Method for preparing ferroferric oxide nano sheet
A technology of ferroferric oxide and nanosheets, which is applied in the fields of iron oxide/hydroxide, nanotechnology, nanotechnology, etc., and can solve problems such as difficulty in preparing nanosheet particles, uneven thickness distribution, and long production cycle , to achieve the effects of low raw material cost, short preparation cycle and low product cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] 1) under stirring, 2.3353g FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O and 120mL deionized water were mixed thoroughly;
[0022] 2) Add 0.64g of NaOH reagent into 80mL of deionized water, stir fully to dissolve it completely, and then add 6.89g of sodium acetate to the stirred strong alkali aqueous solution;
[0023] 3) While treating the mixed solution in step 2) with an ultrasonic processor, add the aqueous solution in step 1) to the mixed solution in step 2) dropwise, after the addition, continue the ultrasonic reaction for 1 hour to obtain a suspension , the ultrasonic power is controlled at 80W, and the frequency is at 25KHz;
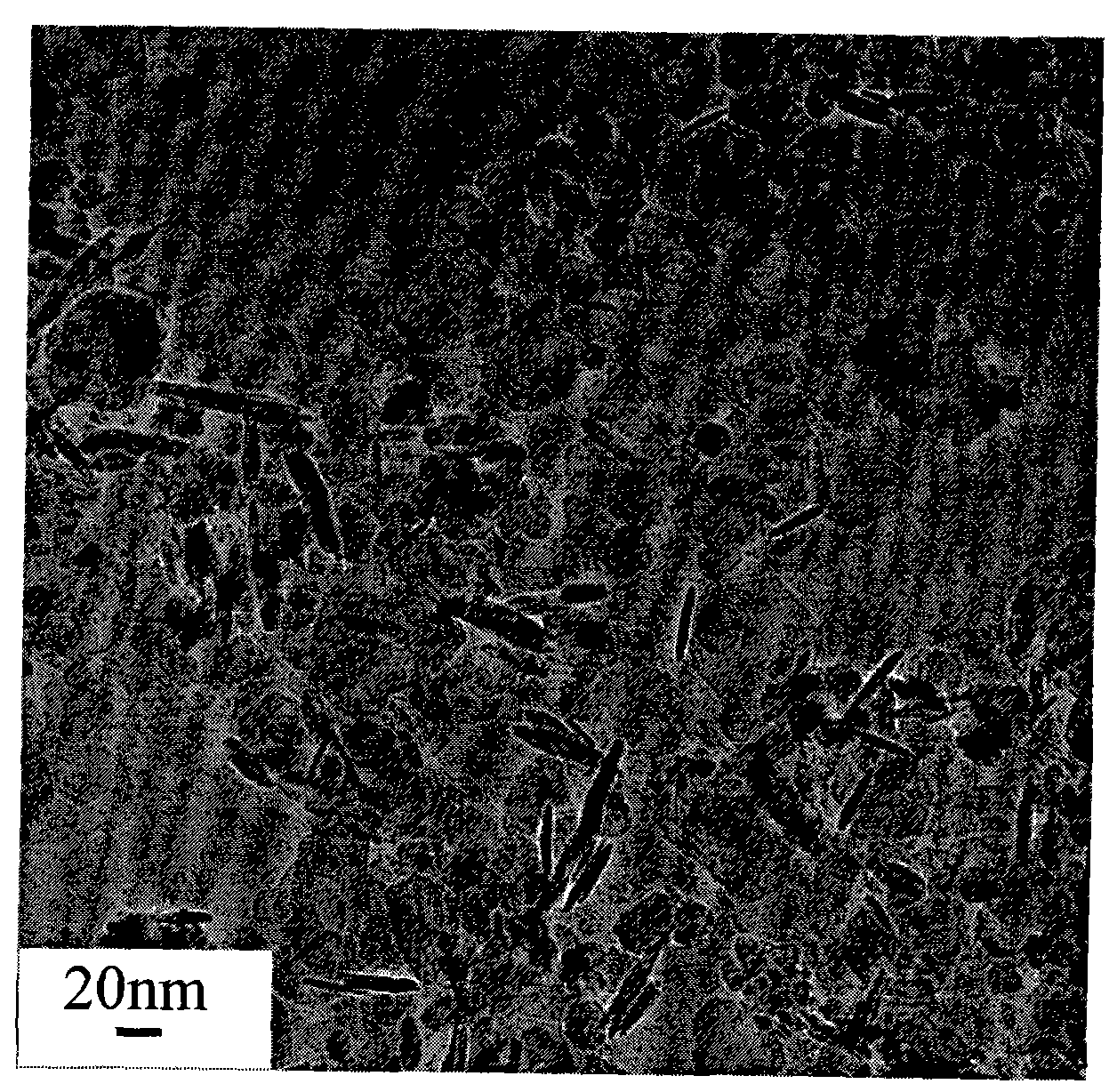
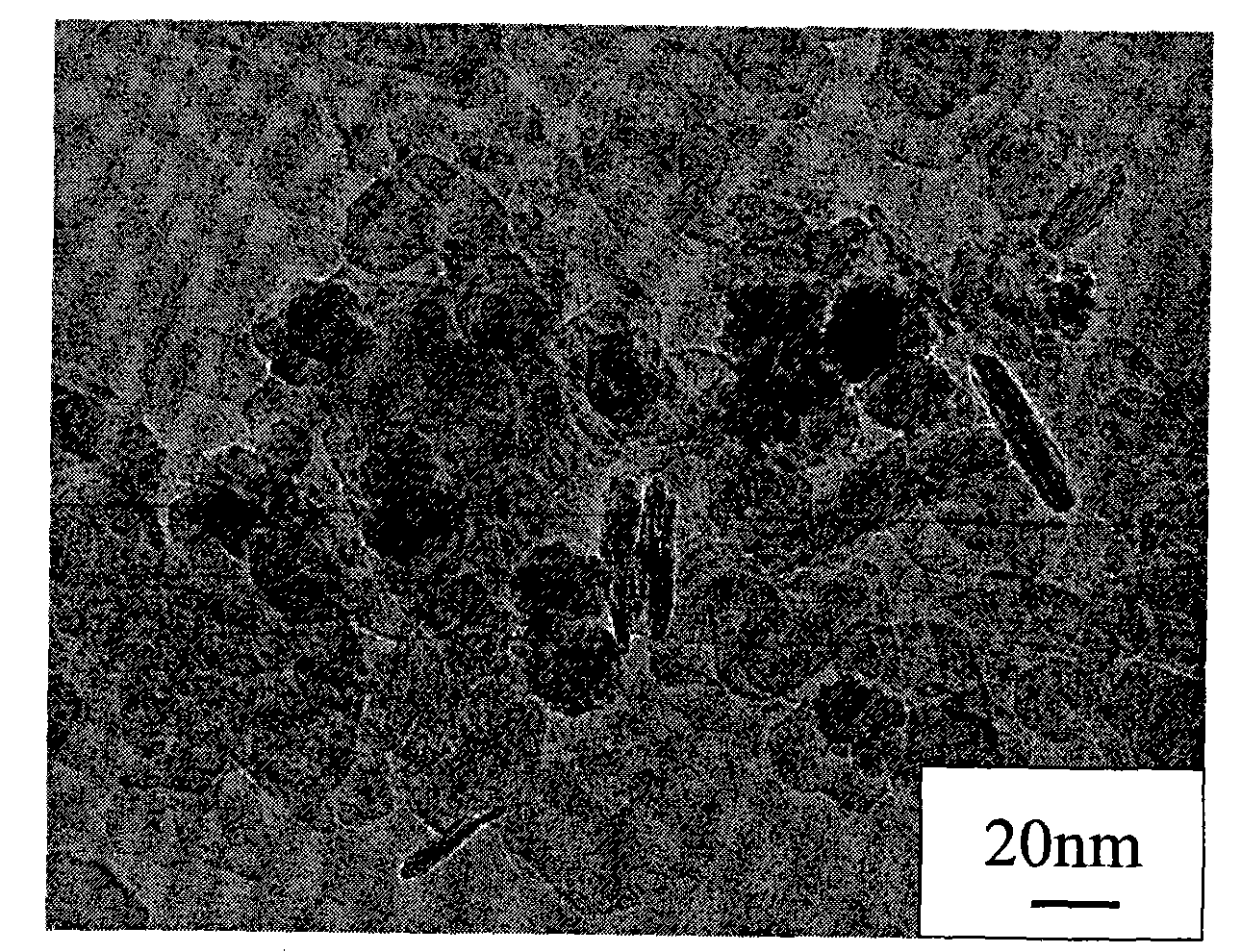
[0024] 4) Filter out the solid phase in the suspension in step 3) with filter paper, wash four times with distilled water and absolute ethanol, and vacuum-dry at 60° C. to obtain ferric oxide nanosheets. looks like figure 1 As shown, it is a two-dimensional sheet with an average thickness of 5 nm or less.
Embodiment 2
[0026] 1) Under stirring, 1.6701g FeCl 2 4H 2 O and 120mL deionized water were mixed thoroughly;
[0027] 2) Add 0.7093g of KOH reagent into 80mL of deionized water, stir fully to dissolve it completely, then add 3.3402g of polyvinylpyrrolidone to the stirred strong alkali aqueous solution;
[0028] 3) While treating the mixed solution in step 2) with an ultrasonic processor, add the aqueous solution in step 1) dropwise to the mixed solution in step 2), after the addition, continue the ultrasonic reaction for 0.5 hours to obtain a suspension , the ultrasonic power is controlled at 120W, and the frequency is at 25KHz;
[0029] 4) Filter out the solid phase in the suspension in step 3) with filter paper, wash with distilled water and absolute ethanol four times respectively, and vacuum-dry at 100° C. to obtain ferric oxide nanosheets. looks like figure 2 As shown, it is a two-dimensional sheet with an average thickness of 5 nm or less.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com