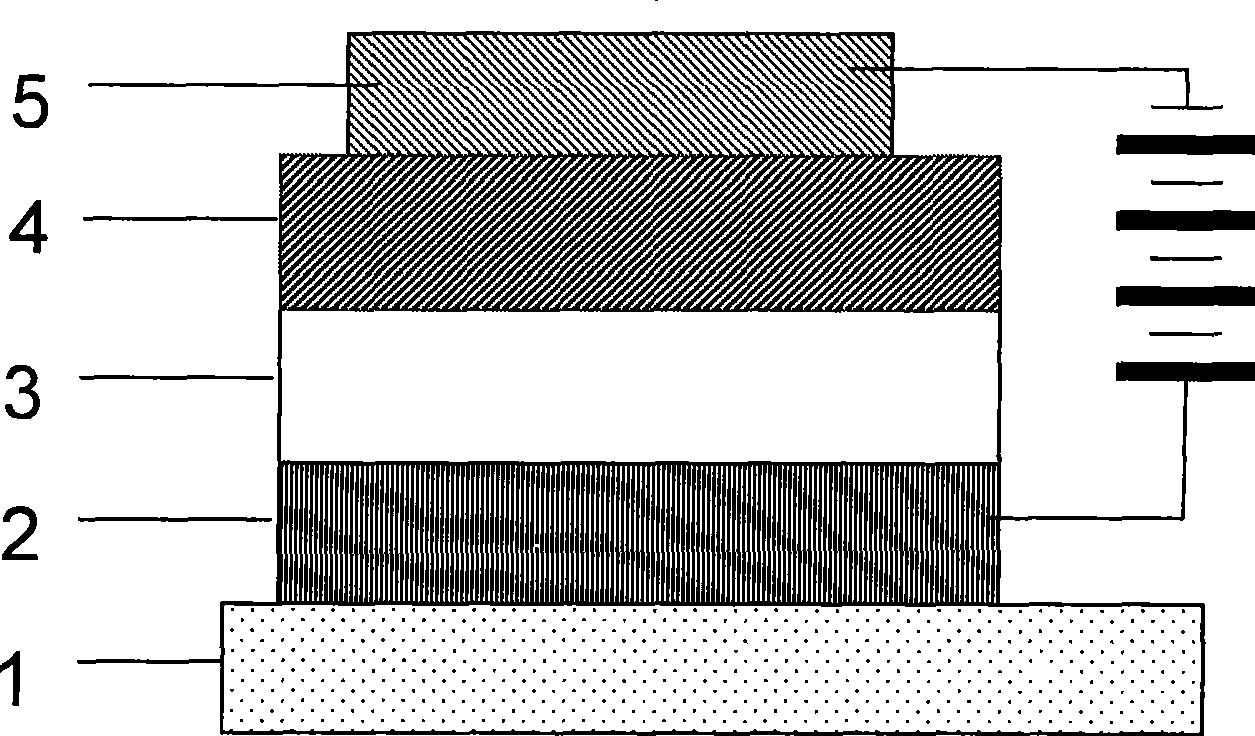
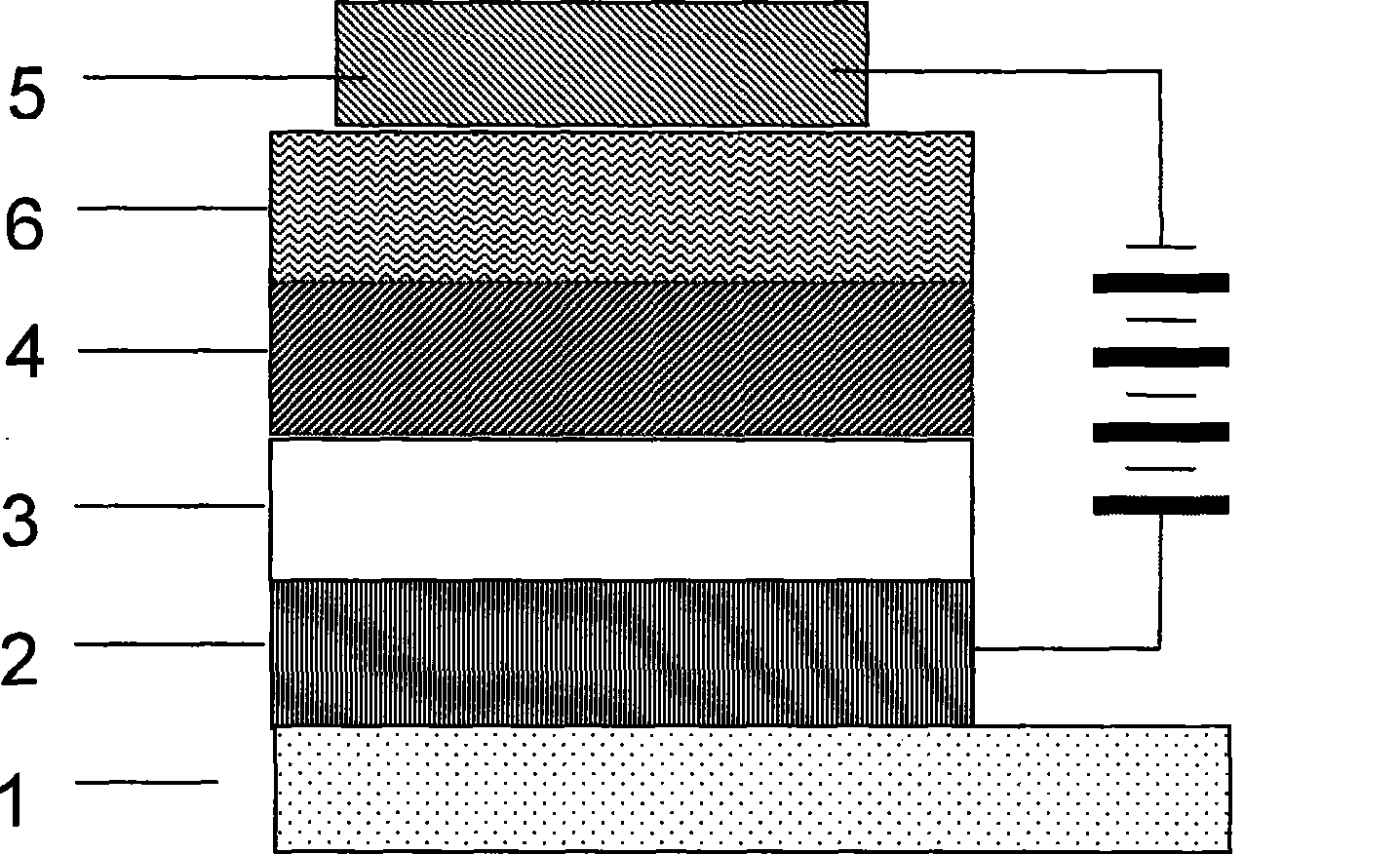
Polymer electroluminescent device and method for producing same
A technology of electroluminescent devices and polymers, which is applied in the direction of electric solid-state devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of unbalanced efficiency, low, carrier loss, etc., and achieve simple preparation process, Effects of improving efficiency performance and reducing losses
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Select the high-resistance poly(3,4-dioxyethylthiophene)-poly(p-styrenesulfonic acid) purchased from H.C.STARCK company model as BAYTRON P CH 8000, and rotate it at a speed of 2000 rpm for 60 seconds to prepare A pre-coated anode buffer layer was obtained. The thickness of the anode buffer layer is 80 nanometers, the actual measured longitudinal resistance is (202±23) ohms, and the corresponding longitudinal resistivity is (4.29±0.49)×10 6 ohm cm. When mixing PEDOT:PSS (BAYTRON P CH 8000) and 1% glycerol aqueous solution with a mass concentration of 1:1 and 1:4 respectively, after the secondary film formation of the previously obtained high-resistance BAYTRON P CH8000, Its thickness is changed to 50 nanometers and 23 nanometers respectively, the normal resistance is measured to be (54.3±18.0) ohms and (16.4±3.5) ohms respectively, and the converted normal direction resistivity is (1.63±0.54)×10 6 Ohm cm sum (1.07±0.23)×10 5 ohm cm. In other words, the conductivity o...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Repeat Example 1, using p-type organic semiconductor and green light polymer polyphenylene substituted phenylene (P-PPV) as the light emitting layer, and other conditions remain unchanged. The effects of different anode buffer layers on the performance of polymer light-emitting devices based on polyphenylene-substituted styrene as the light-emitting layer are shown in Table 2.
[0062] Table 2
[0063]
[0064] Table 2 shows that the polymer electroluminescent device based on the anode buffer layer of high resistivity (with p-type conjugated polymer, green light-emitting material P-PPV as the light-emitting layer), can obtain more than the conventional device (BAYTRON P AI 4083) and higher current efficiency and external quantum efficiency of high-conductivity anode buffer layer devices (BAYTRON P).
Embodiment 3
[0066] It has been shown from Examples 1-2 that the device structure, method and anode buffer layer involved in the present invention are especially useful for polymer light-emitting devices (most of the light-emitting layer is a p-type semiconductor material) or p-type organic semiconductor-based doping type (doped Incorporating organometallic complexes) light-emitting devices have obvious effects. We also found that the high-resistivity anode buffer layer has the effect of further enhancing its performance (current efficiency, external quantum efficiency) for other high-efficiency p-type organic semiconductor-based doped (doped with organic metal complexes) light-emitting devices ( See the impact of different anode buffer layers in Table 3 on the performance of other doped (doped with organometallic complexes) light-emitting devices. Among the various device performance parameters in Table 3, the first row provides the corresponding current density-voltage- Performance; the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com