Synthetic human insulin gene and use thereof in cultivation of transgenic tomatoes
A human insulin, artificial synthesis technology, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve problems such as limitations, low yield of culture devices, and inability to carry out mammalian protein translation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] The artificial synthesis of embodiment 1 human insulin:
[0068] According to the situation of codon usage in plants provided by Murray E.E. et al., it is speculated that plants prefer codons. The summary is shown in Table 1.
[0069] Find the sequence of human proinsulin in GENEBANK, get the sequences of human insulin A chain and B chain, and design the replacement bases according to the plant preferred codons. Add the designed connecting short peptide between the B chain and A chain of the designed synthetic human insulin; add the start codon ATG before the B chain, and add the DNA sequence encoding KDEL and the stop codon TAA after the A chain and adding two restriction endonuclease sites BamHI and EcoRI before and after the synthetic gene; the human insulin gene designed and synthesized is obtained.
[0070] Divide the double strands of the synthetic human insulin gene into 8 segments (see Table 2), so that one of the 5' ends of the two strands is slightly shorter...
Embodiment 2
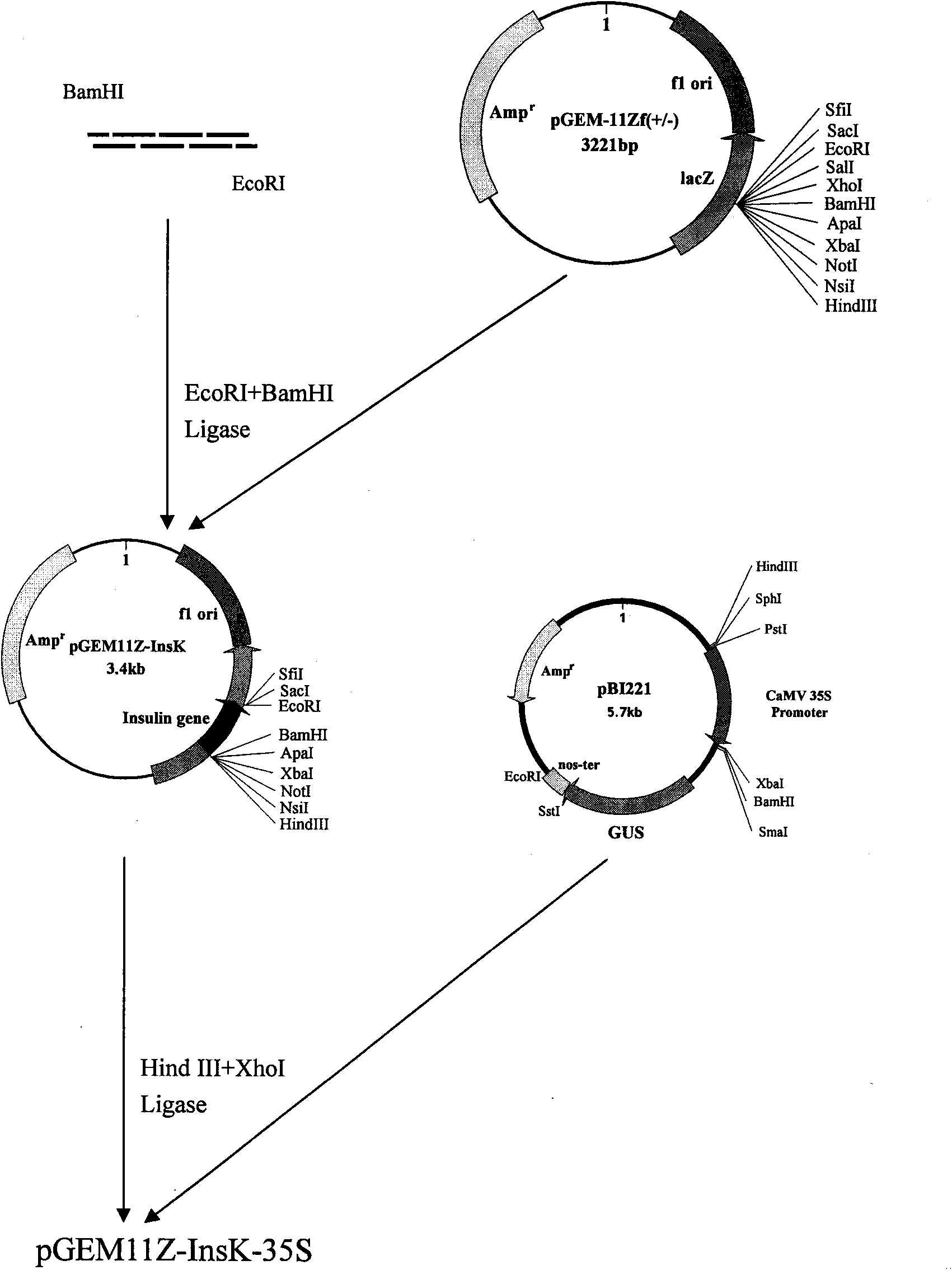
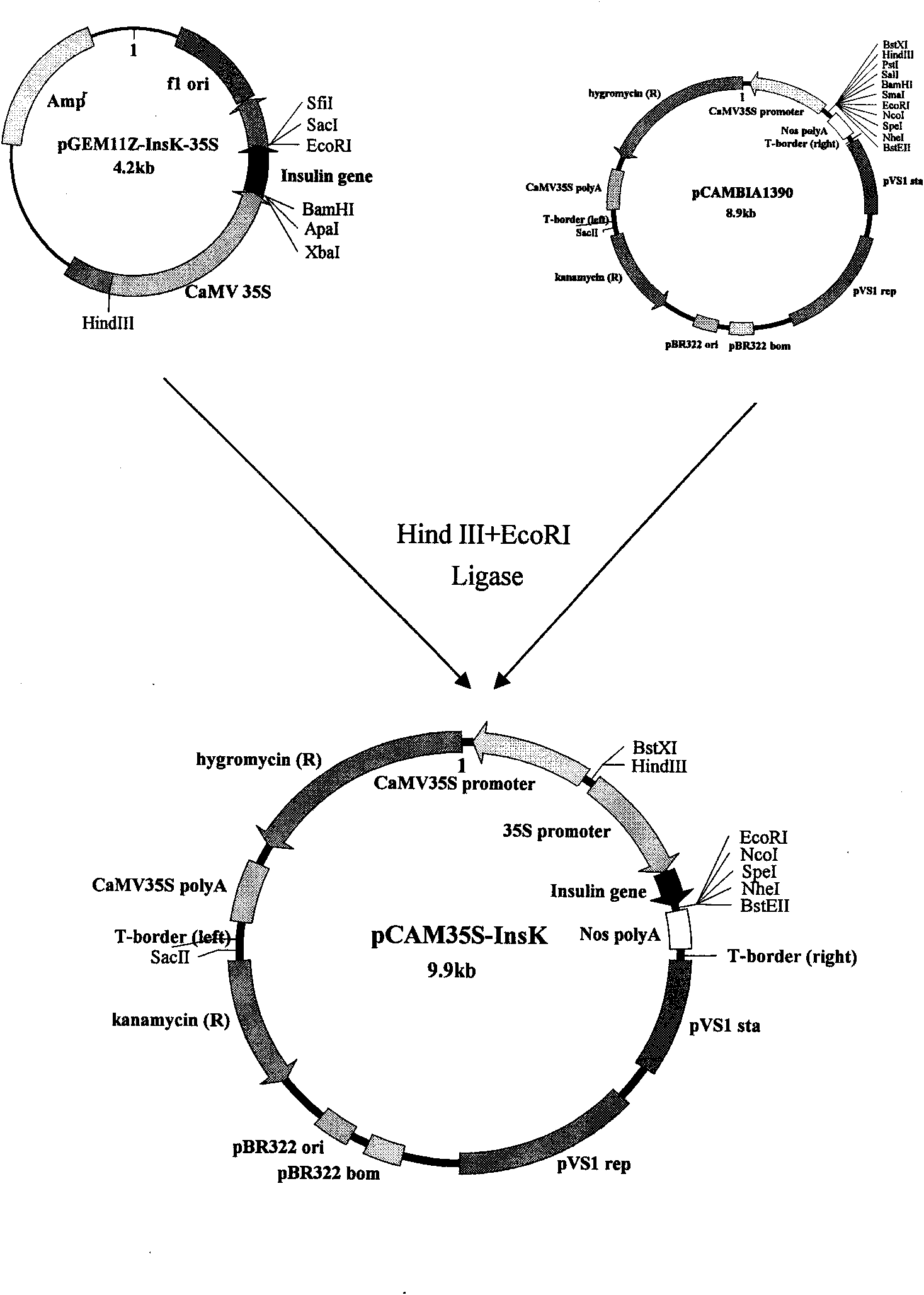
[0115] Example 2 Construction of plant expression vector pCAM35S-InsK:
[0116] For the construction procedure of the plant expression vector pCAM35S-InsK, see figure 1 and Figure 1 continued :
[0117] (1) The pBI221 plasmid and p11Z-InsK plasmid containing the 35S promoter were completely digested with HindIII and XbaI respectively, and the vector and insert were recovered after agarose gel electrophoresis, and the molar ratio of insert:vector was 3:1 Connecting, so that 35S is inserted into the upstream of the synthetic human insulin gene, named p11Z-InsK-35S;
[0118] (2) The constructed p11Z-InsK-35S containing the insulin gene driven by the 35S promoter and plant expression were completely digested with HindIII and EcoRI in the vector pCAMBIA1390, and then ligated to obtain the plant expression vector pCAM35S-InsK.
[0119] HinidIII and BamHI double enzyme digestion cut out a small fragment of 0.8kb, PCR amplification can also obtain a small fragment of 0.8kb, which ...
Embodiment 3
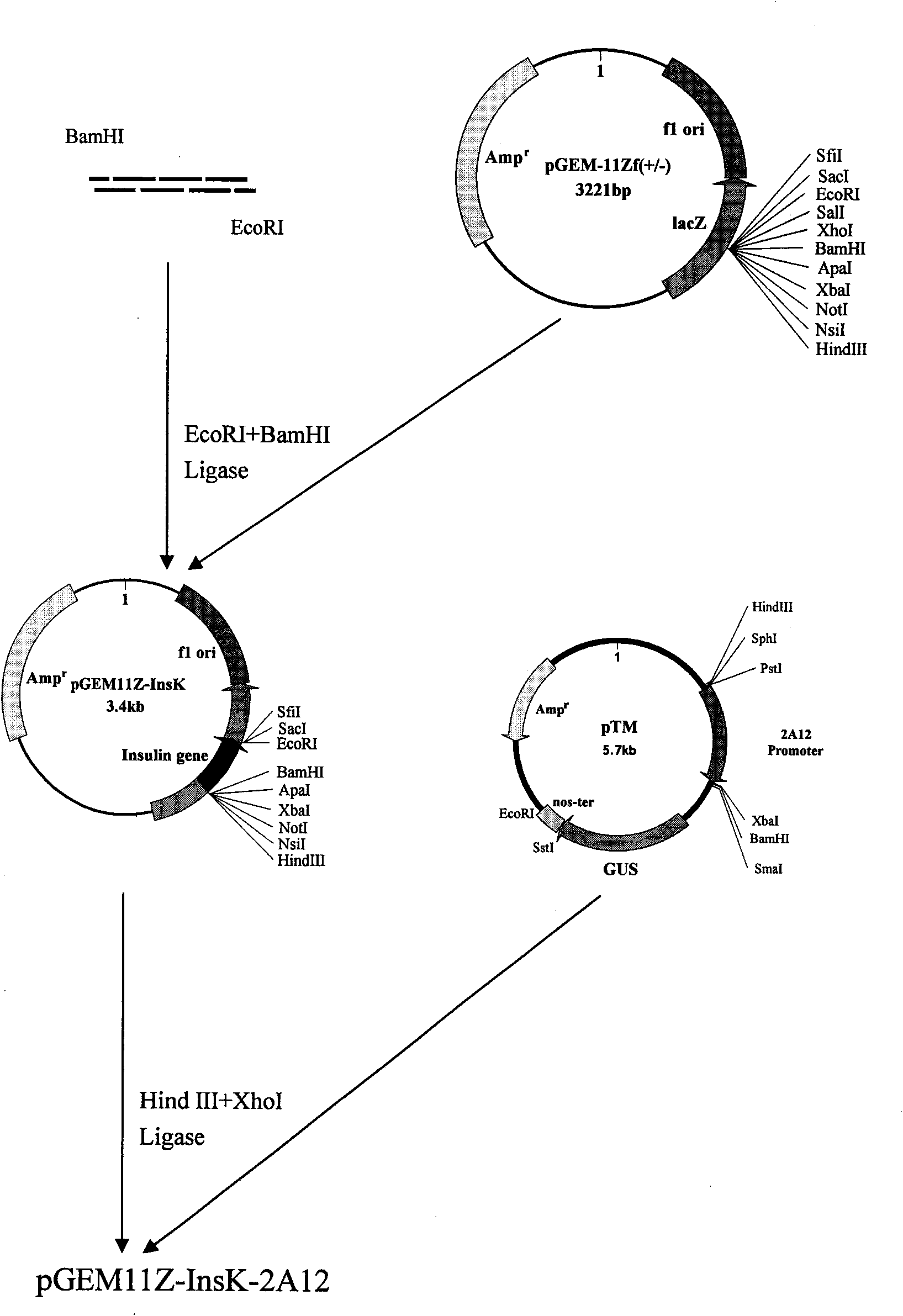
[0120] Example 3 Construction of plant expression vector pCAM2A12-InsK:
[0121] For the construction procedure of the plant expression vector pCAM35S-InsK, see figure 2 and Figure 2 continued :
[0122] (1) The pTM plasmid and p11Z-InsK plasmid containing the 2A12 promoter were completely digested with HindIII and XbaI respectively, and the vector and insert were recovered after agarose gel electrophoresis, and the molar ratio of insert:vector was 3:1 Connecting 2A12 into the upstream of the synthetic human insulin gene and naming it p11Z-InsK-2A12;
[0123] (2) The constructed p11Z-InsK-2A12 containing the insulin gene driven by the 2A12 promoter and plant expression were completely digested with HindIII and EcoRI in the vector pCAMBIA1390, and then ligated to obtain the plant expression vector pCAM2A12-InsK.
[0124] A small fragment of 0.8 kb was cut out by HinidIII and BamHI double enzyme digestion, and a small fragment of 0.8 kb could also be obtained by PCR amplifi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com