Method for preparing bacterial cellulose membrane with high rehydration
A bacterial cellulose membrane and high rehydration technology, applied in the field of biomaterials, can solve the problems of application limitations, gel membranes not having the state and properties of gel membranes, and damage to the excellent properties of gel membranes, achieving high rehydration rates and high Effect of rehydration and reswellability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] A preparation method of high rehydration bacterial cellulose membrane, the preparation steps are:
[0025] (1) 100 g of bacterial cellulose hydrogel membranes (containing 1.13 g of bacterial cellulose) from which bacteria and culture medium have been removed are immersed in a 2% NaOH aqueous solution, and treated with stirring for 1 hour at room temperature;
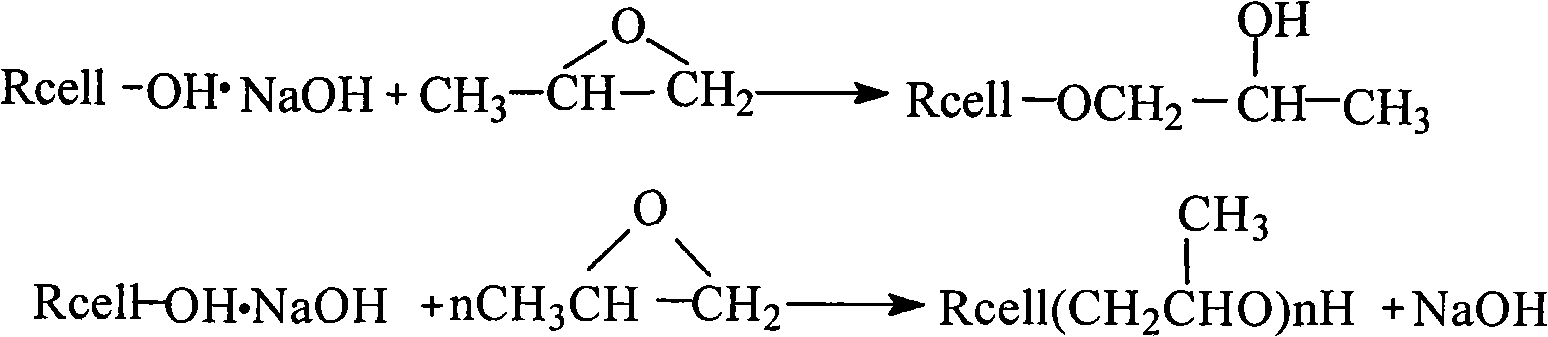
[0026] (2) soaking the treated film with etherifying agent propylene oxide at a constant temperature of 30°C for 20 hours;
[0027] (3) neutralize the reaction solution with an acidic solution of acetic acid to neutrality and stir for 1 hour, and finally rinse the membrane with a large amount of distilled water to obtain a hydroxypropylated bacterial cellulose membrane.
[0028] (4) The hydroxypropylated bacterial cellulose membrane is placed on a polytetrafluoroethylene membrane, dried in a 60° C. blast dryer for 2.5 hours, and taken out to obtain a highly rehydrated bacterial cellulose membrane.
[0029] Detect...
Embodiment 2
[0032] A preparation method of high rehydration bacterial cellulose membrane, the preparation steps are:
[0033] (1) Immerse 100 g of bacterial cellulose hydrogel membrane (containing 1.12 g of bacterial cellulose) from which bacteria and culture medium have been removed in a NaOH / urea aqueous solution with a concentration of 2% / 2%, and stir at room temperature. 1 hour.
[0034] (2) Soak the treated membrane with etherifying agent propylene oxide at a constant temperature of 30° C. for 20 hours.
[0035] (3) neutralize the reaction solution with an acidic solution acetic acid to neutrality and stir for 1 hour, and then rinse the membrane with a large amount of distilled water to obtain a hydroxypropylated bacterial cellulose membrane.
[0036] (4) The hydroxypropylated bacterial cellulose membrane is placed on a polytetrafluoroethylene membrane, dried in a 60° C. blast dryer for 2.5 hours, and taken out to obtain a highly rehydrated bacterial cellulose membrane.
[0037] Te...
Embodiment 3
[0039] A preparation method of high rehydration bacterial cellulose membrane, the preparation steps are:
[0040] (1) 100 g of bacterial cellulose hydrogel membranes (containing 1.14 g of bacterial cellulose) from which bacteria and culture medium have been removed are immersed in a 4% NaOH aqueous solution, and treated with stirring at room temperature for 1 hour.
[0041] (2) Soak the treated membrane with etherifying agent propylene oxide at a constant temperature of 40° C. for 20 hours.
[0042] (3) neutralize the reaction solution with an acidic solution of acetic acid to neutrality and stir for 1 hour, and finally rinse the membrane with a large amount of distilled water to obtain a hydroxypropylated bacterial cellulose membrane.
[0043] (4) The hydroxypropylated bacterial cellulose membrane is placed on a polytetrafluoroethylene membrane, dried in a 60° C. blast dryer for 2.5 hours, and taken out to obtain a highly rehydrated bacterial cellulose membrane.
[0044] Det...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com