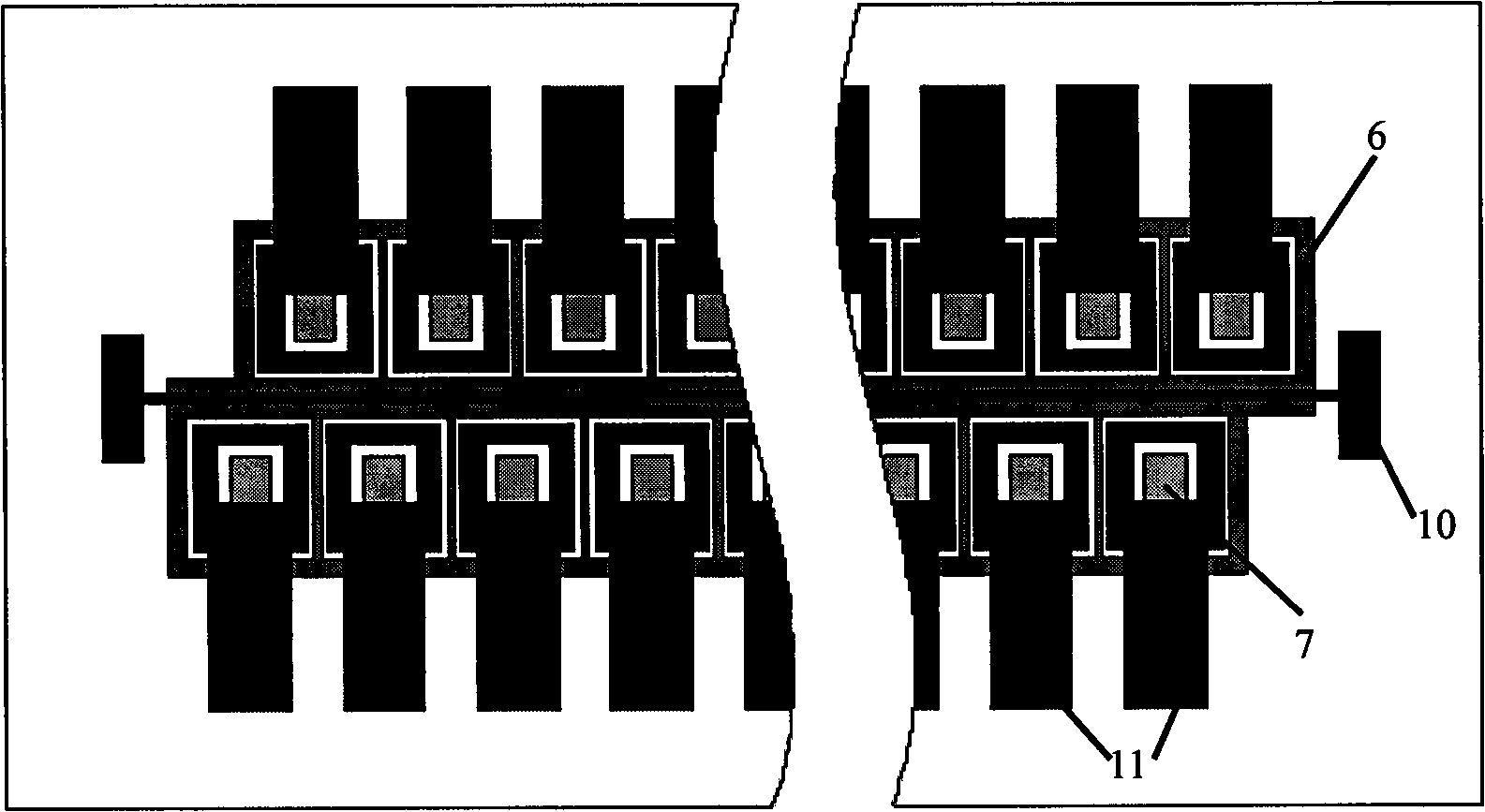
Plane-structure InGaAs array infrared detector
An infrared detector and a planar structure technology, applied in the field of photodetectors, can solve problems such as the difficulty in defining the photosensitive surface, limiting the performance of InGaAs detectors, and large leakage currents, so as to suppress the expansion phenomenon and reduce the expansion phenomenon of the photosensitive surface , the effect of suppressing crosstalk
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0012] The specific embodiments of the present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and examples:
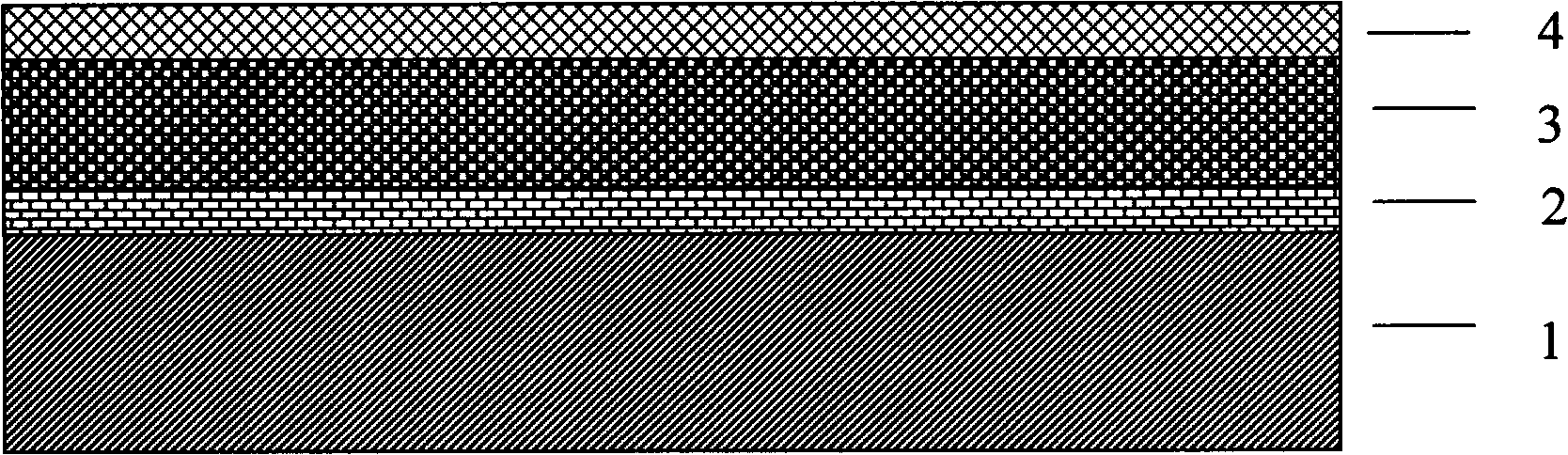
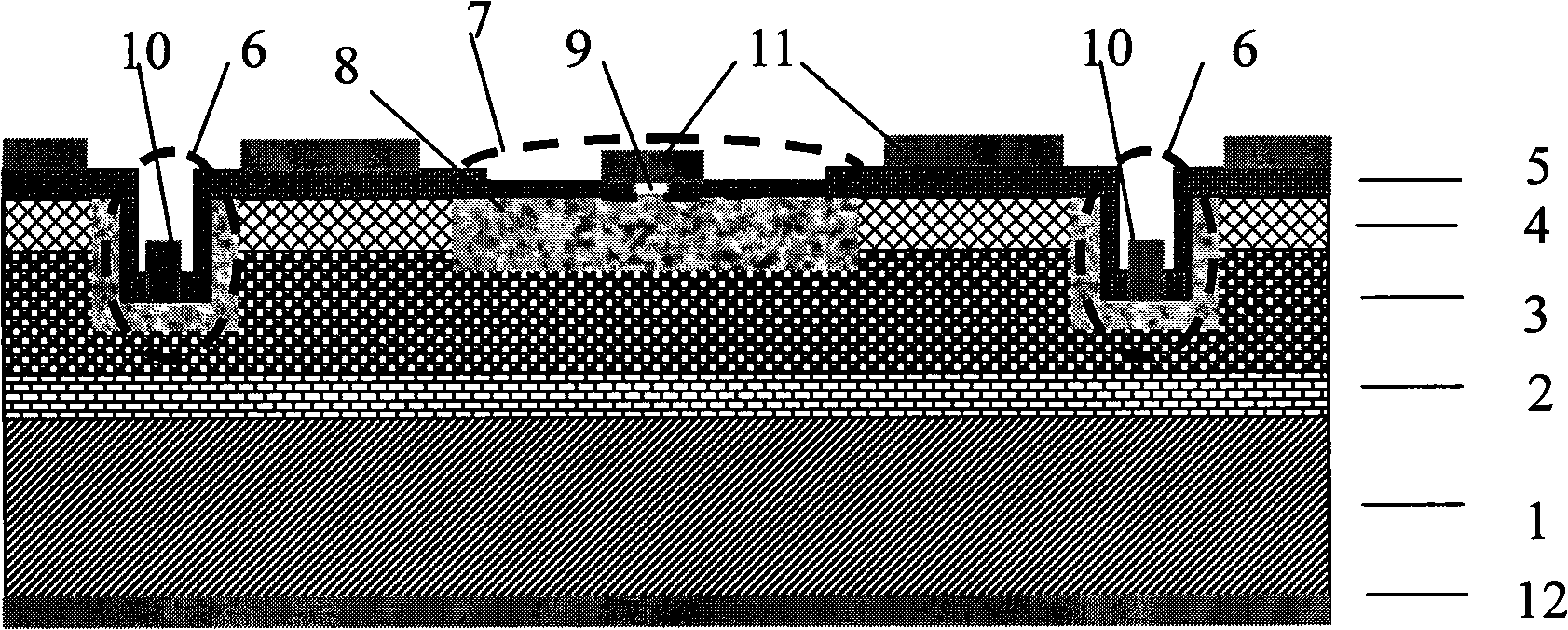
[0013] See figure 1 , the epitaxial wafer used in this embodiment is MOCVD technology with a thickness of 600 μm and a carrier concentration of 3 × 10 18 cm -3 N-type InP layers 2 with a thickness of 1 μm are sequentially grown on the N-InP substrate 1, and the carrier concentration is 2×10 18 cm -3 ; In thickness of 2.5 μm 0.53 Ga 0.47 As intrinsic absorption layer 3, carrier concentration 5×10 16 cm -3 ; N-type InP cap layer 4 with a thickness of 1 μm, carrier concentration 5 × 10 16 cm -3 .
[0014] The device preparation process of this embodiment is as follows:
[0015] 1. Use chloroform, ether, acetone, and ethanol to ultrasonically clean the epitaxial wafer in sequence for more than 2 minutes, and then blow dry with nitrogen;
[0016] 2. Growth of SiO 2 Diffusion mask 5;
[0017] 3. Preparation of S...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com