Process for producing dispersions of highly fluorinated polymers
A highly fluorinated, polymer-based technology, applied in the field of ion-exchange polymer dispersions, can solve the problems of expensive preparation of PFSA final product dispersions, difficult control of distillation and dilution steps, and difficulty in regeneration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1 to 9
[0097] Examples 1 to 9: Preparation of polymer powders
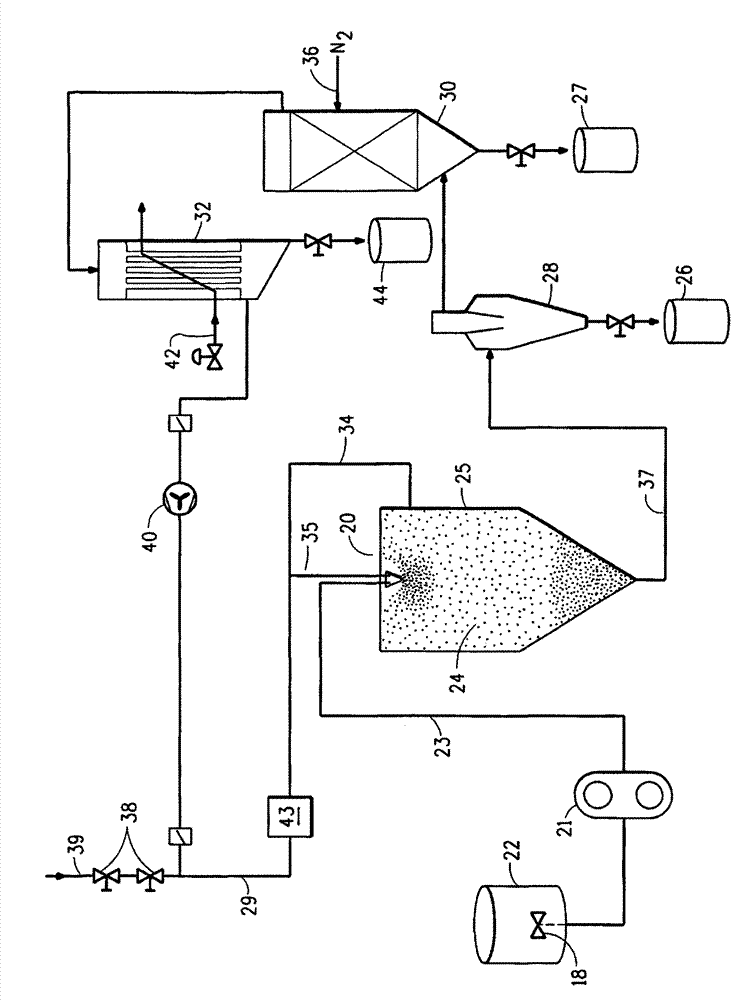
[0098] By feeding the above fluoropolymer dispersions A, B, C, D and E to figure 2 The spray dryer shown was used to prepare polymer particle powders. For Examples 1 to 9, the spray dryer used was a Niro Mobile Minor TM Closed cycle spray dryer from Niro Inc., Columbia, Maryland. In each example, the liquid dispersion was injected into the spray dryer through a two-fluid nozzle. One fluid is pressurized nitrogen and the other is a dispersion. Pressurized nitrogen was used to atomize the dispersion as the nitrogen and dispersion exited the two-fluid nozzle. Orient the nozzle downwards from the upper center of the spray dryer, as figure 2 shown. The dispersion is vented into hot nitrogen in a spray dryer and the liquid in the dispersion evaporates rapidly causing the particles of polymer and optionally additives to agglomerate and dry as the particles fall through the chamber.
[0099] The specific processing co...
Embodiment 10 to 18
[0105] Examples 10 to 18: Redispersions of powders
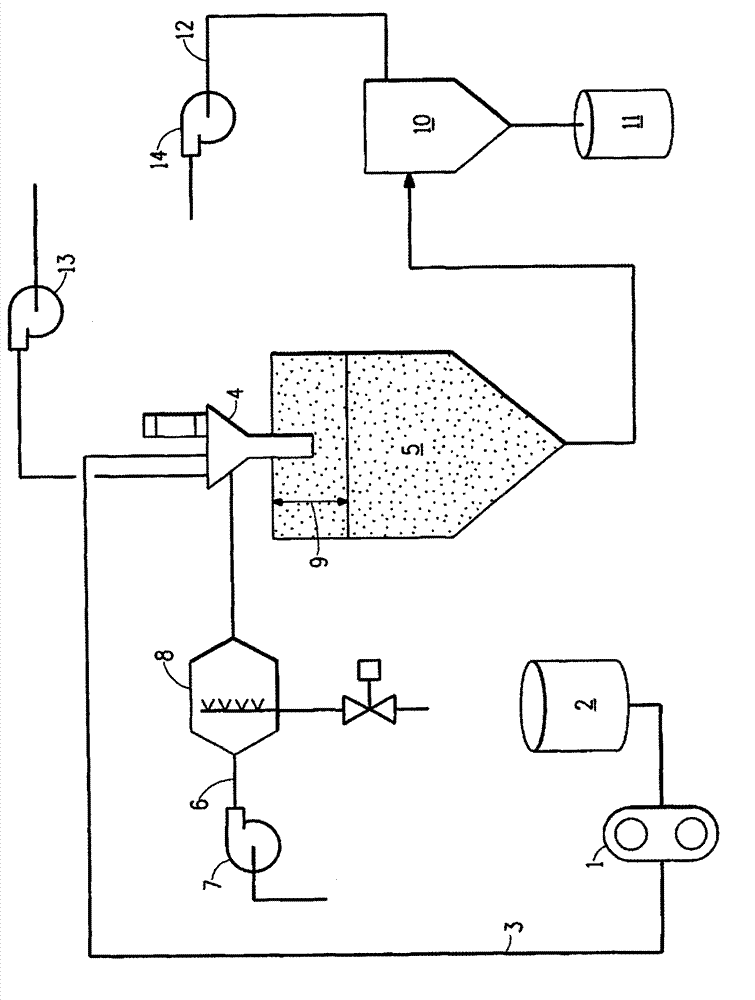
[0106] For each of Examples 10 to 18 below, 1-propanol was placed at room temperature and atmospheric pressure in a stainless steel vessel with an air-driven stirrer rotating at approximately 250 rpm. For Redispersion Examples 10, 12 and 14 to 18 below, the polymer powder from one of Examples 1 to 9 was weighed and added to 1-propanol. The examples from which the polymer powders were obtained and the weights of the powders are listed in Table 2 below. Depending on the example, the weight ratio of 1-propanol to polymer is from 1:1 to 9:1. The contents were stirred for at least one hour until the polymer powder was completely wetted and dispersed in 1-propanol. Distilled water, about the same weight as the 1-propanol, was added to the vessel and stirring was continued for several more hours until the dispersion was clear and colorless.
[0107] In Examples 11 and 13, where larger amounts of dispersion were produced, the i...
Embodiment 19
[0115] Example 19: Cast film
[0116] Solution cast perfluorosulfonic acid membranes were prepared from the redispersion of Example 13 according to the following procedure. The dispersion of Example 13 was drawn from the slot die to a moving on the film. The slot opening is 5 mil thick and 14 inches (35.6 cm) wide. Pump speed and line speed were adjusted to achieve a film thickness of approximately 1 mil. The film carries the film through a three zone gas flame dryer which dries the film from top to bottom. Each dryer zone was 10 inches long and the temperatures in each zone were as follows:
[0117] Zone 1: 45°C
[0118] Zone 2: 73°C
[0119] Zone 3: 96°C
[0120] Then by using The PFSA film on thin film heat treats the dried film by moving it through a three-zone gas flame dryer heating the film from top to bottom to coalesce the polymer. The dwell time of the film in each zone was 45 seconds for a total heating time of 135 seconds (+ / - 2 seconds). Each dryer ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com