Method for preparing metallic titanium by electrolyzing sodium titanate-sodium hydroxide melt
A technology of sodium hydroxide and sodium titanate, which is applied in the field of producing metal titanium by electrolysis of sodium titanate-sodium hydroxide melt, can solve the problems of complicated process, high production cost, and high comprehensive energy consumption, and achieve cost reduction, The effect of low cost and high current efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
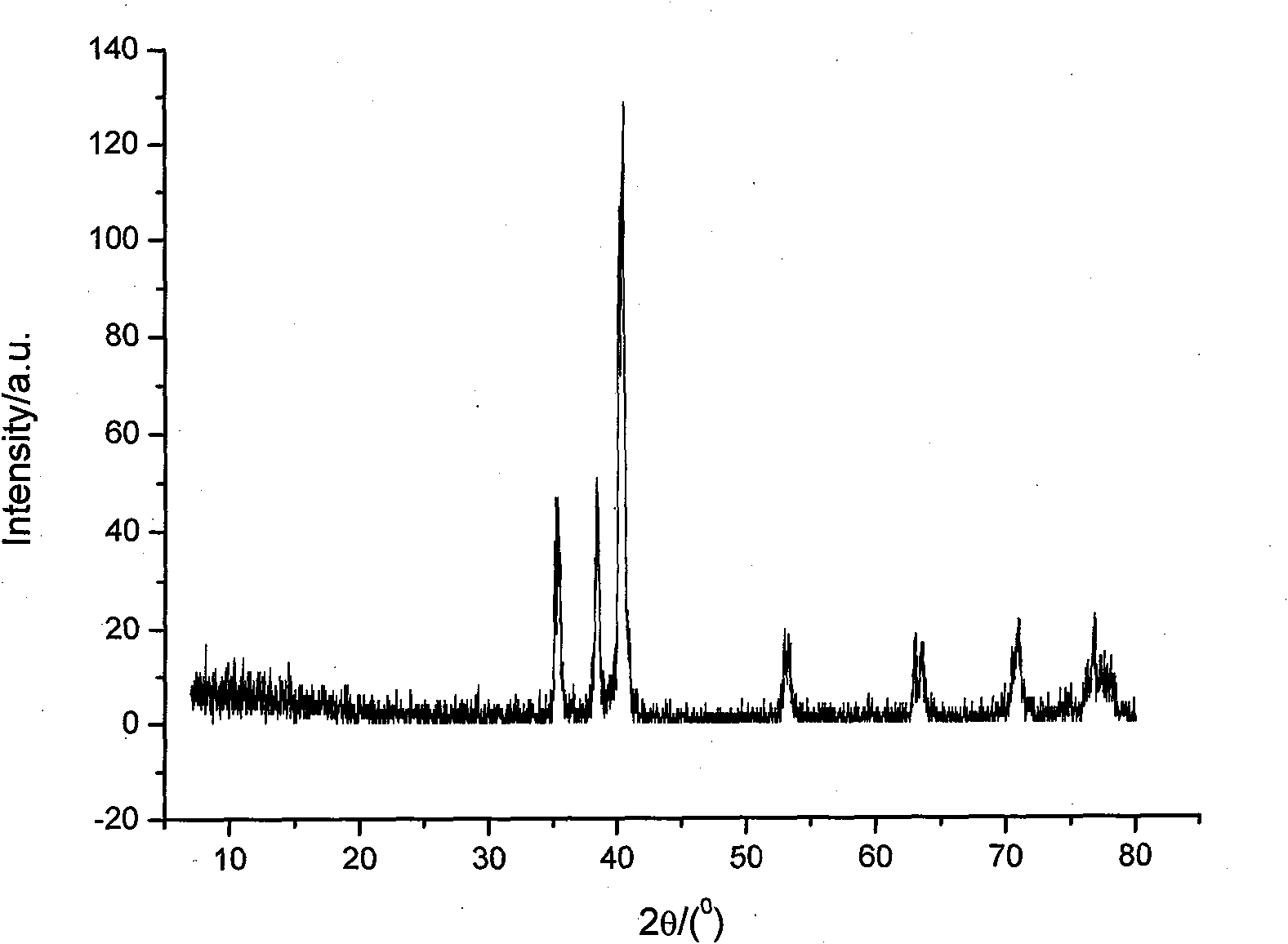
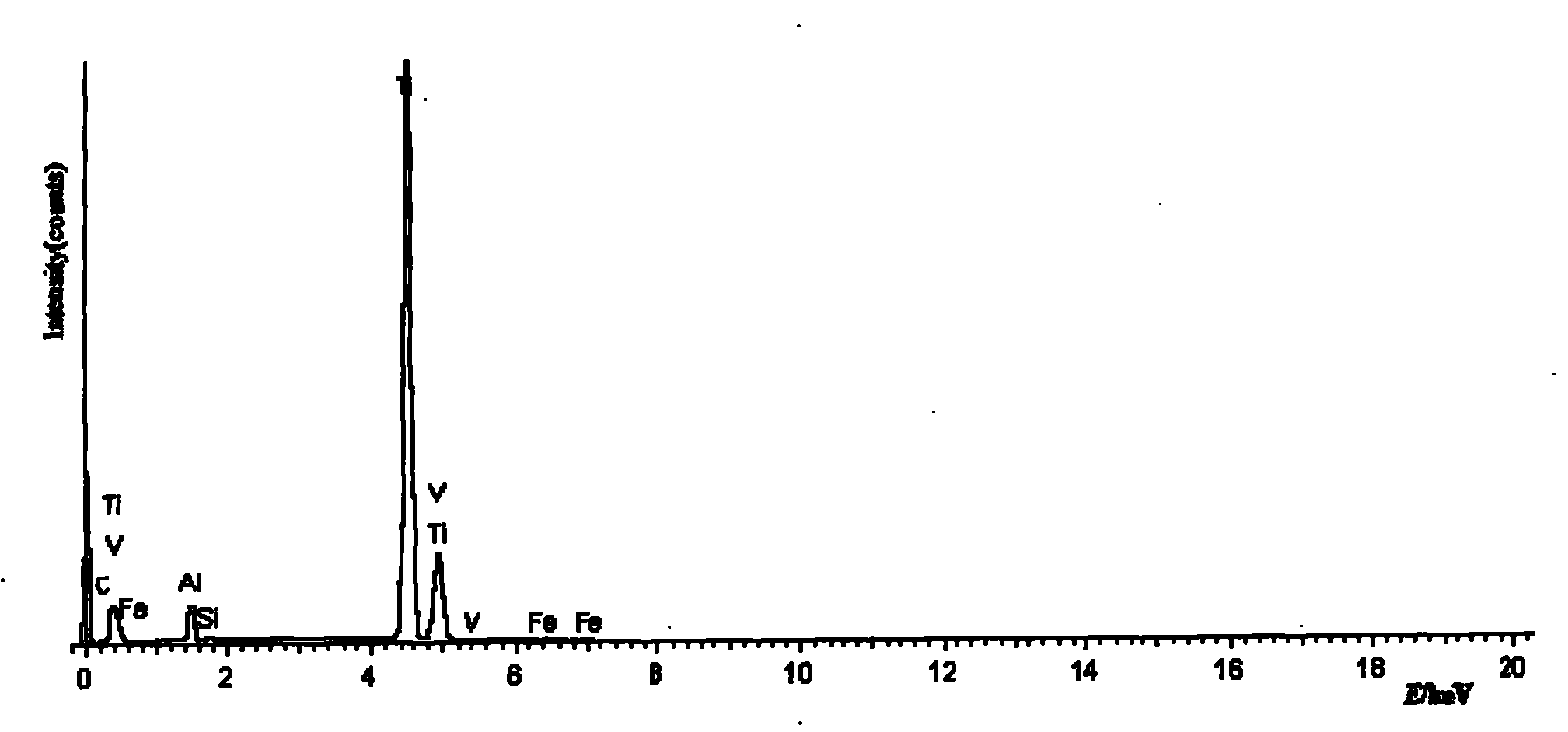
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] B. Put the mixture in a magnesia crucible, and melt the mixture of titanium dioxide and sodium hydroxide at a heating temperature of 380°C. At this time, titanium dioxide and molten sodium hydroxide react to form sodium titanate, sodium titanate Soluble in molten sodium hydroxide to form sodium titanate-sodium hydroxide melt;
[0026] C. After melting for 2-3 minutes, insert two electrodes into the sodium titanate-sodium hydroxide melt. The cathode is made of stainless steel, and the anode is made of graphite. Fix the electrodes and electrolyze for 2 hours under the conditions of voltage 6V and current intensity 6A. ;
[0027] D. Take out the gray matter produced by the cathode, wash the gray matter in distilled water, filter and dry to obtain titanium metal.
[0028] The amount of titanium metal produced by the method is 7.3g, and the calculated current efficiency is 77.2%.
[0029] Because the discharge potential of sodium ions is lower than that of titanium ions: a...
Embodiment 2
7.50
[0041] The current efficiency data of electrolytic titanium are listed in Table 2.
[0042] Table 2
[0043] Electrolysis time / h
Theoretical due mass of titanium / g
The mass of titanium actually obtained / g
Current efficiency / %
1.94
8.3
6.85
82.5
[0044] Example 3: See Table 3 for the relationship between the mass ratio of titanium dioxide and sodium hydroxide and the melting point. The larger the mass ratio of sodium hydroxide, the lower the melting temperature, and lowering the heating temperature also helps to reduce unnecessary consumption of electric energy.
[0045] table 3
Embodiment 3
[0047] Embodiment 4: See Table 4 for the relationship between electrolysis efficiency and voltage. In this experiment, the heating temperature is 371 ~ 373 ° C, TiO 2 The mass ratio to NaOH is 2:5, TiO 2 The total consumption with NaOH is 40g. The higher the voltage, the greater the current through the system, so the faster the electrolysis rate and the higher the efficiency. The theoretical decomposition voltage of titanium dioxide is 2.8V, and a voltage above 6V will cause excessive local current, causing the sodium ions in it to discharge.
[0048] Table 4
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com