Non-volatile memory device having a gap in the tunnuel insulating layer and method of manufacturing the same
A non-volatile storage and non-volatile technology, applied in the field of manufacturing such devices, can solve the problems of undisclosed low-k tunnel dielectric materials, mismatched semiconductor manufacturing processes, and reduced reliability of storage devices, and achieve improved Effect of charge retention time, improved reliability and data retention time, and reduced leakage current
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
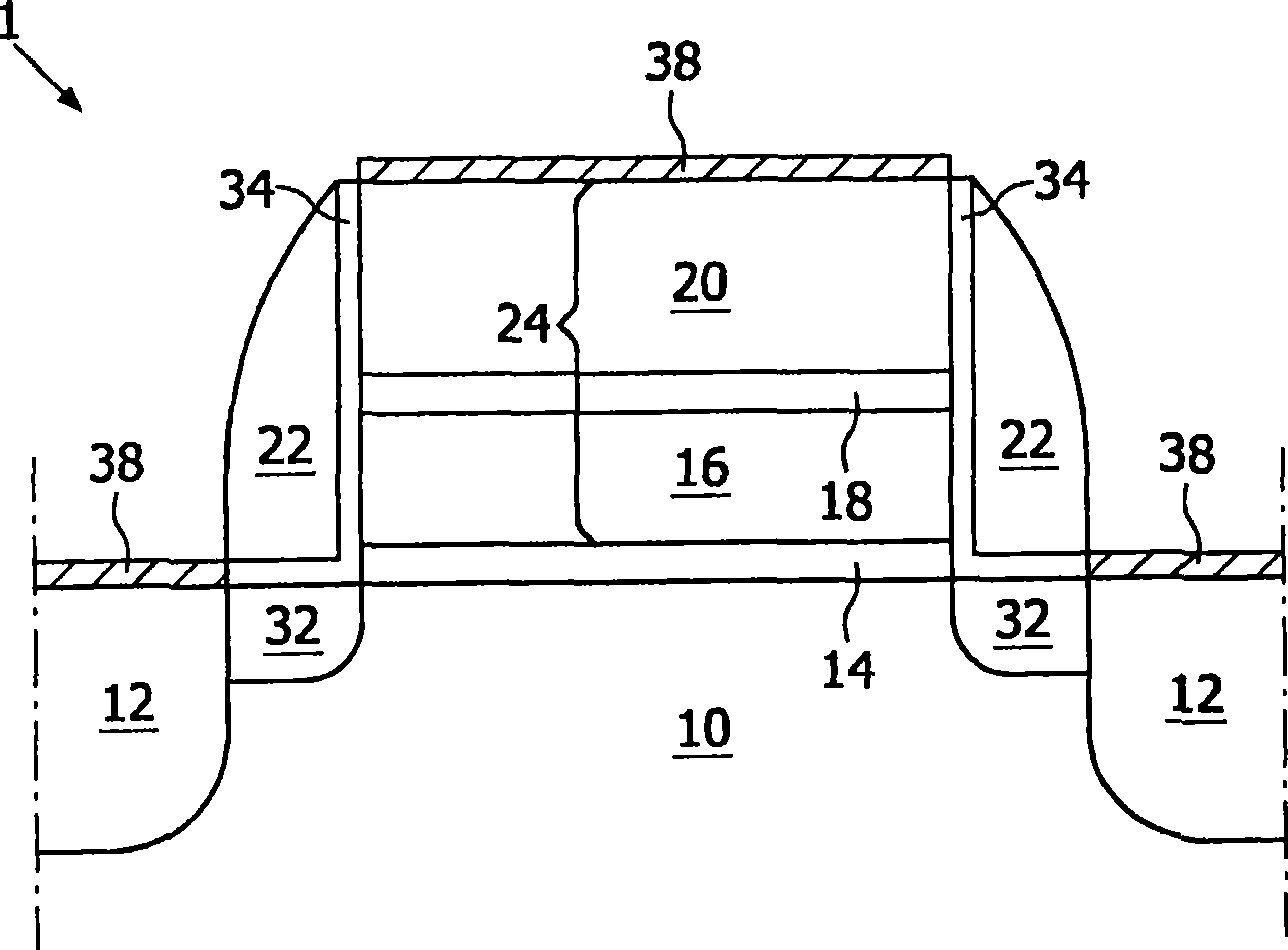
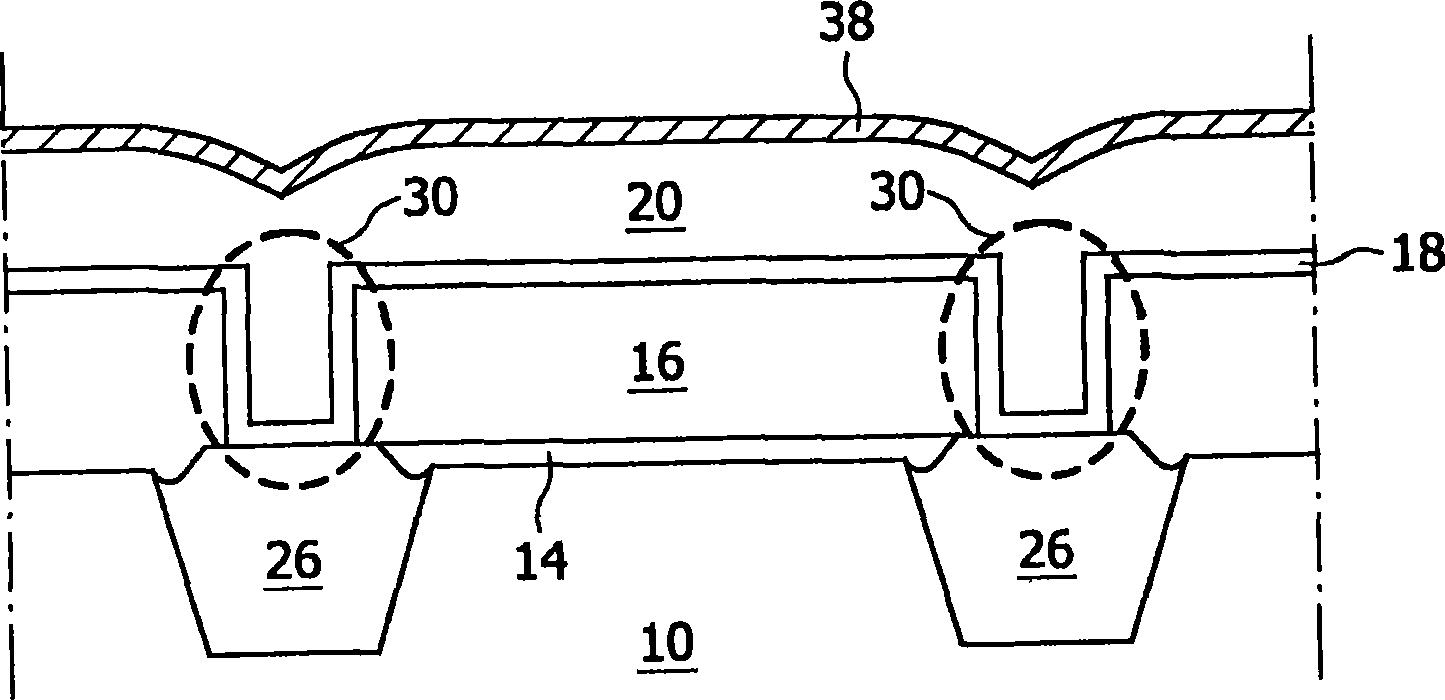
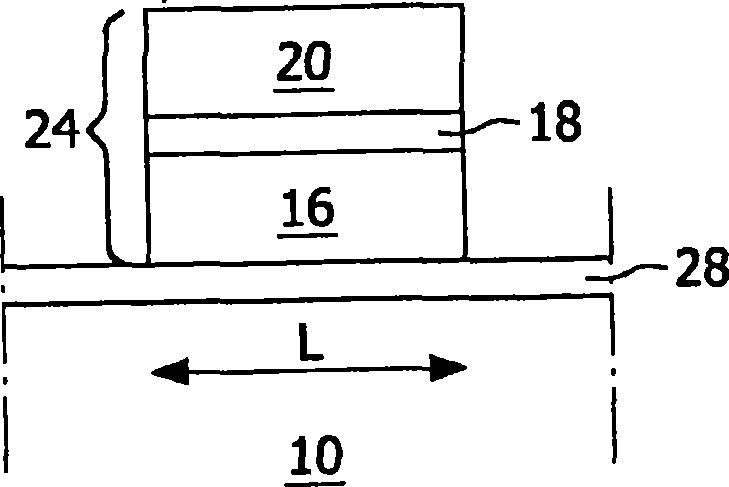
[0044] According to the invention, in a first step, a substrate is provided. In embodiments of the present invention, the term "substrate" includes any underlying material or material on which devices, circuits or layers may or have been formed. Examples of semiconductor substrates are: doped silicon, gallium arsenide (GaAs), gallium arsenide phosphide (GaAsP), germanium (Ge) or silicon germanium (SiGe). The substrate may include, for example, silicon dioxide or silicon nitride other than the semiconductor substrate portion. Thus, the term substrate also includes: silicon on insulator, silicon on glass (SOG), silicon on sapphire (SOS) and silicon on any material (SOA). Thus, the term substrate is used to broadly define a layer serving as a basis for a layer or portion of interest. Furthermore, the substrate may be any basis on which a layer is formed, for example a glass or metal layer. Also it should be pointed out that the substrate need not have a flat surface.
[0045]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com