Method for screening microbe producing polyunsaturated fatty acid
An unsaturated fatty acid and microorganism technology, which is applied in the field of screening polyunsaturated fatty acid-producing microorganisms, can solve the problems of cumbersome operations, cumbersome, inability to directional rapid high-throughput screening of microorganisms producing polyunsaturated fatty acids, etc., to simplify the screening process, The effect of improving screening efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
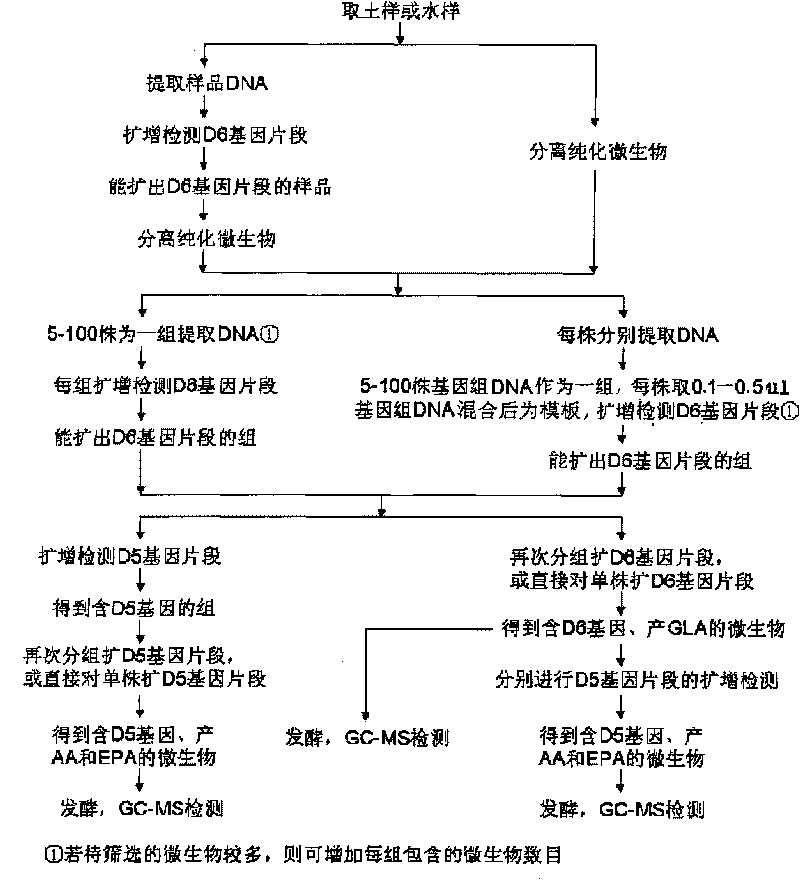
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] The soil was collected from Yujiashan, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, and the topsoil was shoveled off with a cleaning tool, and about 150 grams of soil at a distance of 5-15 cm was taken and packed in a sterilized bottle. DNA was extracted from the collected soil samples using a soil microbial genome DNA extraction kit, and the D6 gene fragment was amplified using the extracted DNA as a template. The PCR reaction system consists of extracted microbial genomic DNA, 50 μM D6-F and 50 μM D6-R, 100 μM dNTPs, 5 μL 10×PCR reaction buffer, 1units Taq DNA polymerase, and sterilized ddH 2 O to make up to 50 μL. The PCR amplification conditions were: 94°C, 6min; 94°C, 1min, 50°C, 45sec, 72°C, 1min for a total of 32 cycles; after that, 72°C for an additional 8min. The results of agarose gel electrophoresis showed that there was D6 gene in the soil sample DNA.
[0064] Microorganisms in the collected soil samples were isolated using conventional microbial isolati...
Embodiment 2
[0078] Soil was collected from Huazhong Agricultural University campus flower garden. Microorganisms in the soil were isolated using conventional microbial isolation methods. Put the soil sample in a sterile empty petri dish, put in the lure, see that mycelium grows on the lure, and immediately transplant it to a PDA plate added with streptomycin and penicillin for cultivation. They were cultured statically in an incubator at 22°C. According to the growth of microorganisms, 35 strains of microorganisms were obtained by separating and purifying the top of mycelia.
[0079] 35 strains of microorganisms were respectively inoculated into 40 mL of PDA liquid medium, cultured at 25°C and 160 rpm for 5 days, the genomic DNA of these microorganisms was extracted, and 0.3 μL was taken for group screening. Every 10 strains of microbial genome DNA constituted a screening group, with A, Group B, and another screening group C containing 15 strains of microbial genomic DNA. The D6 gene fr...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Soil was collected from the vegetable garden of Huashan Town, Hongshan District, Wuhan City, and microorganisms were isolated by conventional microbial separation methods. Under aseptic conditions, pick 0.1-0.25mg of soil particles and place them on the surface of the PDA plate added with antibiotics, and place 3 places on each plate in a triangular shape. Cultivate at 30° C. and 220 rpm for 5 days, and if mycelium grows, it is immediately transplanted to a PDA plate added with streptomycin and penicillin for cultivation. According to the growth of microorganisms, 42 strains of microorganisms were obtained by separating and purifying the top of mycelia.
[0089] 42 strains of microorganisms were inoculated into 60mL of PDA liquid medium, cultured at 30°C and 220rpm for 5 days, and the genomic DNA of these microorganisms was extracted, and 0.5 μL was taken for group screening. Every 5 strains of microbial genome DNA constituted a screening group, with A~ There were 8 gr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com