Method for producing a compound semiconductor MMIC (Monolithic Microwave Integrated Circuit) chip on silicon substrate
A silicon substrate and compound technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of power dissipation, microwave power transmission, high cost, etc., to ensure mechanical strength, reduce cost, and reduce power loss Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
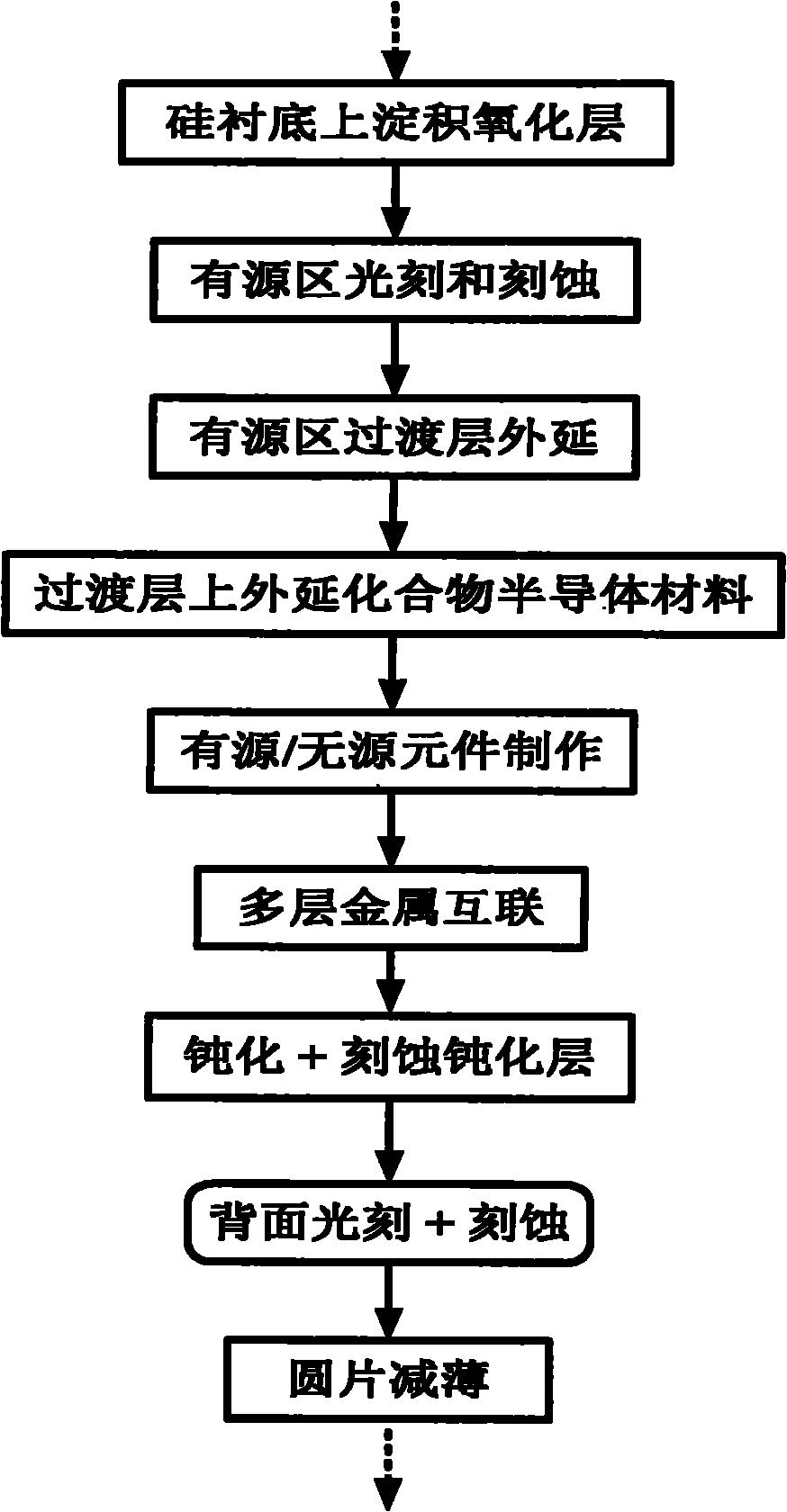
[0039] A kind of technology that prepares compound semiconductor MMIC structure on silicon substrate by dry method, its processing step comprises:
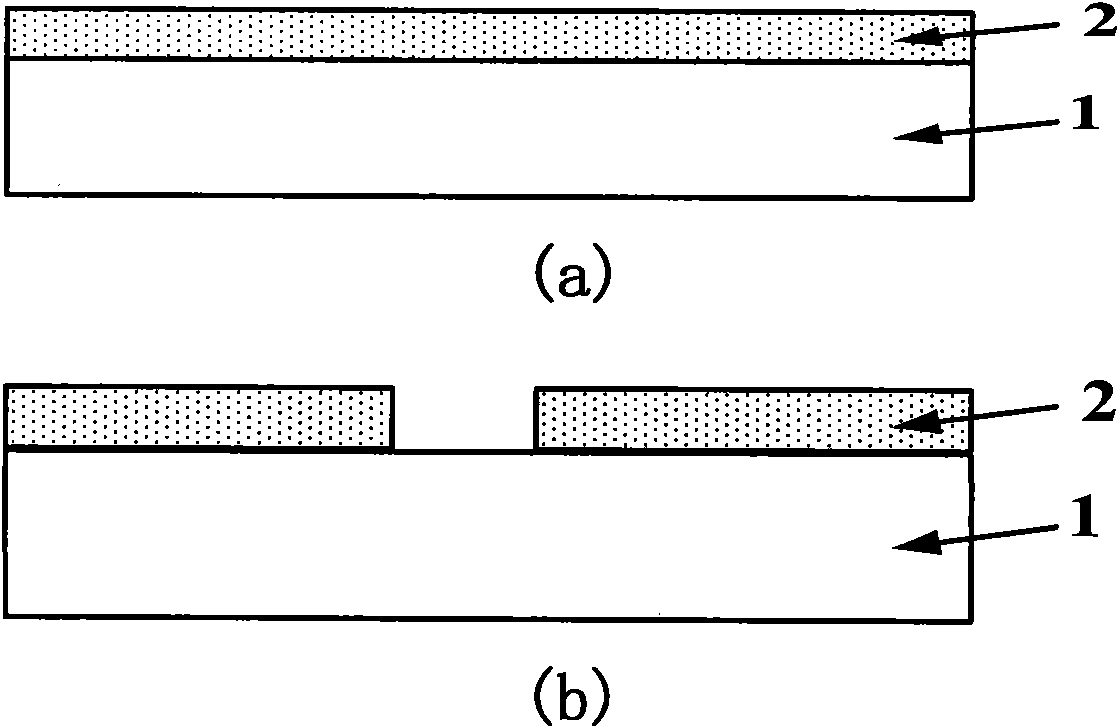
[0040] In the first step, silicon oxide is deposited on the surface of the silicon substrate with a thickness of 300-2000nm.
[0041] In the second step, a window exposing the silicon substrate is obtained by photolithography and etching on the silicon oxide for material growth of active devices.
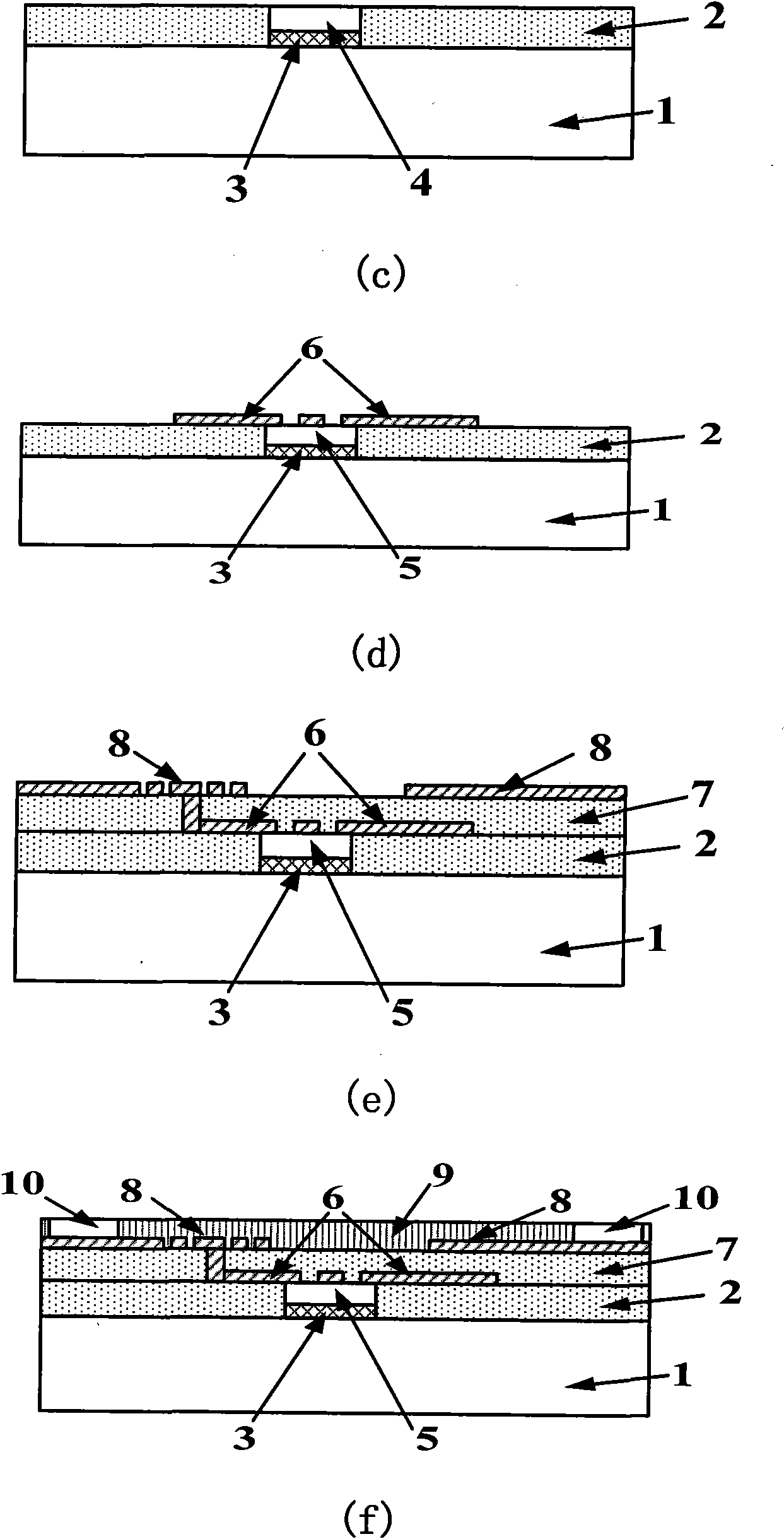
[0042] In the third step, the transition layer and the compound single crystal semiconductor material are grown by selective epitaxy in the window, and the total thickness of the epitaxial layer is the same as that of the oxide layer.
[0043] The fourth step is to make active devices, that is, transistors, from compound single crystal semiconductor materials, and complete the patterning of the first layer of metal. The first layer of metal realizes the functionalization of transistors and is used as the bottom of spiral inductors and c...
Embodiment 2
[0049] A process for preparing compound semiconductor MMIC structures on silicon substrates by wet etching, the process steps comprising:
[0050] In the first step, silicon oxide is deposited on the surface of the silicon substrate with a thickness of 300-2000nm.
[0051] In the second step, a window exposing the silicon substrate is obtained by photolithography and etching on the silicon oxide for material growth of active devices.
[0052]In the third step, the transition layer and the compound single crystal semiconductor material are grown by selective epitaxy in the window, and the total thickness of the epitaxial layer is the same as that of the oxide layer.
[0053] The fourth step is to make active devices, that is, transistors, from compound single crystal semiconductor materials, and complete the patterning of the first layer of metal. The first layer of metal realizes the functionalization of transistors and is used as the bottom of spiral inductors and capacitors....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com