Double-chamber algae microbial fuel cell and its method for treating wastewater to achieve zero carbon emissions
A fuel cell and waste water treatment technology, applied in biochemical fuel cells, fuel cells, biological water/sewage treatment, etc., to achieve the effects of simple invention, zero carbon emissions, and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
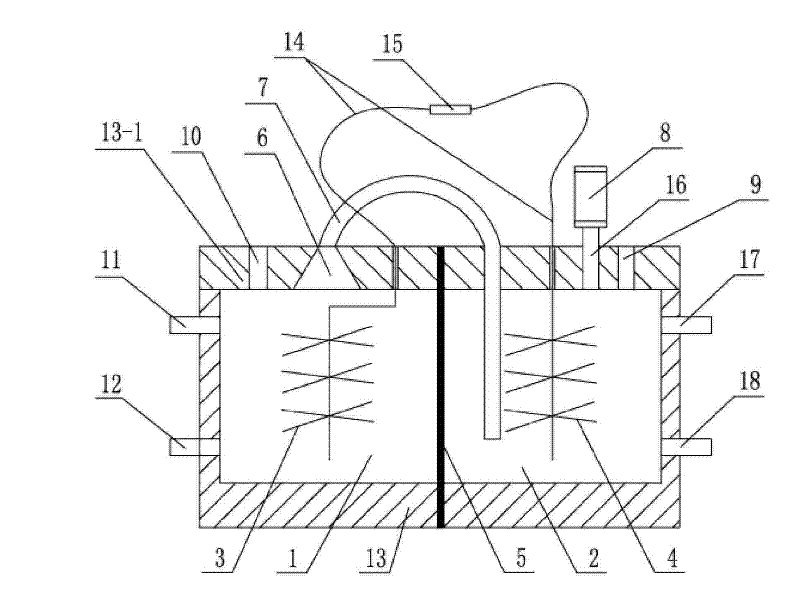
[0010] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the double-chamber algae microbial fuel cell of this embodiment is made up of reactor casing 13, lead wire 14, external circuit 15, anode 3, cathode 4, cation exchange membrane 5, air duct 7 and gas collection device 8, The cation exchange membrane 5 is vertically arranged in the reactor casing 13, and the inside of the reactor casing 13 forms an anode chamber 1 and a cathode chamber 2, the anode 3 is arranged in the anode chamber 1, and the cathode 4 is arranged in the anode chamber 1. In the cathode chamber 2, the two ends of the wire 14 are connected to the anode 3 and the cathode 4 through the upper cover plate 13-1 of the reactor box 13, and the external circuit 15 is arranged on the outside of the reactor box 13 to connect with the wires. 14 connection, the upper cover plate 13-1 of the reactor box 13 above the anode 3 is provided with a gas collection chamber 6, one end of the air guide ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0011] Specific implementation mode two: combination figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the anode 3 is carbon cloth, carbon paper, carbon felt, carbon brush, activated carbon particles, graphite plate, graphite particles, stainless steel plate, stainless steel mesh, Titanium plate or titanium mesh. Other compositions and connections are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0012] Specific embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 2 is that the carbon brushes are pretreated, and the pretreatment method of the carbon brushes is as follows: heat the carbon brushes at 450°C for 30 minutes, Then cool to room temperature, and put the carbon brush into 10% H 2 SO 4 Soak in the solution for 10 minutes, then put it into a NaOH solution with a mass concentration of 10% for neutralization, and then wash it with distilled water. Other compositions and connections are the same as in the first embodiment.
[0013] Specific implementation mode four: combination figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiments 1 to 3 is: the cathode 4 is carbon cloth, carbon paper, carbon felt, carbon brush, activated carbon particles, graphite plate, graphite particle, stainless steel plate, stainless steel mesh , titanium plate or titanium mesh. Other compositions and connections are the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com