Catalyst containing rare earth for ammoxidation of alkane
An oxidation reaction and catalyst technology, which is applied in the preparation of hydrocarbon ammoxidation, physical/chemical process catalysts, bulk chemical production, etc., can solve the problems of poor catalyst stability, complicated preparation process, and low yield, and achieve high oxidation efficiency. - The effect of reduction rate, good repeatability, and easy availability of raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] 13.7 grams of ammonium heptamolybdate and 4.43 grams of telluric acid are dissolved in 40.0 grams of hot water to make solution (I); 3.07 grams of ammonium metavanadate are dissolved in 70.0 grams of hot water to make solution (II); 5.77 grams of niobium oxalate are dissolved in 17.0 grams of hot water to make solution (III); 1.7 grams of cerium nitrate and 1.8 grams of calcium nitrate are dissolved in 5.0 grams of water to make (IV); 2.32 grams of oxalic acid are dissolved in 5 grams of water to make into a solution (V); 1ml of 98% concentrated sulfuric acid was dissolved in 9 grams of water to make a solution (VI). Add solution (II) to solution (I) under stirring, then add solution (III), solution (IV), solution (V) and solution (VI) in sequence, and finally add 50 grams of silicon with a weight concentration of 40%. Sol, prepare catalyst slurry, stir and evaporate the slurry at 90°C to obtain a viscous slurry, then dry, grind, and roast in a nitrogen atmosphere at 60...
Embodiment 2~7 and comparative example 2~4
[0049] Catalysts with different compositions in the following table were prepared by the same method as in Example 1, and the ammoxidation of propane to acrylonitrile was carried out under the following reaction conditions with the prepared catalyst. See Table 1 for specific changes and results.
[0050] The reaction conditions of above-mentioned embodiment and comparative example are:
[0051] Fixed bed reactor with an inner diameter of 8 mm
[0052] Reaction temperature 400°C
[0053] Reaction pressure Atmospheric pressure
[0054] Catalyst loading 2.0 grams
[0055] Catalyst contact time 1.2 g·s / ml
[0056] Raw material ratio (mole) propane / ammonia / air=1 / 1.2 / 10
Embodiment 7
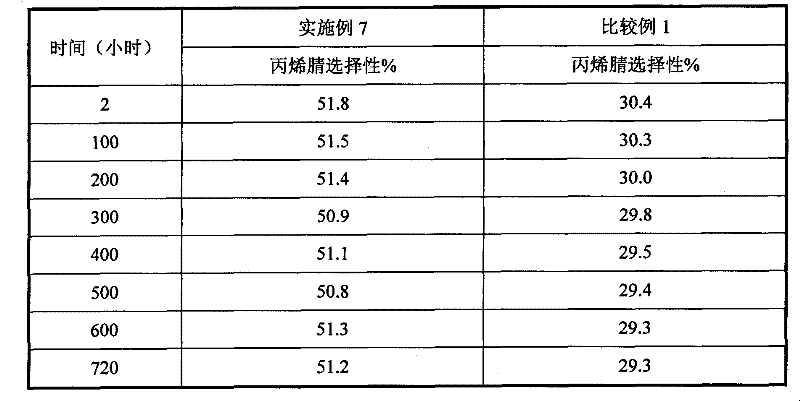
[0057] The stability evaluation results of Example 7 and Comparative Example 1 are shown in Table 2.
[0058] Table 1
[0059]
Example
Catalyst composition
Preparation key steps
Acrylonitrile Yield
(%)
Example 1
Mo 1 V 0.34 Nb 0.24 Te 0.25 Ce 0.05 Ca 0.1 o x +50% SiO2 2
The reducing agent is oxalic acid, acid
for sulfuric acid
51.6
Example 2
Mo 1 V 0.31 Nb 0.22 Te 0.96 Nd 0.05 Fe 0.08 o x +40%SiO2 2
The reducing agent is acetol
48.8
Example 3
Mo 1 V 0.37 Nb 0.26 Te 0.25 PR 0.6 W 0.01 o x +70% SiO2 2
Roasting in nitrogen at 500°C 2
Hour
45.3
Example 4
Mo 1 V 0.11 Nb 0.95 Te 0.25 Nd 0.1 PR 0.01 Bi 0.01 o x +60% SiO2 2
The reducing agent is oxalic acid, acid
for nitric acid
50.3
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com