A Method for Removing Heavy Metals from Surplus Activated Sludge
A residual activity, sludge technology, applied in biological sludge treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of low metal dissolution, high chemical method cost, difficult operation, etc. The effect of high metal dissolution rate, low treatment cost and low acid consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] 1. Determination of heavy metal content in sludge before treatment
[0045] The remaining activated sludge from the sewage treatment plant is centrifuged to obtain the precipitated part, and after drying at 105 ° C, 1.0 g is digested with a mixed acid solution of concentrated nitric acid and perchloric acid, using 1% HNO 3 Clean the flask, elute the precipitate completely, filter it with filter paper, adjust the volume of the filtrate to 25mL, then filter it with a 0.45μm filter membrane, take 10mL of the filtrate, and use the ICP method to detect the heavy metal content.
[0046] 2. Preparation of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans T.f
[0047] Preparation of medium, prepare the liquid part: (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 0.6g, KCl 0.02g, K 2 HPO 4 0.1g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.1g, Ca(NO 3 ) 2 4H 2 O 0.002g, distilled water 200mL, with H 2 SO 4 Adjust the pH to 2.0, sterilize with high pressure steam at 121°C for 20min; prepare the solid part: FeSO 4 .7H 2 O 8.8g, sterilized by ultravi...
Embodiment 2
[0059] 1. the mensuration of sludge heavy metal content before treatment is the same as embodiment 1
[0060] 2. The preparation of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans is the same as in Example 1
[0061] 3. The preparation of Thiobacillus thiooxidans is the same as in Example 1
[0062] 4. Heavy metal removal --- biological leaching operation
[0063] Prepare the triangular flask and the liquid composition in the same example 1, add 20.0g dewatered sludge in the bottle, 4mL T.f bacterial liquid and 4mL T.t bacterial liquid, 8.8g FeSO 4 and 2g S.
[0064] The initial pH of the leachate is H 2 SO 4 Adjust to 5.0. The bioleaching reaction was carried out in a shaking incubator at a temperature of 28° C., and the rotation speed was adjusted at 150 rpm. The leaching reaction was stopped after 12 days.
[0065] 5. the mensuration of sludge heavy metal content after treatment is the same as embodiment 1
[0066] 6. Experimental results
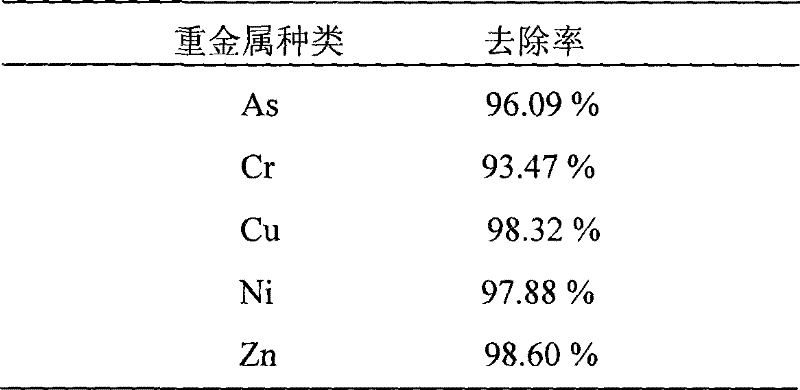
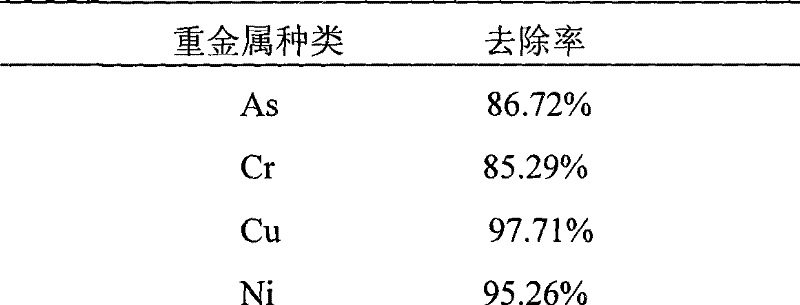
[0067] Heavy metal removal rate before and aft...
Embodiment 3
[0071] 1. the mensuration of sludge heavy metal content before treatment is the same as embodiment 1
[0072] 2. The preparation of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans is the same as in Example 1
[0073] 3. The preparation of Thiobacillus thiooxidans is the same as in Example 1
[0074] 4. Heavy metal removal --- biological leaching operation
[0075] Prepare the triangular flask and the inner liquid composition with example 1, add 40.0g dewatered sludge in the bottle, 8mL T.f bacterium liquid and 8mL T.t bacterium liquid, 8.8g FeSO 4 and 2g S.
[0076] The initial pH of the leachate is H 2 SO 4 Adjust to 7.0. The bioleaching reaction was carried out in a shaking incubator at a temperature of 35° C., and the rotation speed was adjusted at 150 rpm. The leaching reaction was stopped after 6 days.
[0077] 5. the mensuration of sludge heavy metal content after treatment is the same as embodiment 1
[0078] 6. Experimental results
[0079] Heavy metal removal rate before and after...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com