New gene mutation recombination method and application thereof
A mutant, target gene technology, applied in combinatorial chemistry, chemical library, library creation, etc., can solve the problems of not widely used and few literature reports.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0013] Example 1: Amplification of target gene
[0014] This method intends to select the kanamycin resistance gene (kan) as the target gene for error-prone PCR. The kan gene expression unit from the plasmid vector pCMABIA1302 is amplified by PCR and then inserted into the pUC18 vector to obtain a gene containing kan. and ampicillin (amp) resistant recombinant plasmid p18Kan, and then using the p18Kan vector as a DNA template, the kan gene fragment was amplified with a pair of artificially synthesized primers (see below), and the conditions were optimized. As shown in the table below:
[0015]
[0016] PCR primers are: upstream primer; 5′-CCTGTGATCA CCGCGG TTTC-3', the underline is the restriction enzyme SacII cleavage site. Downstream primer; 5′-CTGTTTCTTCCCC GATATC CTCC-3', the underline is the restriction enzyme EcoRV cleavage site. The pair of primers amplified the expected PCR product with a size of 0.89 bp, which included the 5' end coding region and non-coding ...
Embodiment 2
[0018] Example 2: Error-prone PCR of a gene of interest
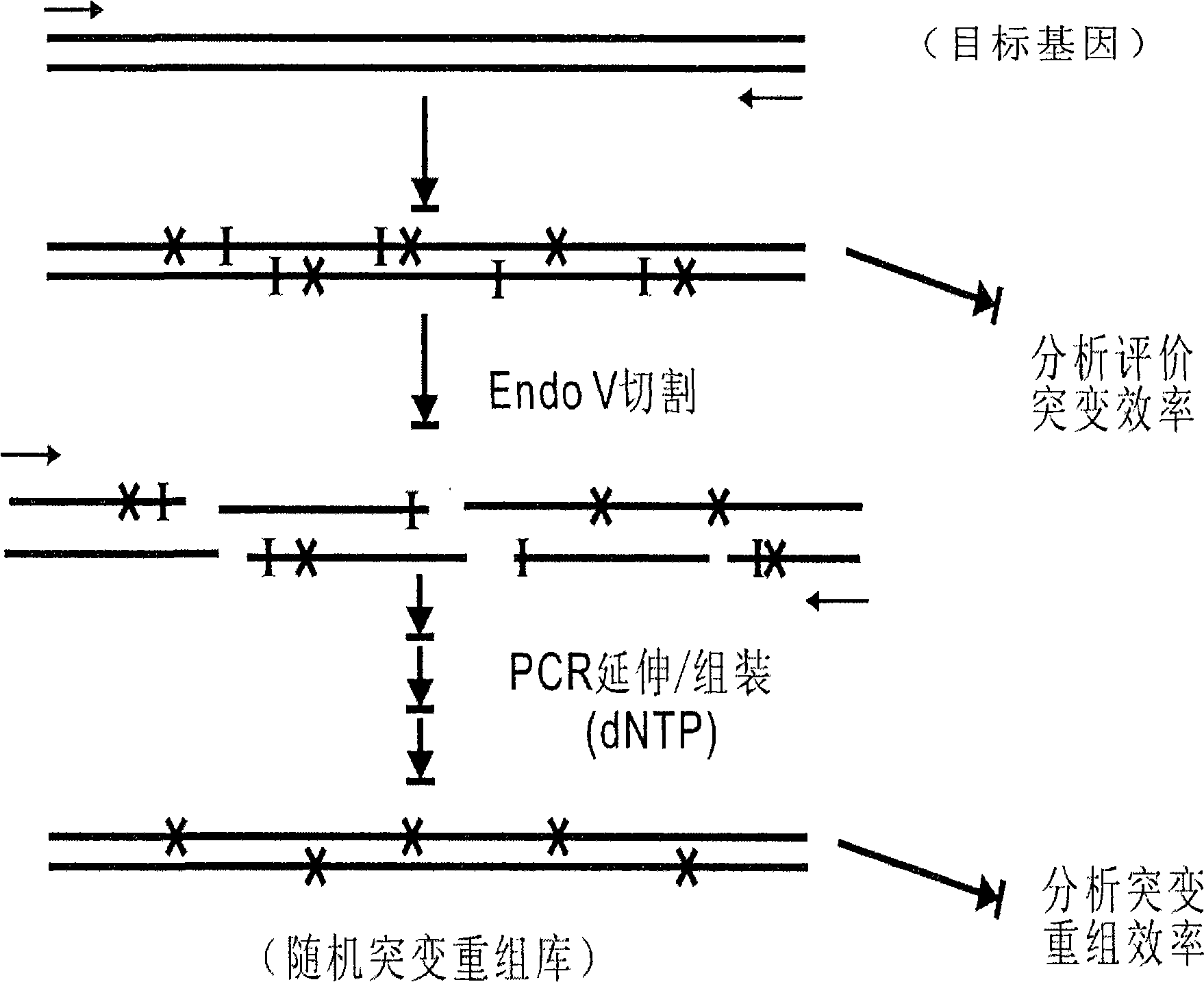
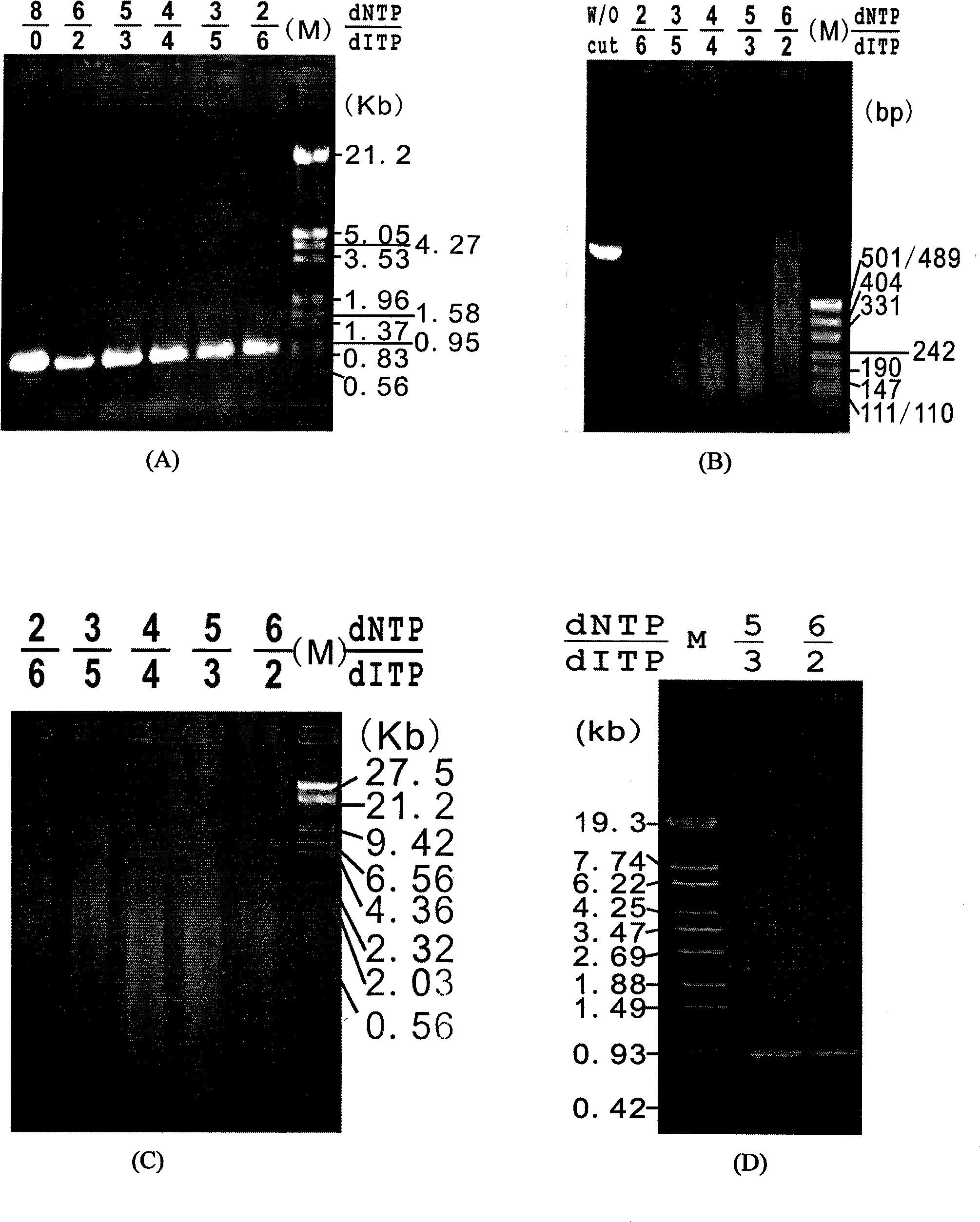
[0019] According to Example 1, error-prone PCR was performed with the kanamycin resistance gene (kan) as the target gene. This method is different from the conventional error-prone PCR method, but nucleotide analogs (dITP) are randomly incorporated into the product sequence through PCR technology, thereby forming random point mutations. In order to control the frequency and number of dITP incorporated into the target sequence during the PCR reaction, so that small fragments of the target gene of appropriate size can be obtained in the subsequent enzyme digestion step, it is first necessary to adjust the ratio of dNTP and dITP in the PCR reaction system. optimization. The specific steps required are: in a 100 μl PCR system, adjust the ratio of dNTP:dITP in the system to 8:0, 6:2, 5:3, 4:4, 3:5, and 2:6 as shown in the table below.
[0020] dNTP (2.5mM) 8μl 8μl 8μl 4μl 3μl 2μl dITP (2.5mM) 0μl...
Embodiment 3
[0022] Example 3: Random Fragmentation of Mutant Genes
[0023] Use endo V to digest the obtained mutant gene. The enzyme digestion reaction system is 20 μl, including 10 μl of PCR product, 2 μl of endo V buffer, 1 U of endonuclease endo V (MBI company), and 60 μl of enzyme digestion at 65 ° C. Minutes, the digestion reaction was terminated by heating at 95°C for 15 minutes, and the product was detected by 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis. The results are shown in the attached figure 2 Shown in B: As the ratio of dNTP:dITP decreases, the fragments produced after endoV digestion become smaller, which also indicates that the site of incorporated dITP increases. When the ratio of dNTP:dITP is 2:6, the digested DNA fragments are mainly concentrated below 150bp; when the ratio of dNTP:dITP is 3:5, the digested fragments are mainly distributed at 200-50bp. This range is generally considered suitable for DNA assembly.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com