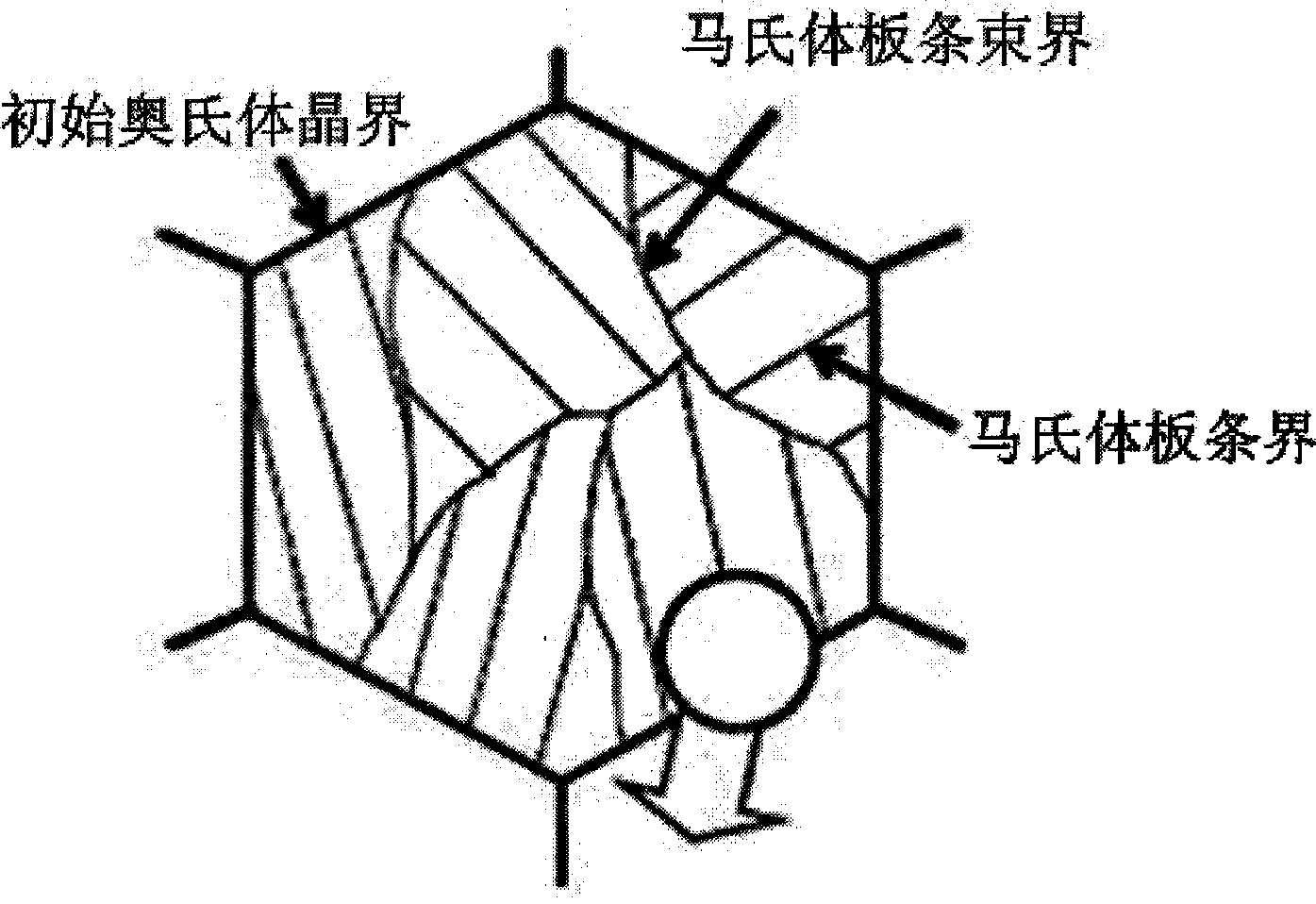
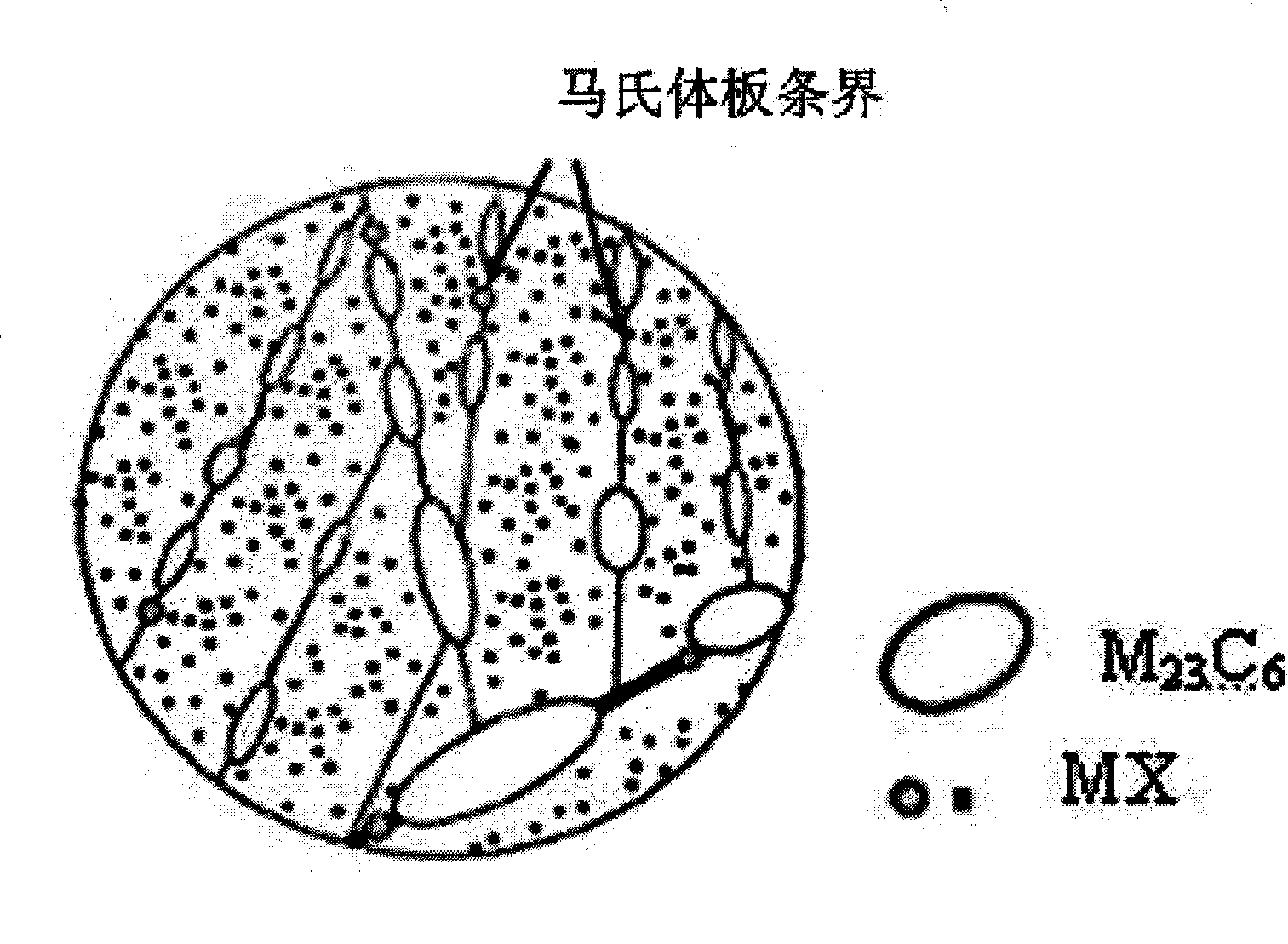
High-chromium ferrite heat-resistant steel fine-deformation martensite lath microstructure refinement method
A technology of high-chromium ferrite and heat-resistant steel, which is applied in the field of micro-deformed martensitic lath structure refinement of high-chromium ferrite heat-resistant steel, which can solve the problems of deterioration of metal high-temperature performance and affecting equipment safety, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Example 1: Corresponding high-chromium ferritic heat-resistant steel
[0022] The chemical composition range of the high-chromium ferritic heat-resistant steel used in the experiment is shown in Table 1. The purity of the raw materials used are all higher than 99%. According to the predetermined composition ratio, they are smelted in an electric arc furnace or an induction furnace and undergo two processes of vacuum refining and out-of-furnace refining, and then they are hot-rolled into pipes or plates.
[0023] Take the sample of the same composition after fusion, and cut a cylindrical sample from the steel pipe by wire cutting. The size of the linear expansion sample is 5mm in diameter and 10mm in length; after cleaning and drying, put it in a high-frequency induction heat treatment device for treatment: set The fixed program is as follows: the heating rate is 30-80K / min, after rising from room temperature to 1223-1323K, keeping the temperature for 5-15 minutes, then ...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Example 2: Corresponding to T91 high-chromium ferritic heat-resistant steel
[0025] (1) Sample preparation
[0026] The purity of the raw materials used is all higher than 99%. According to the established composition ratio in Table 2 (corresponding to T91 high-chromium ferritic heat-resistant steel), it is melted in an electric arc furnace or an induction furnace, and two processes of vacuum refining and out-of-furnace refining are carried out. Then it is hot-rolled into pipe or plate (wall thickness 1.5 cm).
[0027] Table 2 Chemical composition range of T91 high-chromium ferritic heat-resistant steel
[0028] component Content (wt.%) C 0.09 Si 0.03 Cr 9.1 Mo 1.1 mn 0.4 V 0.2 Nb 0.07 N 0.04 Al 0.01
[0029] (2) micro-deformation treatment
[0030] Put the sample into a high-frequency induction heat treatment device for processing: set the program as follows: the heating rate is 50K / min, after rising ...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Example 3: Corresponding to T92 high-chromium ferritic heat-resistant steel
[0033] (1) Sample preparation
[0034] The purity of the raw materials used are all higher than 99%. According to the established composition ratio in Table 3 (corresponding to T92 high-chromium ferritic heat-resistant steel), they are smelted in an electric arc furnace or an induction furnace, and two processes of vacuum refining and out-of-furnace refining are carried out. Then it is hot-rolled into pipe or plate (wall thickness 1.5 cm).
[0035] Table 3 Chemical composition range of T92 high-chromium ferritic heat-resistant steel
[0036] component Content (wt.%) C 0.08 Si 0.03 Cr 9.1 Mo 0.4 mn 0.4 V 0.2 Nb 0.05 N 0.04 Al 0.01
[0037] W 1.0 B 0.05
[0038] (2) micro-deformation treatment
[0039] Put the sample into a high-frequency induction heat treatment device for processing: set the program as follow...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com