Method for preparing enzymatic hydrolysis (EH) lignin-dimer fatty acid derivative
A technology for enzymatically decomposing lignin and polydiacid, which is applied in the field of enzymatically decomposing lignin-polydiacid modified derivatives and new biomass materials, and can solve the problems of rarely being effectively used and destroying natural lignin active groups. Problems, to achieve good economic value, beneficial to environmental protection, high purity effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
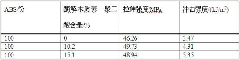
[0033] Example 1: Preparation of lignin-polydiacid derivatives by enzymatically decomposing lignin and polydiacid
[0034] Add 10g of enzymatic lignin, 0.02g of potassium persulfate, 0.02g of copper chloride inhibitor and 0.03g of ZrO in the three-necked round bottom flask 2 / SO 4 2+ Type solid superacid catalyst, then add 45ml of dioxane solvent, stir until the lignin is dissolved, then open the dropping funnel containing 4.5g of polydiacid 12ml-dioxane solution, control the rate of addition, add 15min After completion, heat up to 55°C and protect with nitrogen gas. After the dropwise addition, continue to react for 4.0 hours, and the acidity will not change. The catalyst was recovered by suction filtration while the reaction liquid was cooled, and the grafted product was slowly added dropwise to 180ml of methanol, the reaction product precipitated out, centrifuged and left overnight, filtered by suction and washed with methanol, and then dried at 70°C to constant weight ,...
Embodiment 2
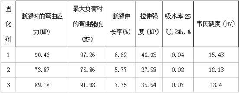
[0035] Example 2: Preparation of lignin-polydiacid derivatives by enzymatically decomposing lignin and polydiacid
[0036] Add 10g of enzymatic lignin, 0.02g of benzoyl peroxide (BPO), 0.02g of hydroquinone inhibitor and 0.04g of 732 type cation exchange resin catalyst into a three-neck round bottom flask, and then add 45ml of di Oxycycline solvent, stirred until the lignin was dissolved, then opened the dropping funnel containing 4.5g of polydiacid 10ml-dioxane solution, controlled the dropping speed, added 15min, heated to 55°C and protected by nitrogen , Continue to react for 4.5h after the dropwise addition, and the acidity does not change any more. The catalyst was recovered by suction filtration while the reaction liquid was cooled, and the grafted product was slowly added dropwise to 170ml of methanol, the reaction product precipitated out, centrifuged and left overnight, filtered by suction and washed with methanol, and then dried at 70°C to constant weight , the prec...
Embodiment 3
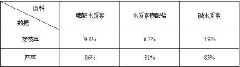
[0037] Example 3: Preparation of lignin-polydiacid derivatives by enzymatically decomposing lignin and polydiacid
[0038] Add 10g of enzymatic lignin, 0.02g of azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN), 0.02g of p-benzoquinone polymerization inhibitor and 0.03g of 732 type cation exchange resin catalyst into a three-neck round bottom flask, and then add 50ml of di Oxycycline solvent, stirred until the lignin was dissolved, then opened the dropping funnel equipped with 4.5g of polydiacid 10ml-dioxane solution, controlled the dropping rate, added 15min, heated to 65°C and protected by nitrogen , Continue to react for 5.0h after the dropwise addition, and the acidity does not change any more. The catalyst was recovered by suction filtration while the reaction liquid was cooled, and the grafted product was slowly added dropwise to 170ml of methanol, the reaction product precipitated out, centrifuged and left overnight, filtered by suction and washed with methanol, and then dried at 70°C to c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com