Microsclerotium bacterial strain and method for biological weed control therewith
A technology of Sclerotinia strains, Sclerotinia microbes, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, chemicals for biological control, biochemical equipment and methods, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
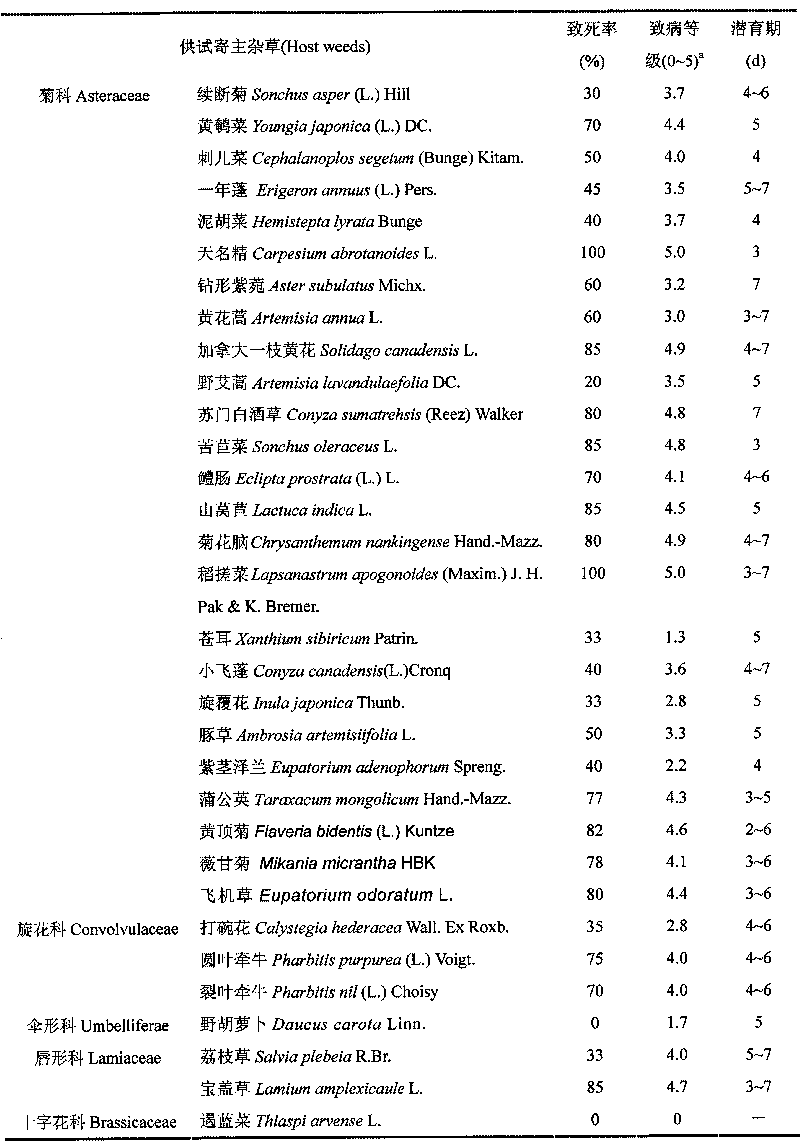
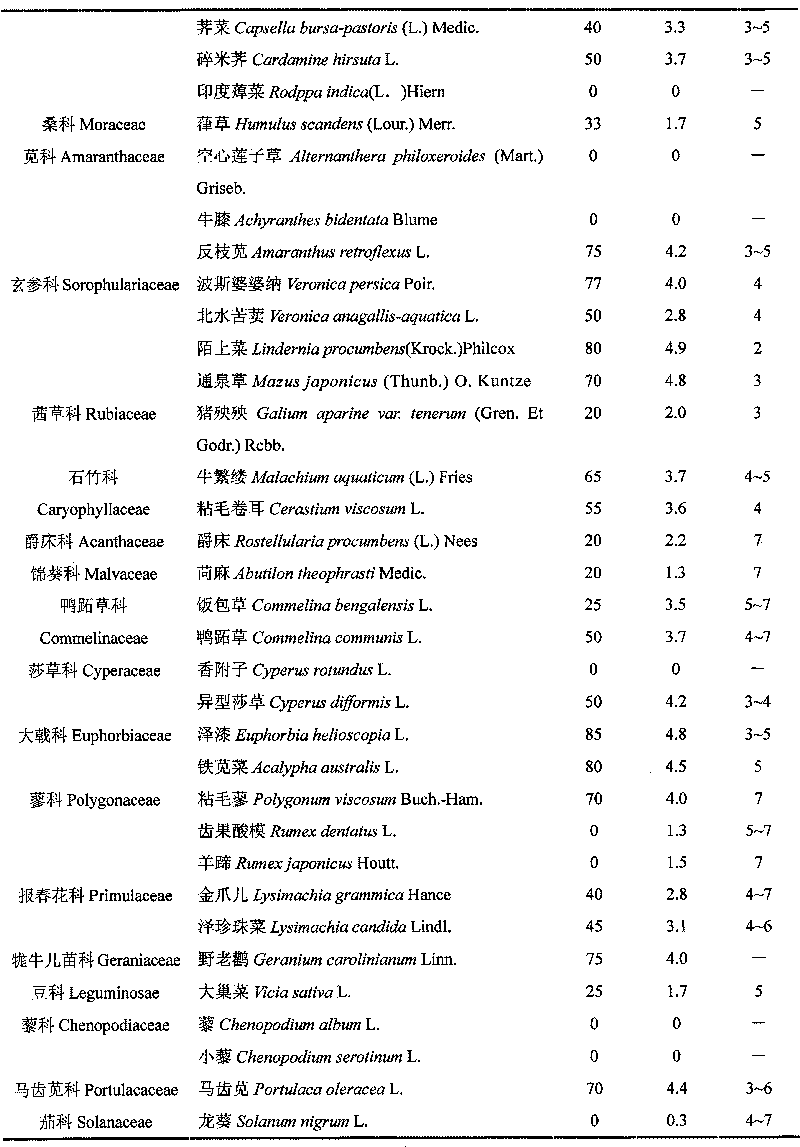
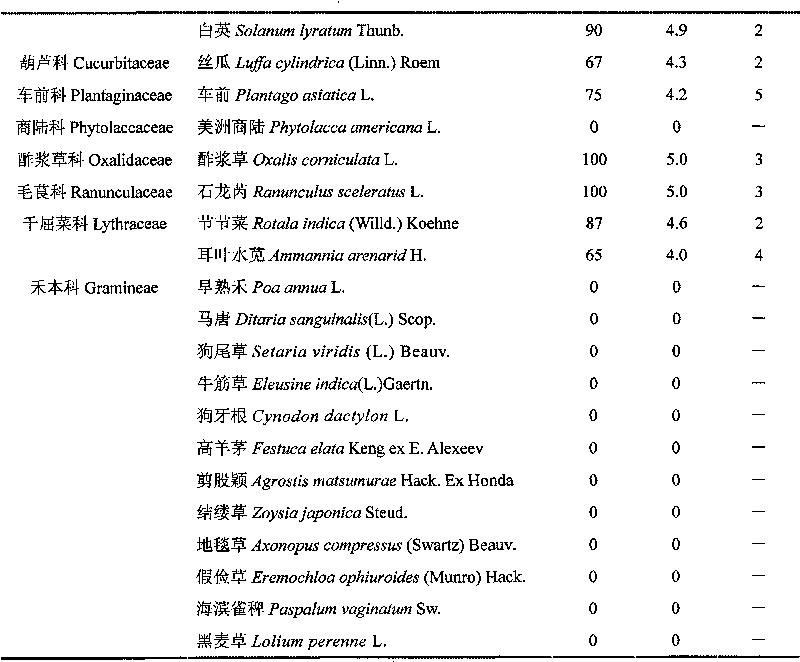
[0105] Example 1: Sclerotinia sclerotiorum was collected and isolated from the diseased plants of Solidago canadensis naturally occurring in Nanjing, and its pathogenicity was tested.
[0106] The stems and roots of diseased Solidago canadensis were collected from the wild, the symptoms of the plants were recorded, and microscopic examination was performed. Isolation of pathogenic fungi was carried out on solidago canadensis sap agar medium. Pick the single sclerotia of the strain, inoculate them on PDA medium respectively, and cultivate them in the dark at 28±1°C, observe the colony characteristics of the pure culture of pathogenic fungi and measure the diameter of each colony.
[0107] The pathogenicity of different Sclerotinia microbes to broad-leaved weeds was compared under greenhouse conditions. Sc085 was isolated from begonia and Sc087 was isolated from peanut. The weeds tested included Conyza canadensis (L.) Cronq., Sonchus asper (L.) Hill), Vicia sativa L., Veronica...
Embodiment 2
[0110] Example 2: After mixing the solid matrix of cottonseed hulls with water according to 1:0.6, routinely sterilize, inoculate the SC64 bacterial classification on the edge of PDA with vigorous growth after cooling, turn over the medium every day, and ferment the bacteria granules after the hyphae are overgrown. Dry the herbicidal bacteria particles in a fume hood and use them in the test in time, and use the sterilized cottonseed hull matrix as a control. The Sclerotinia microbe strain SC64 was tested indoors against Channa sausage (4th true leaf stage), lettuce (4th leaf stage), purslane (4th to 5th true leaf stage), Solidago canadensis (6th leaf stage) ) and Moshangcai (early flowering stage) and other target weeds, the temperature during the test period was 22-30°C.
[0111] Table 4 Control effect of Sclerotinia microbe strain SC64 on several main target weeds
[0112]
[0113] Note: The lowercase letters are significant at the 0.05 level, and the uppercase letters ...
Embodiment 3
[0114] Example 3: According to the method of Example 2, the pathogenicity of different solid fermented herbicidal bacterial granules of Sclerotinia microspermum strain SC64 on the true leaf ages of 2-4 pairs of Channa sausis was tested.
[0115] Table 5 Pathogenic effect of different solid fermented herbicide granules of strain SC64 on snakehead sausage
[0116]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com