Spray-in latex foam for sealing and insulating
A technology for spraying foam and latex, applied in the field of foam latex, which can solve problems such as expensive and time-consuming, downtime of insulation contractors, equipment blockage, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
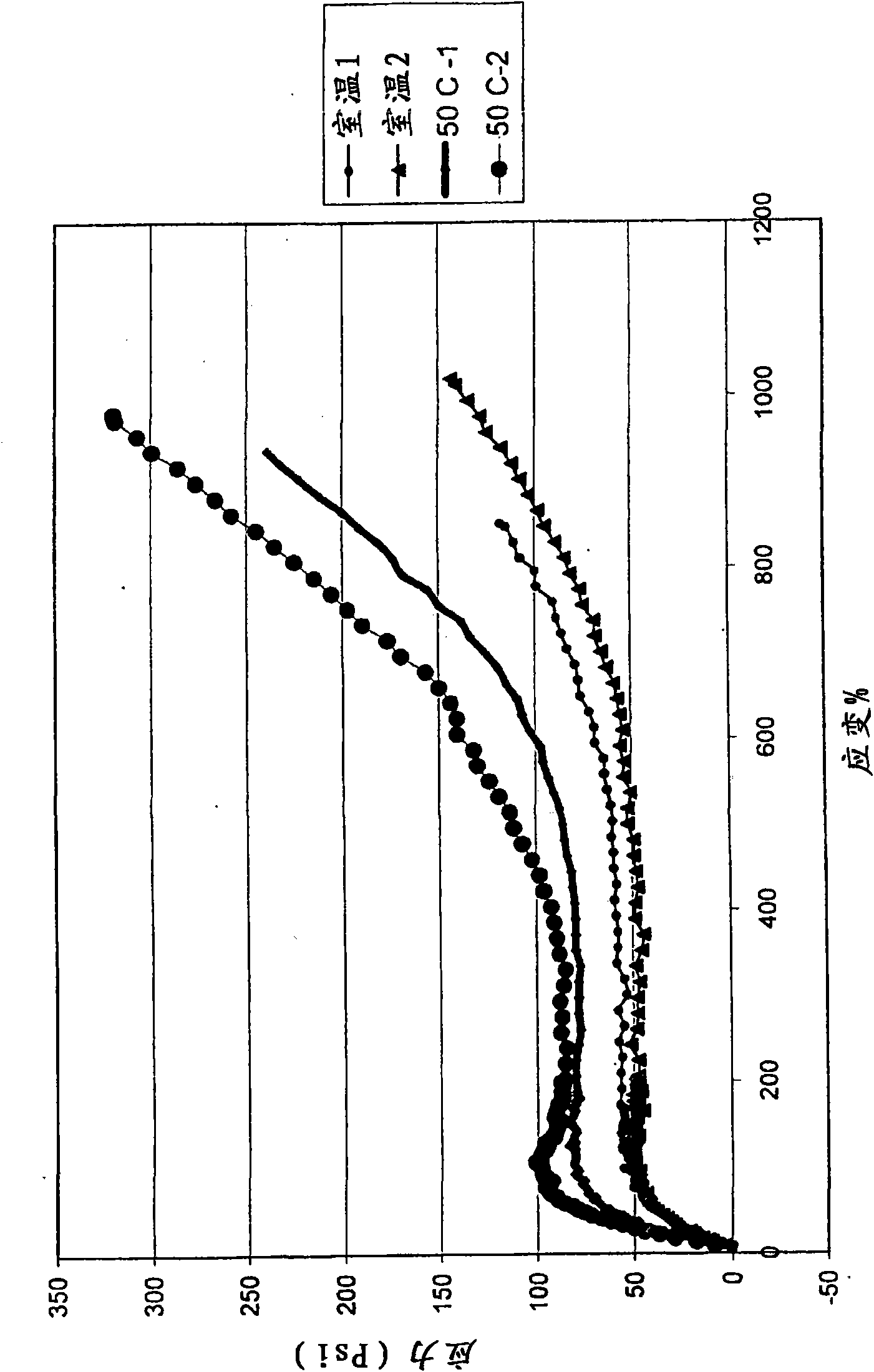
[0061]According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, carbon dioxide is included as a gaseous coagulant and brought to high pressure (eg 100-500 psi) so that it dissolves in the whey (ie water) phase. In the inventive spray foam latex, carbon dioxide reacts with aqueous ammonia to produce carbamate. It should be noted that carbon dioxide was mixed with the latex system to set it and was not used to cure the latex after application.
[0062] The advantages of using carbon dioxide in the spray foam latexes of the present invention are numerous. For example, latex generally requires expensive chemicals and heat treatment for curing. However, the carbon dioxide used in spray foam latex is a low cost, relatively safe chemical. According to at least one embodiment of the present invention, carbon dioxide is used to foam and coagulate the latex, thereby eliminating the need for more expensive chemicals and heat treatments. The elimination of expensive chemicals and ...
Embodiment 1
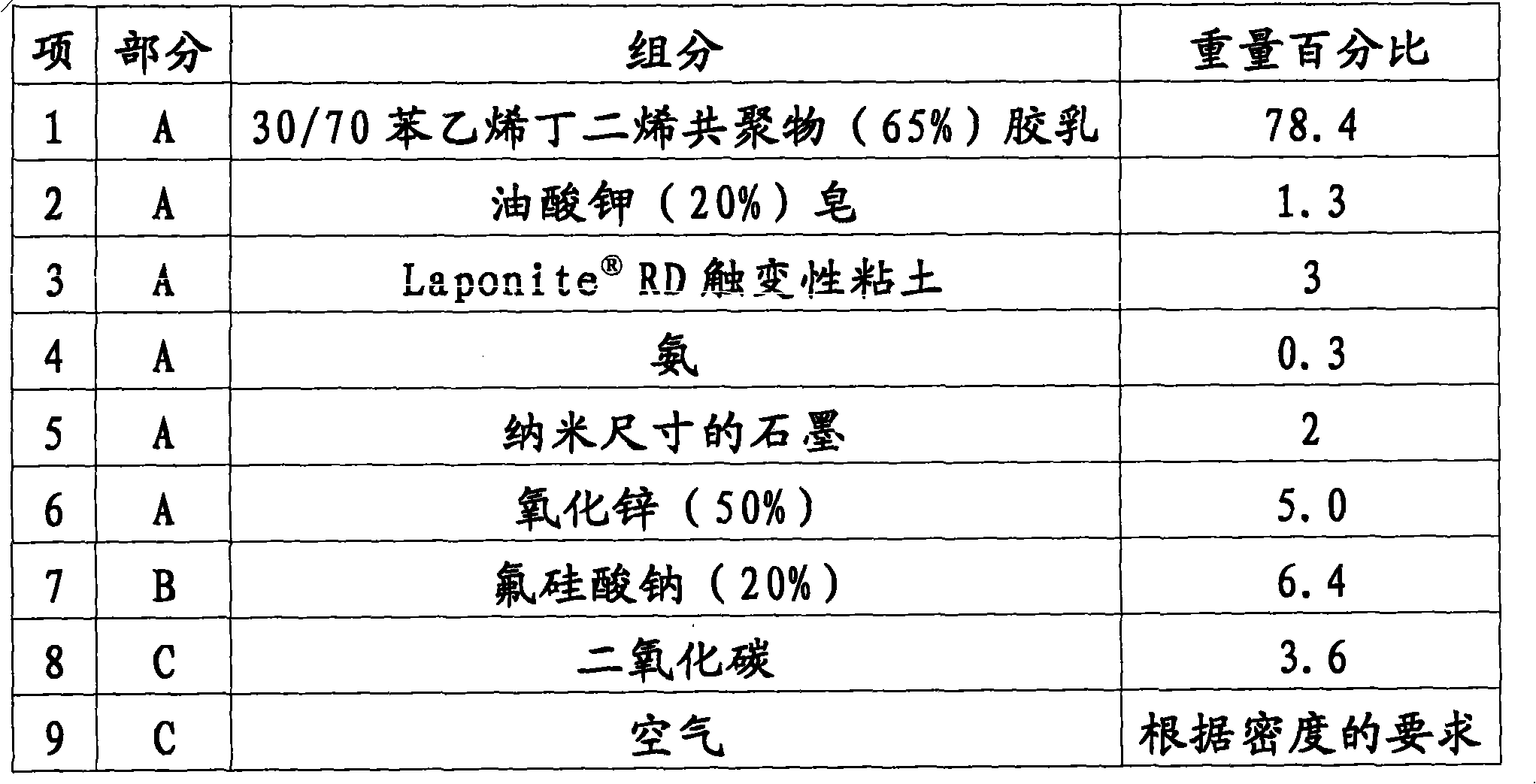
[0090] Example 1: Styrene Butadiene Foam Latex Composition
[0091] Table 1
[0092]
[0093] In this example, the latex system included an SBR latex emulsion. Usually ammonia is already part of the latex emulsion; however, in this example it is shown as a separate component. As previously discussed, ammonia was used to adjust the pH of the latex to produce a stable colloid. In addition to the SBR latex emulsion, the latex system in this example also included a thixotropic agent. It should be understood that although this example uses RD thixotropic clay, but other clays can be used in this example under conditions where the clay "freezes" the water structure when the carbon dioxide completes the setting of the latex. clay products. The latex system also includes potassium oleate as a foam booster, nano-sized graphite as an opacifier and zinc oxide as a foam stabilizer. Carbon dioxide is used as a gaseous coagulant, and air is used as a blowing agent.
Embodiment 2
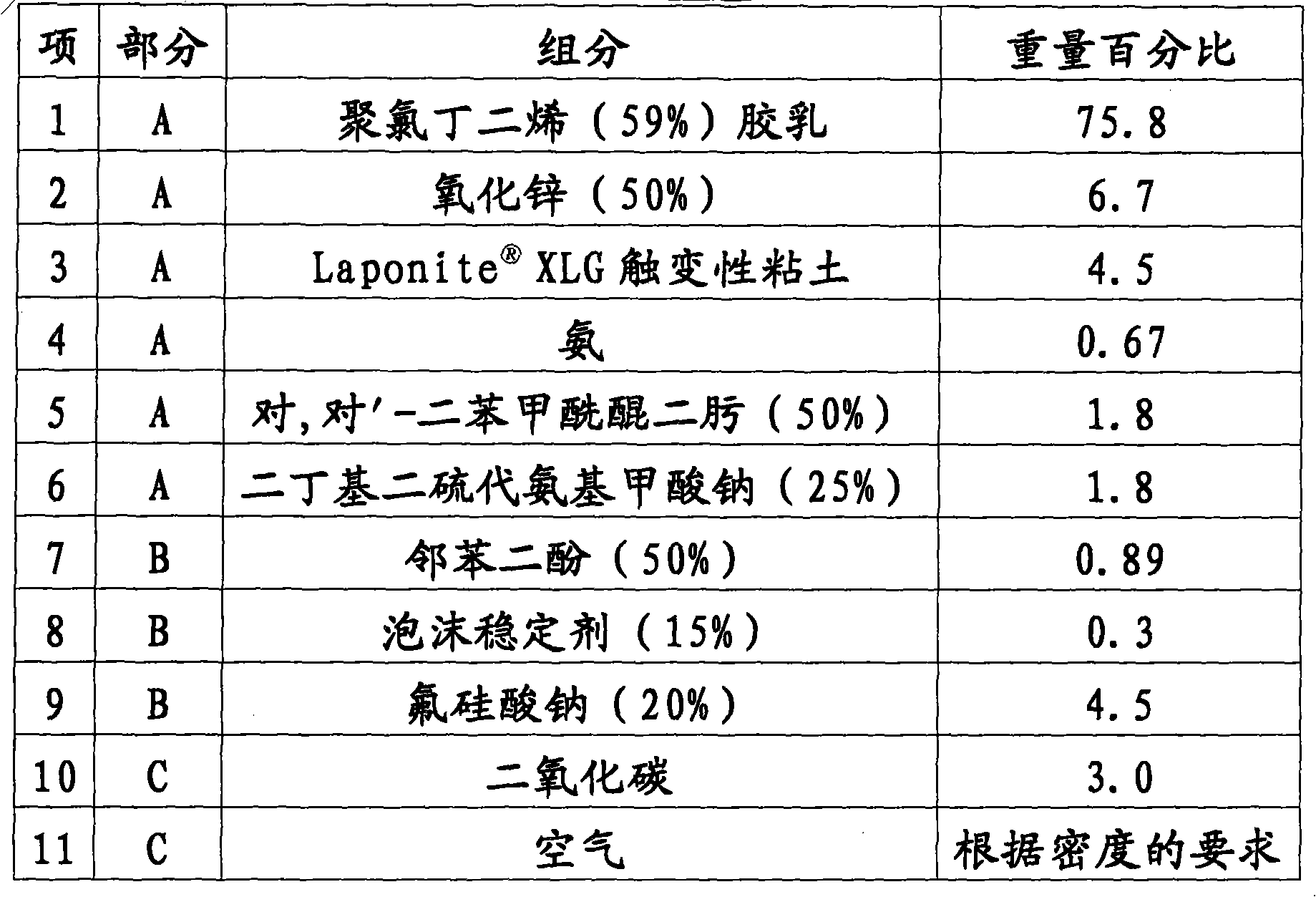
[0094] Embodiment 2: polychloroprene foam latex composition
[0095] Table 2
[0096]
[0097] In this embodiment, the latex emulsion includes polychloroprene latex. In addition to the latex emulsion, the latex system in this example includes a thixotropic agent. The latex system also included zinc oxide as a foam stabilizer, and p,p'-dibenzoylquinone and sodium dibutyldithiocarbamate as accelerators for the setting process. Catechol acts as a gelling agent and accelerator. Foam stabilizers may contain C-cetyl betaine and wetting agents and sodium alkyl sulfates. Carbon dioxide and air are metered into the mixing head as gaseous coagulants. All B components can be encapsulated separately or together.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com