Method for rapidly extracting tyrosinase from potato
A tyrosinase and potato technology, applied in the direction of oxidoreductase and the like, can solve the problems of large experimental error, high cost, cumbersome process, etc., and achieve the effects of maintaining tyrosinase activity, fast operation and convenient source.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] 1. Extraction of potato TYR crude enzyme:
[0027] (1) Peel and chop fresh potatoes, put them into a pulverizer and perform high-speed homogenization with 0.2 mol / L sodium acetate buffer solution (pH5.6) for 2 minutes, and filter.
[0028] (2) The above-mentioned filtrate was centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 20 min at 4°C, and the supernatant was taken, and 65% saturated ammonium sulfate solution was added to the supernatant for precipitation, and left overnight at 4°C.
[0029] (3) Centrifuge (10000r / min) the above precipitated solution for 20min, retain the precipitate, and dissolve the precipitate with a small amount of 0.2mol / L sodium acetate buffer.
[0030] (4) Use 0.02mol / L Tris-HCl to fully dialyze the above solution until there is no NH 4 + and SO 4 2- , centrifuged to remove a small amount of precipitate, available potato TYR crude enzyme solution.
[0031] 2. FPLC purification of potato TYR:
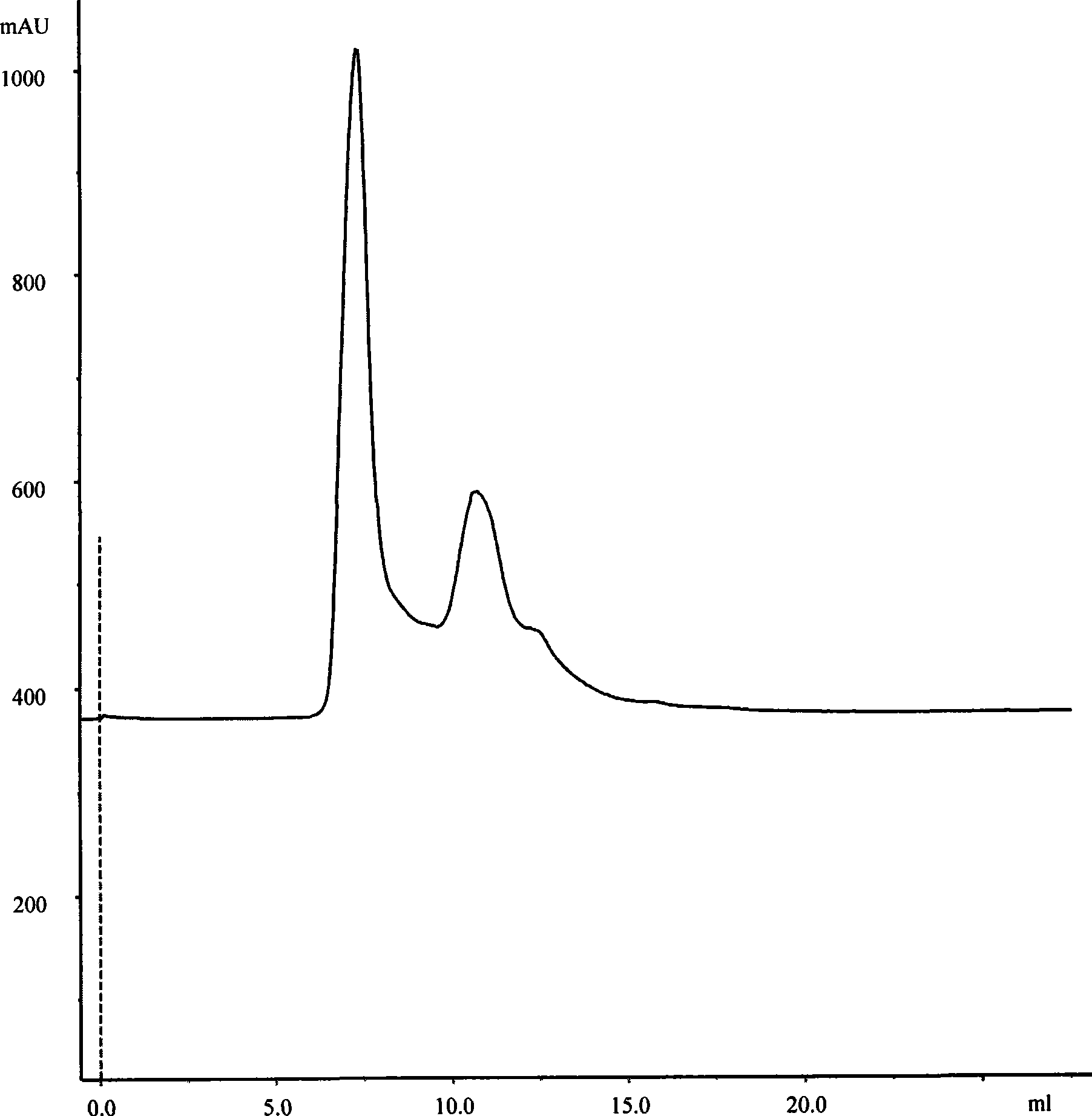
[0032] (1) Molecular sieve gel chromatography. The above crude e...
Embodiment 2
[0038] 1. Extraction of potato TYR crude enzyme:
[0039] (1) Peel and chop fresh potatoes, put them into a pulverizer and perform high-speed homogenization with 0.2 mol / L sodium acetate buffer solution (pH5.6) for 2 minutes, and filter.
[0040] (2) The above-mentioned filtrate was centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 20 min at 4°C, and the supernatant was taken, and 65% saturated ammonium sulfate solution was added to the supernatant for precipitation, and left overnight at 4°C.
[0041] (3) Centrifuge (10000r / min) the above precipitated solution for 20min, retain the precipitate, and dissolve the precipitate with a small amount of 0.2mol / L sodium acetate buffer.
[0042] (4) Use 0.02mol / L Tris-HCl to fully dialyze the above solution until there is no NH 4 + and SO 4 2- , centrifuged to remove a small amount of precipitate, available potato TYR crude enzyme solution.
[0043] 2. FPLC purification of potato TYR:
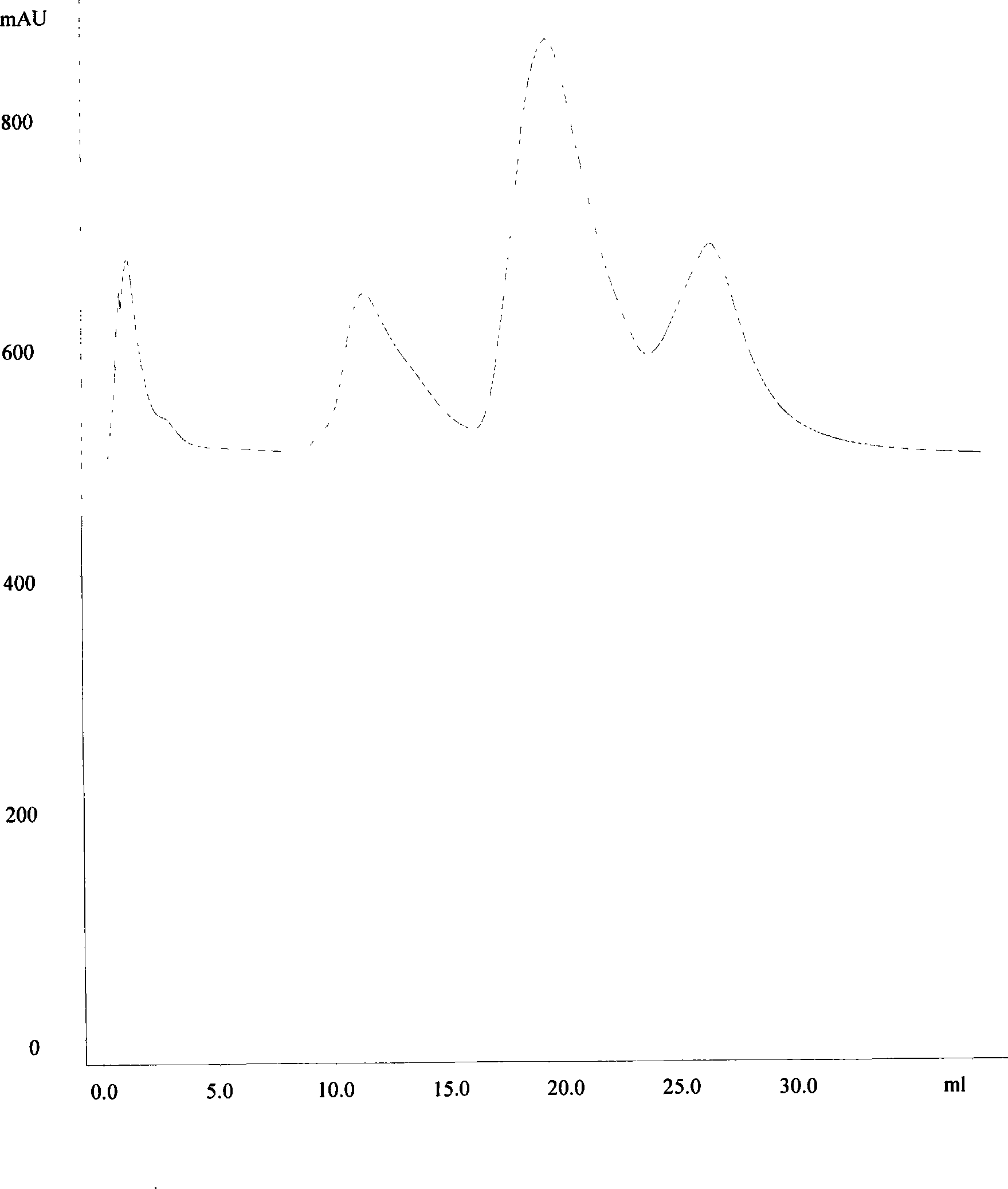
[0044]Molecular sieve gel chromatography. The above crude enzyme...
Embodiment 3
[0047] 1. Extraction of potato TYR crude enzyme:
[0048] (1) Peel and chop fresh potatoes, put them into a pulverizer and perform high-speed homogenization with 0.2 mol / L sodium acetate buffer solution (pH5.6) for 2 minutes, and filter.
[0049] (2) The above-mentioned filtrate was centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 20 min at 4°C, and the supernatant was taken, and 65% saturated ammonium sulfate solution was added to the supernatant for precipitation, and left overnight at 4°C.
[0050] (3) Centrifuge (10000r / min) the above precipitated solution for 20min, retain the precipitate, and dissolve the precipitate with a small amount of 0.2mol / L sodium acetate buffer.
[0051] (4) Use 0.02mol / L Tris-HCl to fully dialyze the above solution until there is no NH 4 + and SO 4 2- , centrifuged to remove a small amount of precipitate, available potato TYR crude enzyme solution.
[0052] 2. FPLC purification of potato TYR:
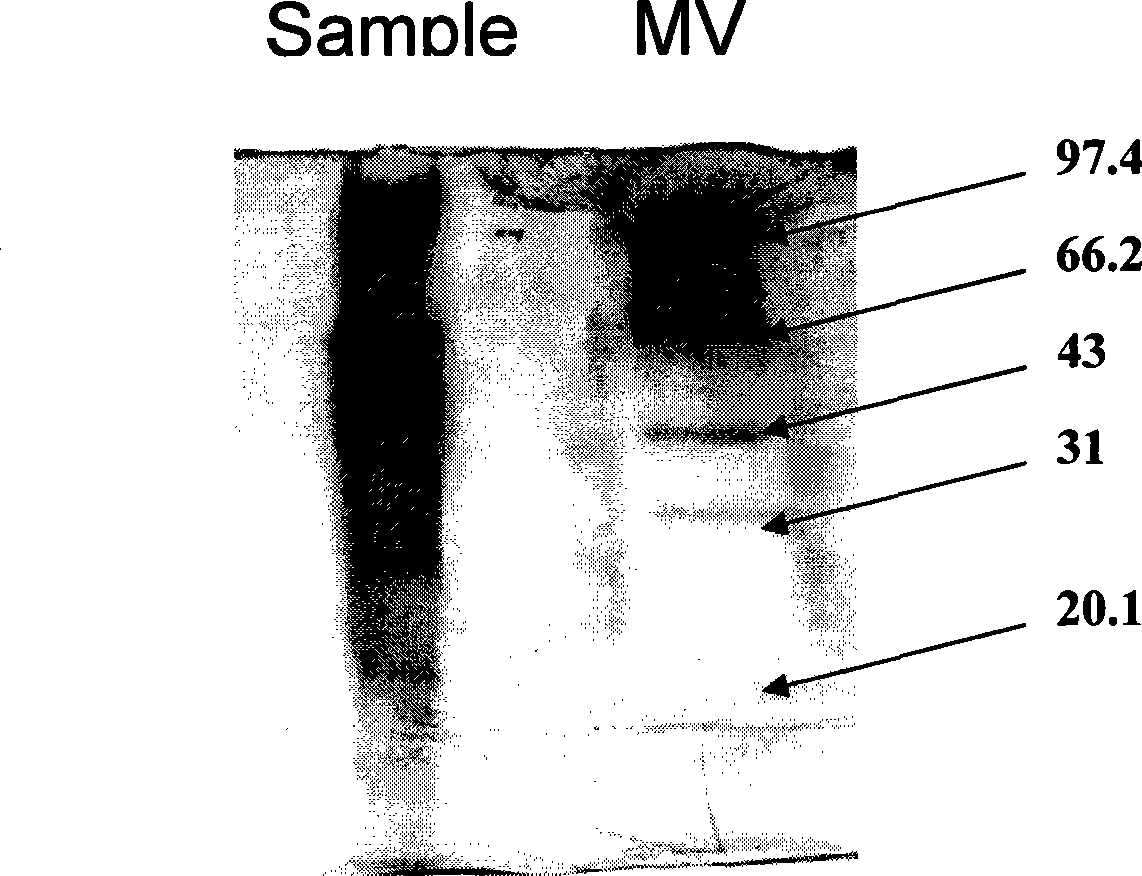
[0053] Ion-exchange chromatography: the above crude enzyme soluti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com