Salts with CRTH2 antagonist activity
A technology of potassium salt and sodium salt, applied in the field of preparation of these salts, can solve the problem of high solubility without expansion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
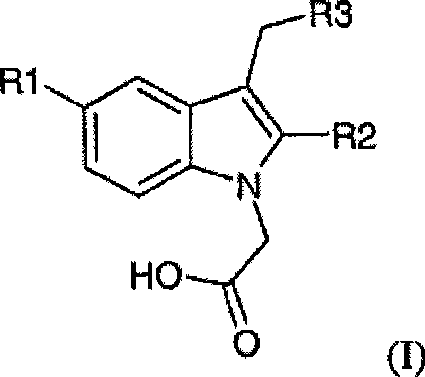
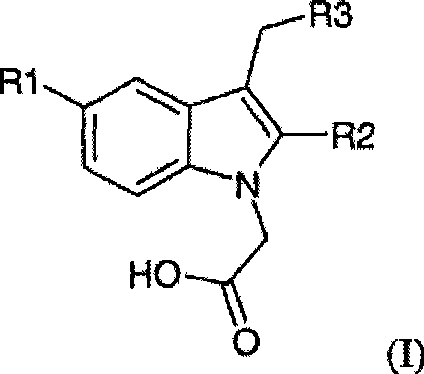
[0095] Embodiment 1: Synthesis of (5-fluoro-2-methyl-3-quinolin-2-ylmethyl-indol-1-yl)acetic acid (compound 1)
[0096] Step 1: Synthesis of (5-fluoro-2-methylindole-1-acetic acid) ethyl ester
[0097]
[0098] Put 5-fluoro-2-methylindole (0.45Kg, 3.017mol, 1.0 weight), powdered potassium carbonate (1.251Kg, 9.05mol, 2.78 weight) and acetonitrile (9.0L, 20 volumes) at 15-25°C into a 20L flanged flask. Ethyl bromoacetate (0.671 L, 2.67 mol, 1.49 vol) was added and the resulting suspension was heated to reflux for 18 hours, after which 1 H NMR in-progress check analysis (reaction sampling, sample concentration, addition of D to residue 6 -DMSO, filter and log 1 H NMR spectrum) indicated 87% conversion. Ethyl bromoacetate (0.333 L, 1.32 mol, 0.74 vol) and powdered potassium carbonate (0.626 Kg, 4.53 mol, 1.39 wt) were further added and refluxed for another 6 hours. 1 H NMR progress check analysis indicated 98.4% conversion. The contents of the flask were allowed to cool ...
Embodiment 2
[0106] Example 2: Solubility of Compound 1 Free Acid
[0107] A basic solubility screen was performed in order to provide information on the intrinsic solubility of the non-ionized form of Compound 1 and the potential increase / decrease in solubility resulting from salt formation. 50 mg of Compound 1 was charged into a vial along with 20 volumes of the indicated solvent. The mixture was stirred at 15-25°C, and if a clear solution was obtained, more solids were added until the solution was fully saturated. If no solution was obtained, the mixture was heated to reflux with stirring and an additional 20 volumes of solvent were added if necessary. The DMSO, NMP and DMF mixture was heated to 100 °C. The mixture was then cooled to 15-25°C. Table 1 below summarizes the experimental results.
[0108] Table 1
[0109]
[0110] The results indicated that Compound 1 was very insoluble ( 50 mg / ml) at 20 volumes at 15-25°C (after obtaining a solution at 100°C).
Embodiment 4
[0143] Example 4: Formation of Salt of Compound 1
[0144] As shown in Example 1, the synthesis of compound 1 involves ester hydrolysis in the final step to generate the carboxylic acid. This was done using 3 equivalents of potassium hydroxide in THF / water as base. Obviously, potassium salts must be formed during the hydrolysis. With this in mind, a vial was charged with 1 g of compound 1 along with 3 equivalents of potassium hydroxide. Water (20 vols) was added and the mixture was heated to 50°C to almost give solution. After cooling to 15-25°C, a solid precipitates and can be collected by filtration. 1 H NMR analysis confirmed that a salt had been formed. The experiment was repeated using 3 equivalents of sodium hydroxide, but after separation a sticky solid was collected which dissolved when washed with ethanol.
[0145] The experiment was repeated using acetonitrile as solvent with a few drops of water to help dissolve the base. This time using 2 equivalents of base,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com