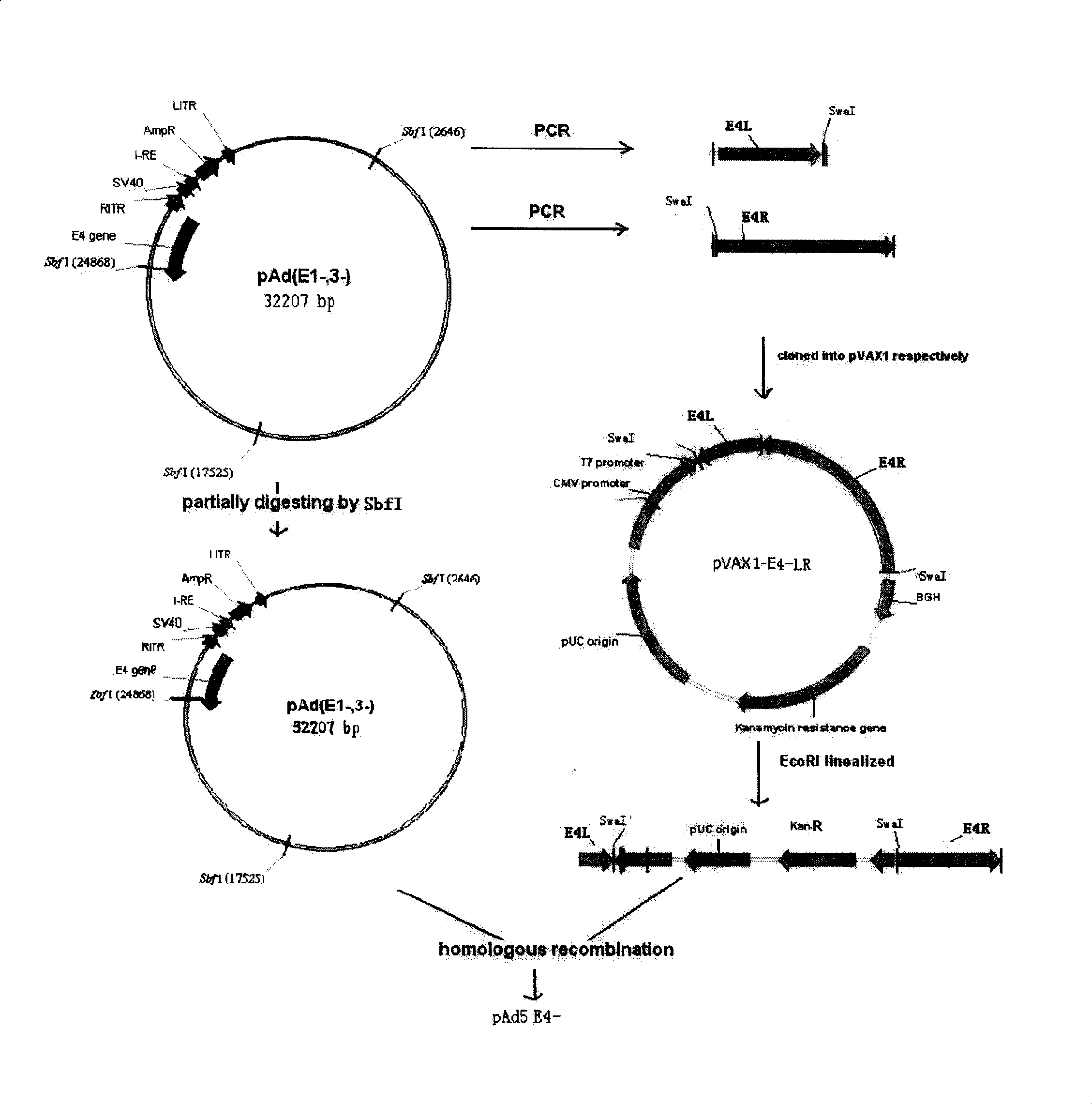
[0058] Elements necessary for adenovirus replication and packaging in CHCAd I include: ITR, packaging signal, E2 gene and late transcription unit. Its acquisition scheme is as follows: the E1 gene and E3 gene have been removed from the first-generation type 5 adenovirus vectors in our laboratory, so the CHCAd I vector can be obtained by removing the E4 gene on this basis. Specifically, the sequences on the left and right sides of the E4 gene to be deleted are first amplified to obtain E4-L and E4-R fragments. These two fragments follow the attached image 3 Inserted into pVAX1 successively in the direction and sequence in order to obtain pVAX1-E4-L-R. EcoRI digested linearized pVAX1-E4-L-R product and SbfI partially digested pAd5 E1-E3- product were transformed into BJ5183 bacteria, and recombined to obtain pAd5E1-E3-E4- (containing the kanamycin resistance gene). If the kanamycin resistance ...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Construction of complementary high-capacity adenoviral vector II (CHCAd II)
[0062] Elements necessary for the replication and packaging of adenovirus in CHCAd II include: ITR, packaging signal and E4 gene. Its acquisition scheme is as follows: from the first generation of adenovirus type 5 vector (from Stratagene's AdEasy TM The E2 gene and the late transcription unit have been removed in the Adenoviral Vector System or other), and only the E4 gene is retained to the CHCAd II vector backbone. Specifically, pAd5 E1-E3 was digested with BstZ17I and HpaI, and the fragments containing the plasmid backbone and E4 gene were recovered and self-ligated to obtain the CHCAd II vector backbone.
[0063] λ-phage genome fragments as filler
[0064] The specific test procedure using λ-bacteriophage genome fragments as fillers is shown in the appendix Figure 4 . Specifically, the sequences on the left and right sides of the selected λ-phage genome fragment are first amplified t...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Optimal selection of λ-bacteriophage genome fragments as fillers
[0075] During the CHCAd II vector construction process, a 23583bp fragment of the adenovirus type 5 genome was deleted, and the average GC content of this fragment was 58%. Use the online software geneGC calculator (http: / / plantst.genomics.purdue.edu / plantst / cgi-bin / geneGC.cgi) to analyze the whole genome of λ-phage, and select the fragment of the λ-phage genome to obtain the 149-21749 interval As a filler, the fragment length is 21601bp, and the average GC content is 567%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com