Method for inhibiting release of substrate sludge nutritive salt of eutrophic water body
A technology of eutrophication and nutrient salt, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, sludge treatment, etc., can solve problems such as poor results, achieve easy control, convenient operation, and increase agglomeration performance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
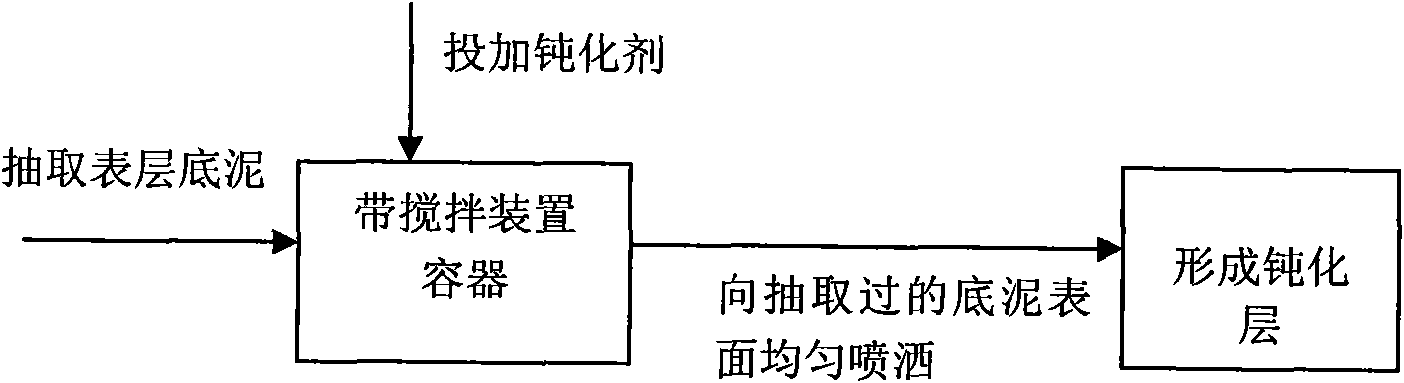
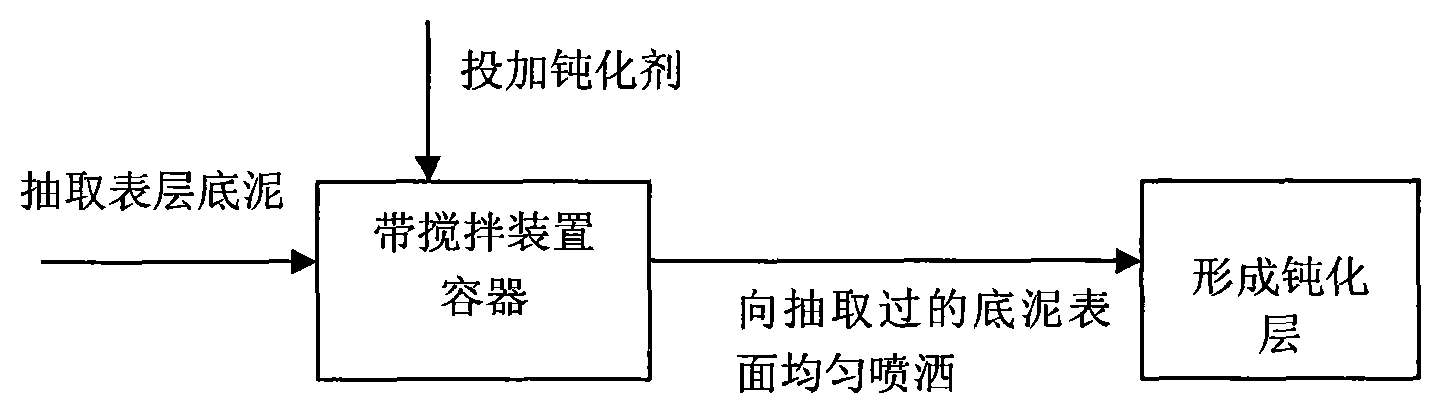
[0024] The treated bottom sludge is black and smelly (or malodorous) bottom sludge, and the content of organic matter and ammonia nitrogen in the bottom sludge is high, TN is higher than 10mg / g, TP is higher than 5mg / g, and DO content is lower than 0.5mg below 50cm from the water surface / L. Use conventional suction equipment to pump the bottom mud within 10cm from the surface into a uniform container with a stirring system, and at the same time add a certain amount of ferrous sulfate (10-30g / m 2 ), magnesium salt (magnesium sulfate (20~50g / m 2 ), calcium nitrate (100~150gN / m 2 ) and other passivators and polyacrylamide (0.5 ~ 5g / m 2 ), using sodium bicarbonate to adjust the pH of the bottom sludge, so that the pH value of the bottom sludge is in the range of 6-9. And stir (stirring intensity is 150-300r / min, mud residence time is 5-20min), and the bottom sludge added with passivating agent is evenly sprayed to the surface layer of the bottom sludge that has been extracted ...
Embodiment 2
[0026] What is being treated is the recent (within two months) dredged water body sediment, the content of organic matter in the sediment is low, TN is lower than 10mg / g, TP is lower than 5mg / g, and DO content is higher than 0.5mg below 50cm from the water surface / L. Use conventional suction equipment to pump the bottom mud within 10cm from the surface into a uniform container with a stirring system, and at the same time add a certain amount of iron sulfate (0.1-0.5gFe 3+ / m 2 ), magnesium hydroxide emulsion (50~100g / m 2 ), calcium nitrate (100~100gN / m 2 ) and other composite passivators and polyaluminum ferric chloride (1 ~ 5g / m 2 ). Sodium bicarbonate is used to adjust the pH of the bottom sludge so that the pH value of the bottom sludge is in the range of 6-9. And stir (stirring intensity is 150-300r / min, mud residence time is 5-20min), and the bottom sludge added with passivating agent is evenly sprayed to the surface layer of the bottom sludge that has been extracte...
Embodiment 3
[0028] What is treated is the sediment of the landscape water body, and the water body is of Class IV~V water quality. Use conventional suction equipment to pump the bottom mud within 10cm from the surface into a uniform container with a stirring system, and at the same time add a certain amount of ferrous sulfate (10-30g / m3) into the container 2 ), magnesium hydroxide emulsion (50~100g / m 2 ), calcium nitrate (100~100gN / m 2 ) and other composite passivators and polyaluminum ferric chloride (1 ~ 5g / m 2), using sodium bicarbonate to adjust the pH of the bottom sludge, so that the pH value of the bottom sludge is in the range of 6-9. And stir (stirring intensity is 150-300r / min, mud residence time is 5-20min), and the bottom sludge added with passivating agent is evenly sprayed to the surface layer of the bottom sludge that has been extracted by ordinary mud pump or sludge pump. By adding the passivating agent, the release of ammonia nitrogen in the sediment to the water body ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com