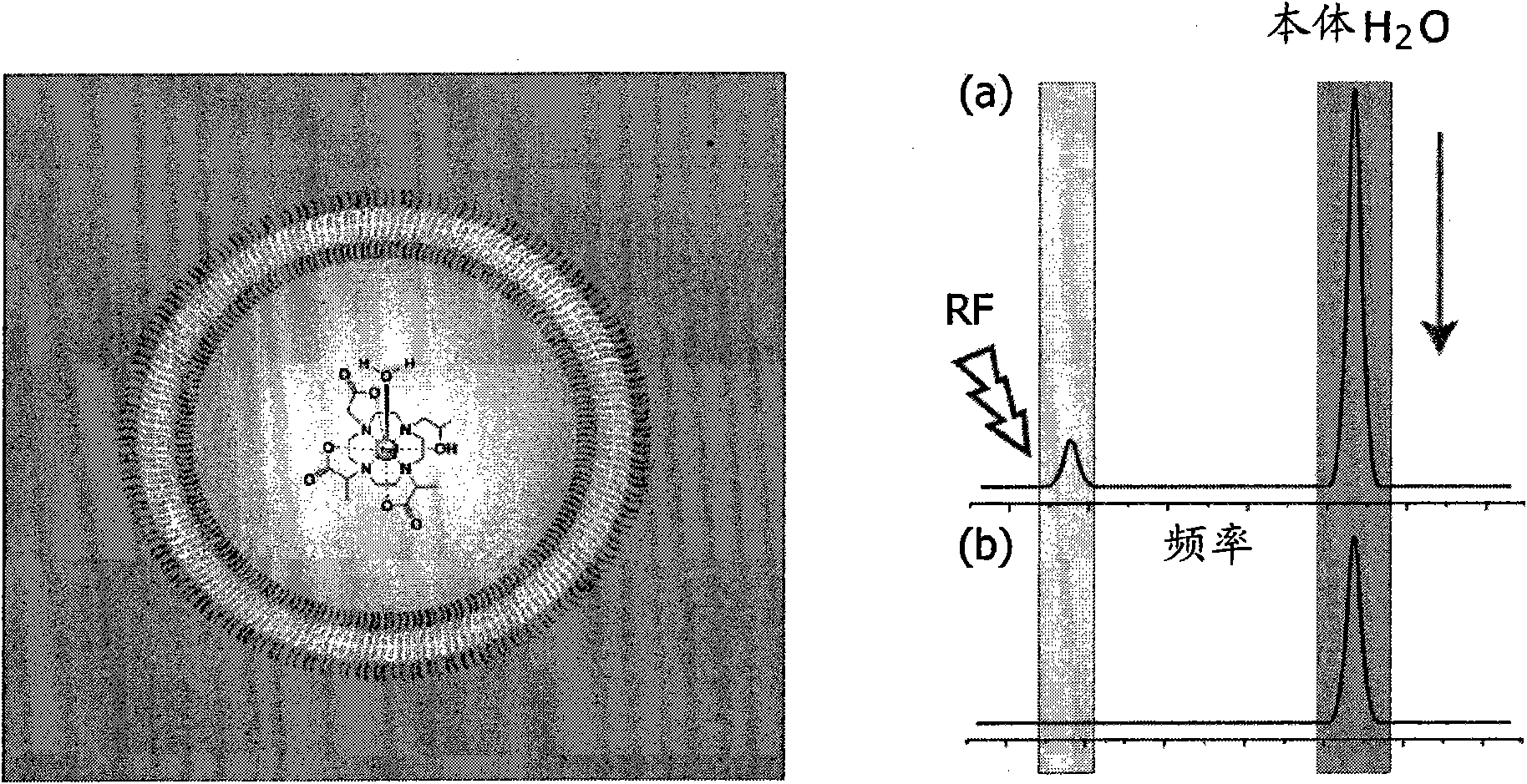
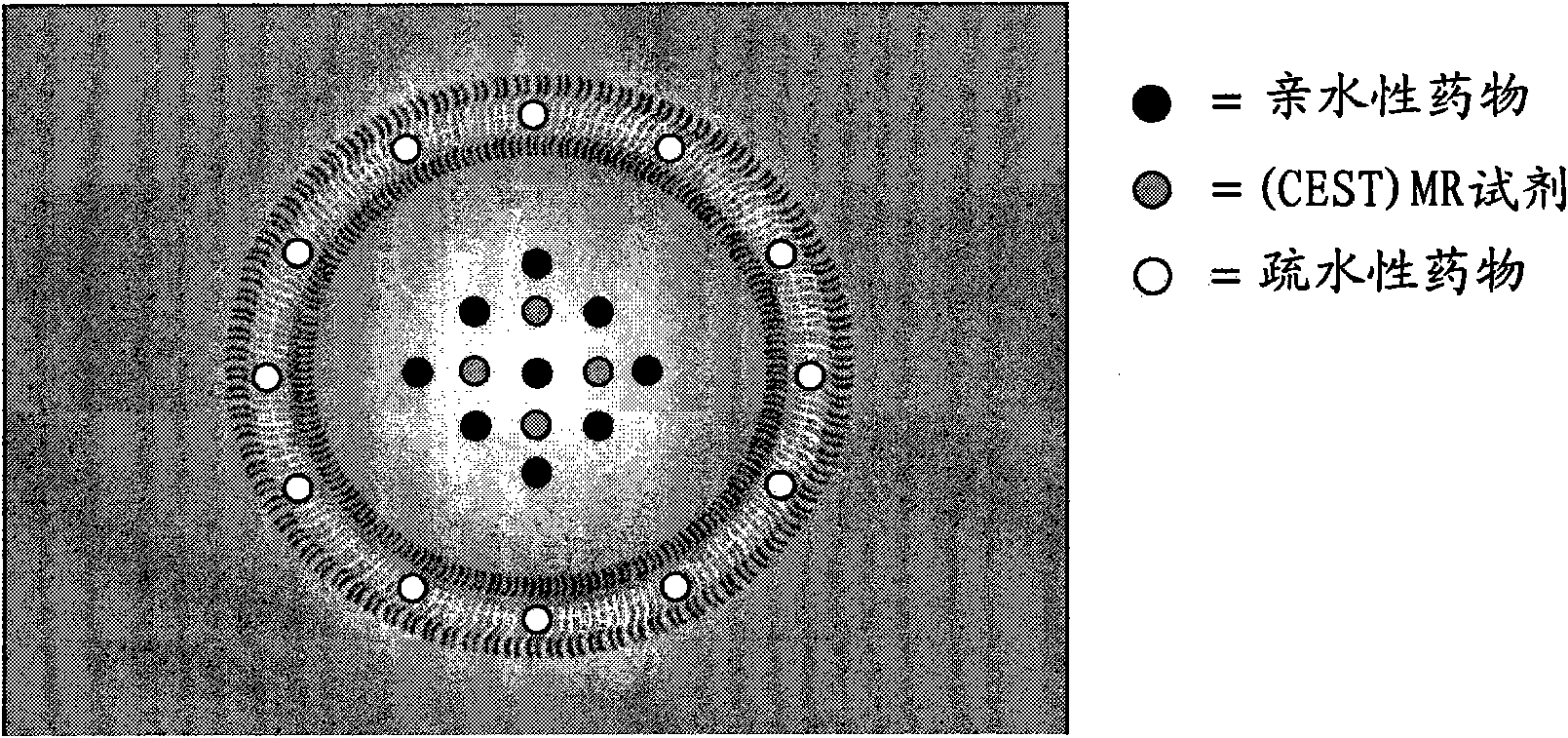
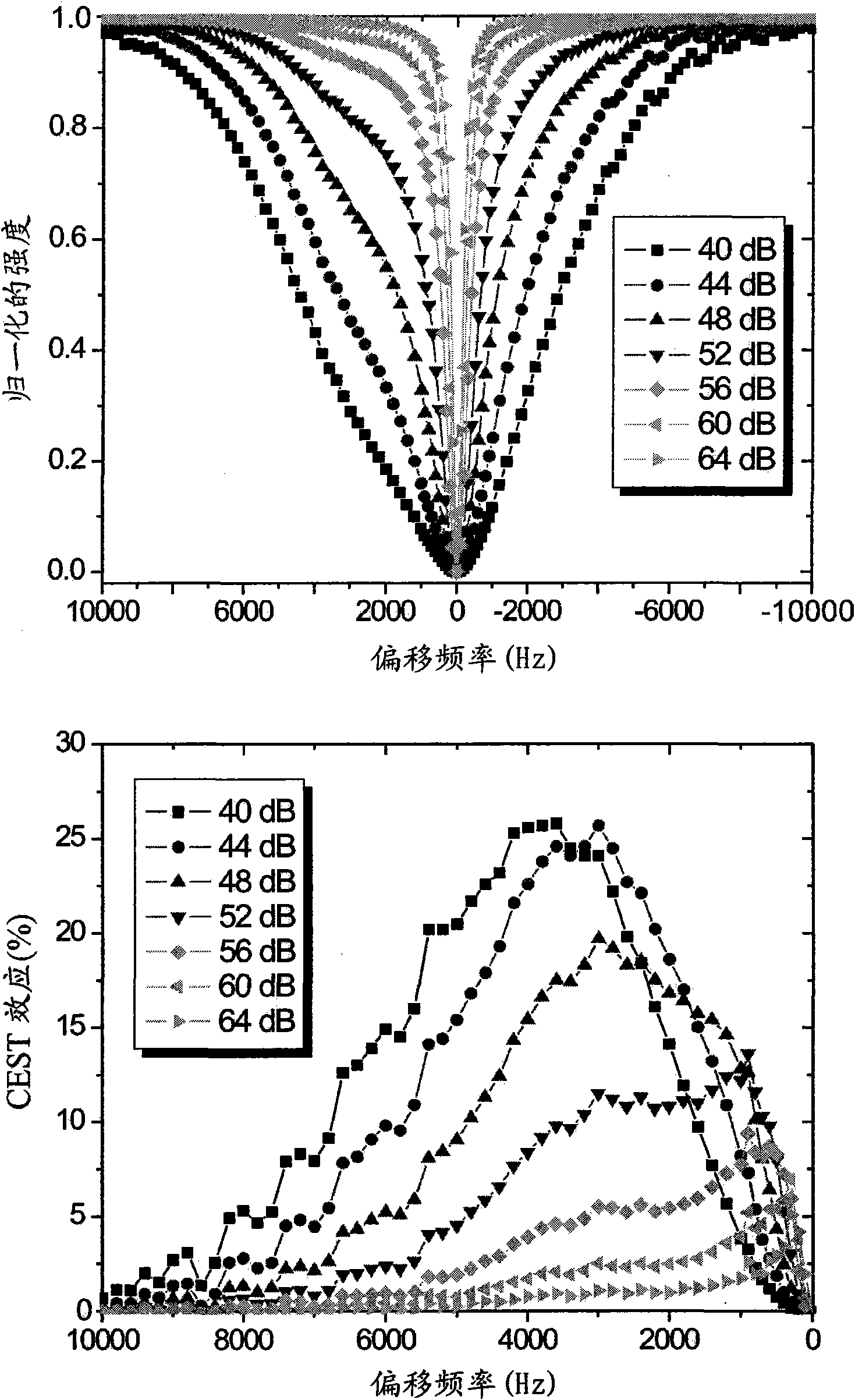
Polymeric drug carrier for image-guided delivery
A polymer, drug technology, applied in or guided delivery, chemical exchange-dependent saturation transfer contrast agent, reagent field of drug carrier
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0106]Abbreviations used in the examples, to the extent not used above: PBD is poly(butadiene), PEO is poly(ethylene oxide), HEPES is (4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1 -piperazineethanesulfonic acid).
[0107] Polymersomes with an average diameter of 100-150 nm were formed by thin film hydration techniques combined with subsequent extrusion. Briefly, Mn(g / mol): PBD(2500)-b-PEO(1300), PD=1.04 and f EO = 0.34 poly(butadiene (1,2-addition)-b-oxirane) dissolved in CHCl 3 middle. The solvent was gently removed under reduced pressure to obtain a thin polymer film. The membrane contained 65mM [Tm(hpdo3a)(H 2 O)] and 5mM carboxyfluorescein in 20mM HEPES solution for hydration. Sonication at 50°C for 30 minutes followed by three freeze-thaw cycles under vacuum using liquid nitrogen at -177°C and a water bath at 50°C resulted in a monodisperse distribution of polymersomes. Subsequently, the dispersion was extruded several times through polycarbonate filters with pore diameters of 1 μm, 0.4 μm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com