Battery
一种电池、电解液的技术,应用在电池电极、锂蓄电池、二次电池等方向,能够解决增加热失控的风险、电解液氧化分解、耐氧化性差等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
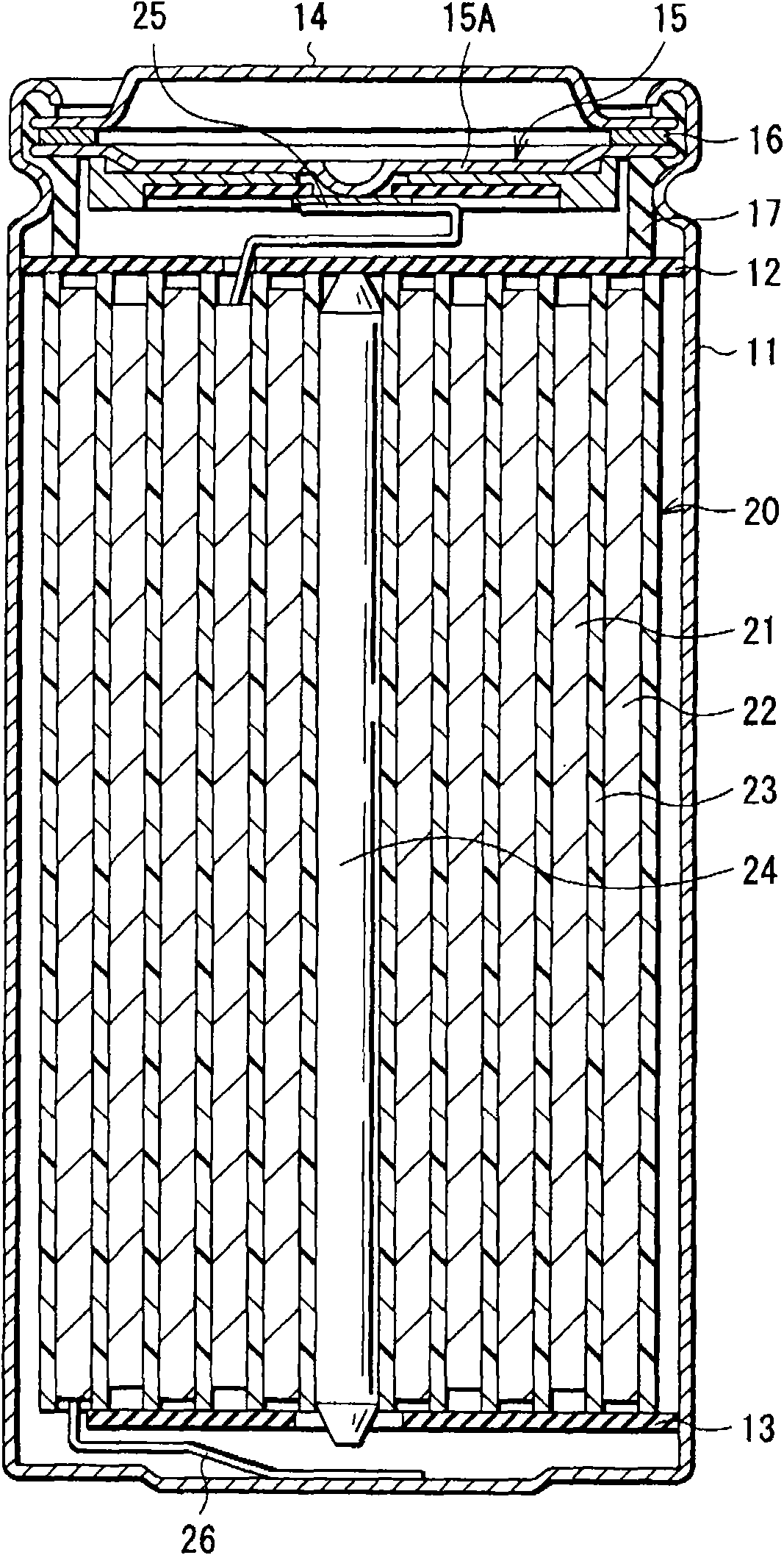
[0020] figure 1 is a cross-sectional view showing the battery structure of the first embodiment of the present invention. The battery is a lithium ion secondary battery, and the capacity of the negative electrode in the battery is represented by insertion and extraction of lithium, and lithium is used as an electrode reactant.
[0021] In this secondary battery, a spirally wound electrode body 20 and a pair of insulating plates 12 and 13 are housed in a battery case 11 . The battery case 11 is an almost hollow cylinder. In the spirally wound electrode body 20 , a positive electrode 21 and a negative electrode 22 are spirally wound with a separator 23 therebetween. The battery case 11 is made of, for example, nickel (Ni)-plated iron (Fe). One end of the battery case 11 is sealed, and the other end is open. A pair of insulating plates 12 and 13 are arranged to sandwich the spirally wound electrode body 20 and extend perpendicular to the spirally wound outer peripheral surfac...
no. 2 approach
[0066] The structure, operation, and effects of the battery of the second embodiment are the same as those of the first embodiment except that the negative electrode 22 has a different structure. The battery of the second embodiment was also produced by the same procedure as that of the first embodiment.
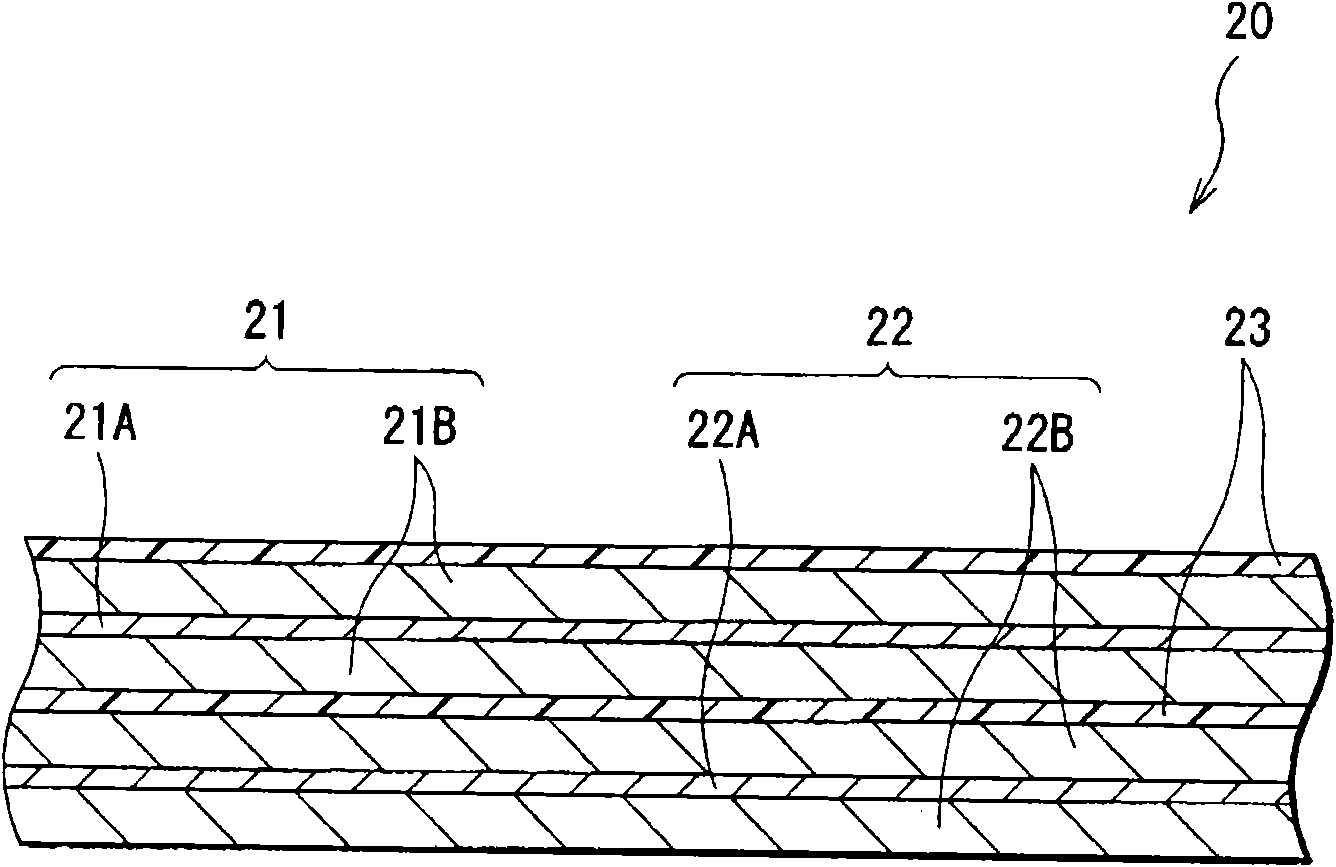
[0067] Similar to the battery of the first embodiment, the negative electrode 22 has negative electrode active material layers 22B arranged on both sides of a negative electrode collector 22A. The anode active material layer 22B includes, for example, a material containing silicon or tin as an element as an anode active material. Specifically, the material contains a simple substance, alloy or compound of silicon, or a simple substance, alloy or compound of tin. The material may contain two or more of the above.
[0068] The anode active material layer 22B is formed using a vapor phase deposition method, a liquid phase deposition method, a spray method, a sintering method,...
no. 3 approach
[0071] The battery of the third embodiment is a lithium metal secondary battery in which the capacity of the negative electrode 22 is expressed by deposition and dissolution of lithium. The structure of the battery of the third embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment except that the negative electrode active material layer 22B is made of lithium metal. The battery of the third embodiment is also produced by the same process as that of the first embodiment,
[0072] In secondary batteries, lithium metal is used as an anode active material. As a result, high energy density can be obtained. The negative electrode active material layer 22B may be provided at the time of assembly. However, the negative electrode active material layer 22B may not exist at the time of assembly, but may be formed by depositing lithium metal when the secondary battery is charged. The negative electrode active material layer 22B can also serve as a current collector, whereby the negati...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| ionic conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com