Frequency controllable GC specificity DNA mutagenesis method
A specific and frequent technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of low mutation frequency, difficult to control mutation frequency, low fidelity and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
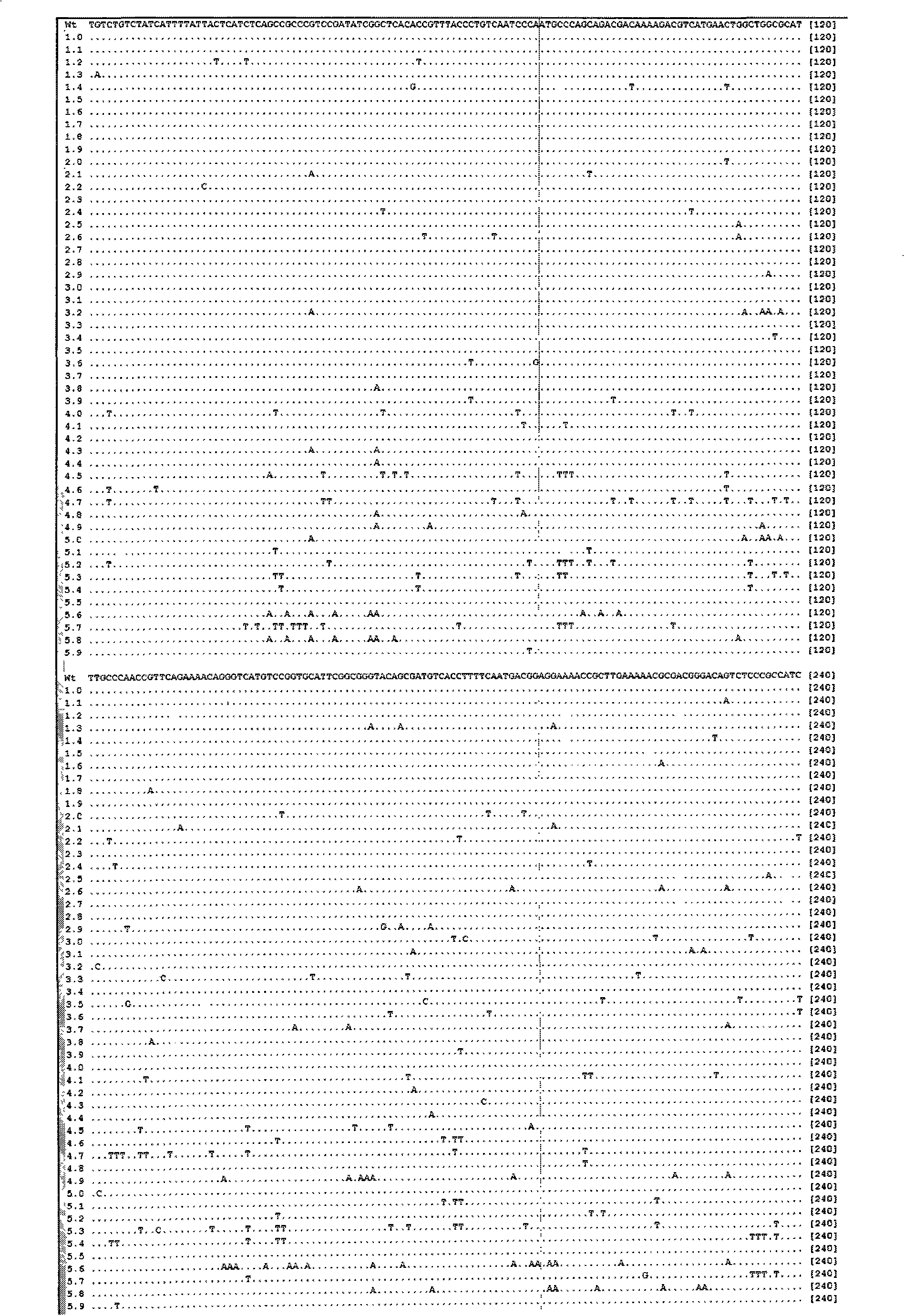
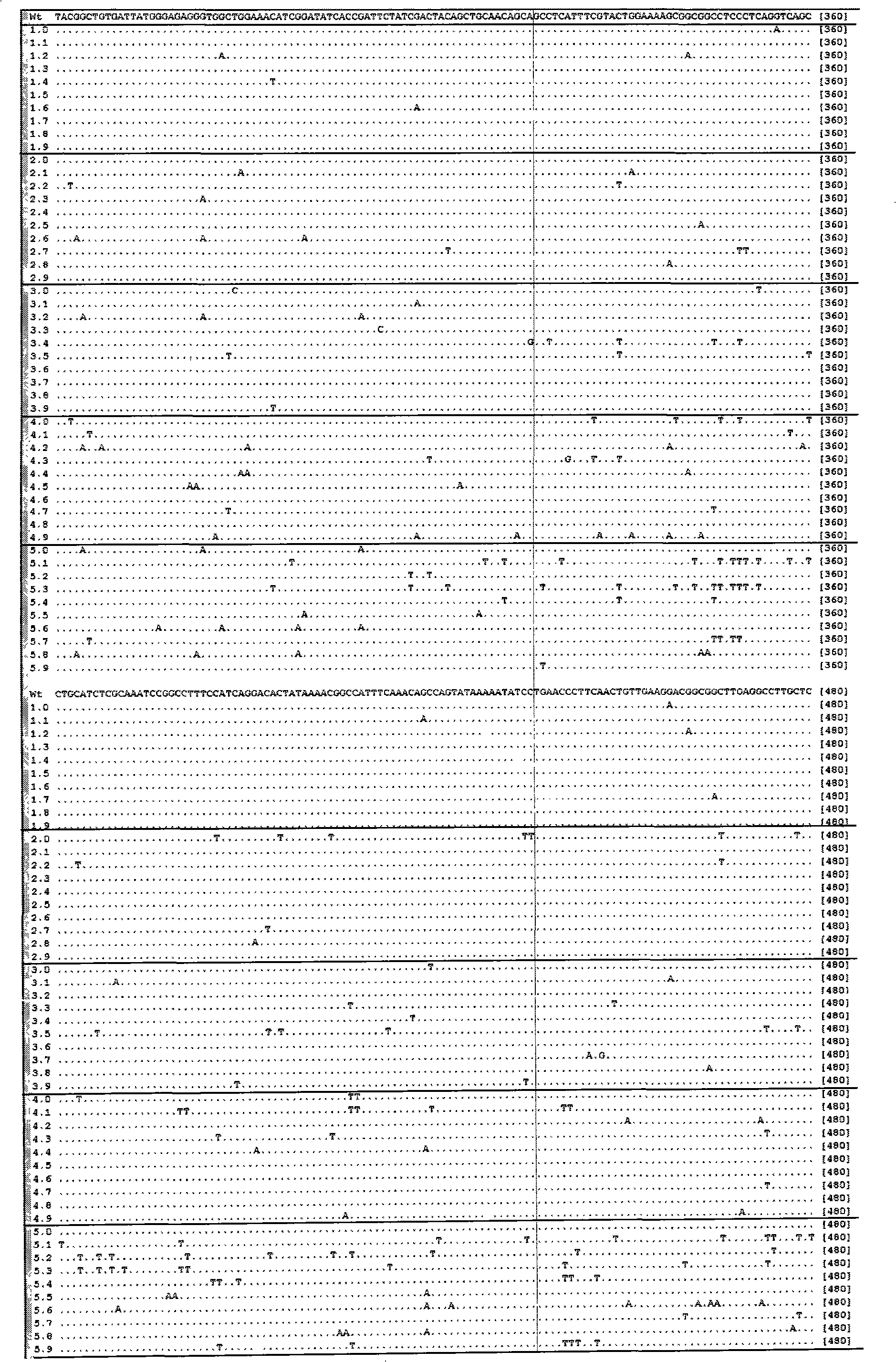
[0056] Embodiment 1 Utilize the method of the present invention to carry out the result of different time mutagenesis to the mannanase (mannanase) gene of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (Bacillus amyloliquefaciens)
[0057] Taking the mannanase from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens clone (see the sequence table SEQ ID NO: 1 for the specific sequence) as the target, carry out mutagenesis with the method of the present invention, and carry out statistical induction to the mutation frequency and results, and draw the induction The law of variable frequency and sodium bisulfite modification conditions. The specific operation is as follows:
[0058] 1. Preparation of Purified Mannanase Gene Fragment
[0059] Using the mannanase cloning vector pGEX-man as a template, the mannanase gene fragment was amplified by PCR.
[0060] The PCR reaction system is:
[0061] 10×PCR buffer (purchased from Qiagen, Cat.No.201203) 5 μL
[0062] pGEX-man 1μL
[0063] dNTP (10μM) 1μL
[0064] Forward prime...
Embodiment 2
[0095] Example 2 Using the method of the present invention to mutate TEM-1 type β-lactamase to change its substrate specificity
[0096] β-lactamase is a class of enzymes that can specifically hydrolyze β-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins and cephalosporins. TEM-I type β-lactamase is the first β-lactamase recognized by people, it is also the most common β-lactamase in Gram-negative bacteria, and it is the most primitive bacterial resistance to β-lactam antibiotics one of the mechanisms. Almost all ampicillin-resistant vectors commonly used in molecular biology experiments use TEM-1 type β-lactamase genes. It is sensitive to ampicillin and other first-generation cephalosporins, but has no hydrolysis effect on third-generation cephalosporins such as ceftazidime and cefotaxime.
[0097] In order to verify the feasibility and practicability of the method of the present invention, we selected the TEM-1 type β-lactamase gene bla from pGEX series vectors as the target, and car...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com