Protective method for hearth of vanadium titano-magnetite rotary hearth furnace used for coal-based direct reduction
A rotary hearth furnace bottom, vanadium-titanium magnetite technology, applied in the manufacture of converters, etc., can solve the problems of worn out discharge spiral, titanium slag pollution, titanium slag pollution, etc., achieve simple manufacturing and maintenance, and prolong service life , easy maintenance effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
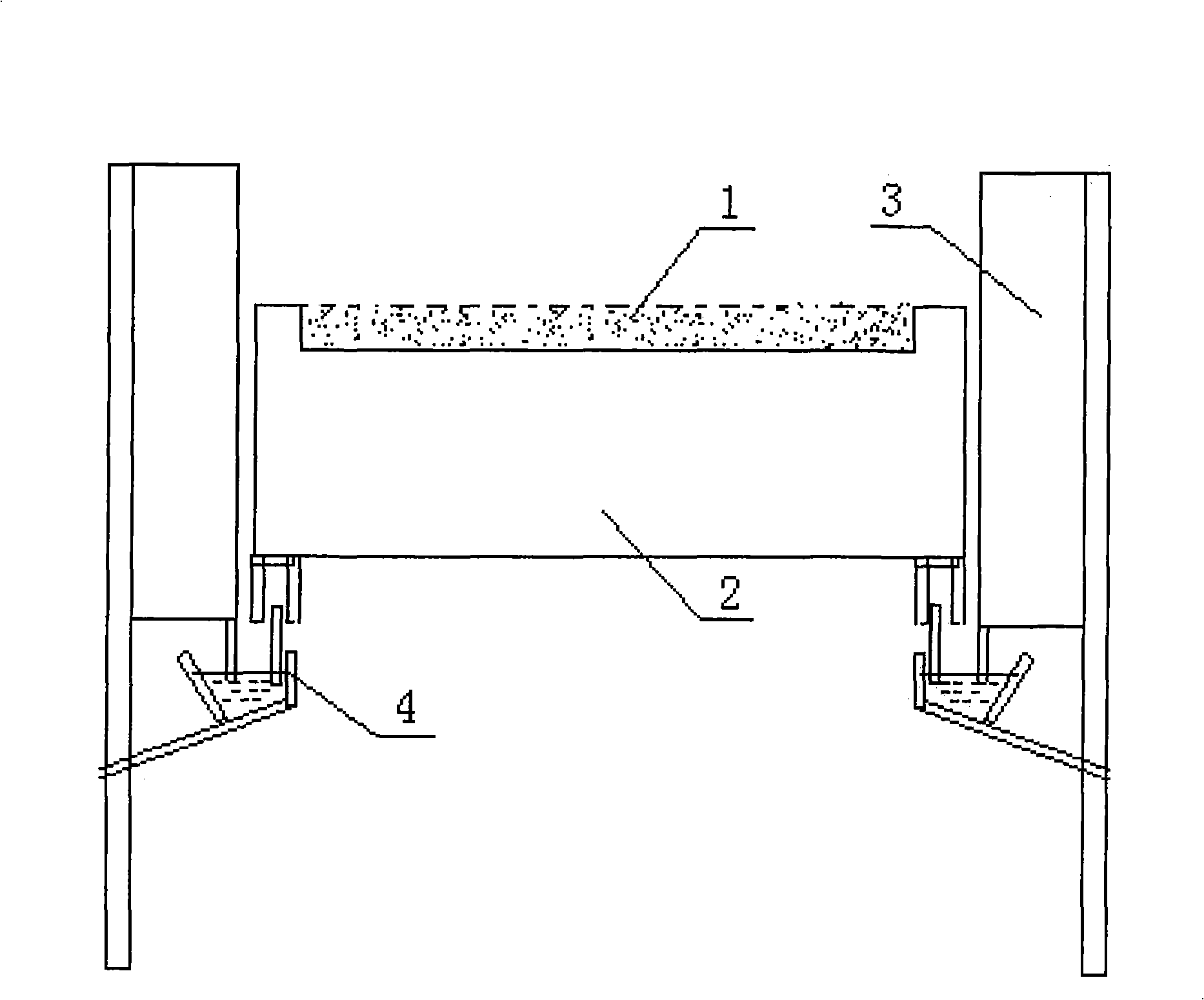
[0020] Accompanying drawing is the furnace bottom schematic diagram of rotary hearth furnace. After reducing the vanadium-titanium magnetite through the rotary hearth furnace, all the reduced charge enters the electric furnace for melting, and after melting, the liquid titanium slag 1 from the electric furnace is broken to a certain particle size, and spread in the rotary hearth furnace made of refractory materials. On the surface layer of the furnace bottom 2, they are in direct contact with the charge. Below the titanium slag, the furnace bottom is built with ordinary refractory materials, and the vanadium-titanium magnetite lumps are laid on the titanium slag to form a "soft furnace bottom". Because the bottom of the furnace is "soft", it can avoid the phenomenon that the bottom of the furnace rises due to the expansion and bonding of the bottom of the refractory material, which plays a role in protecting the bottom of the furnace. As shown in the figure, since the furnace...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com