Genetically engineered strain of streptomyces coeruleorubidus producing epi-daunorubicin and preparing method thereof
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and epidaunorubicin, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of low epidaunorubicin yield and low genetic stability, and achieve the effects of accelerated screening, good repeatability and increased yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
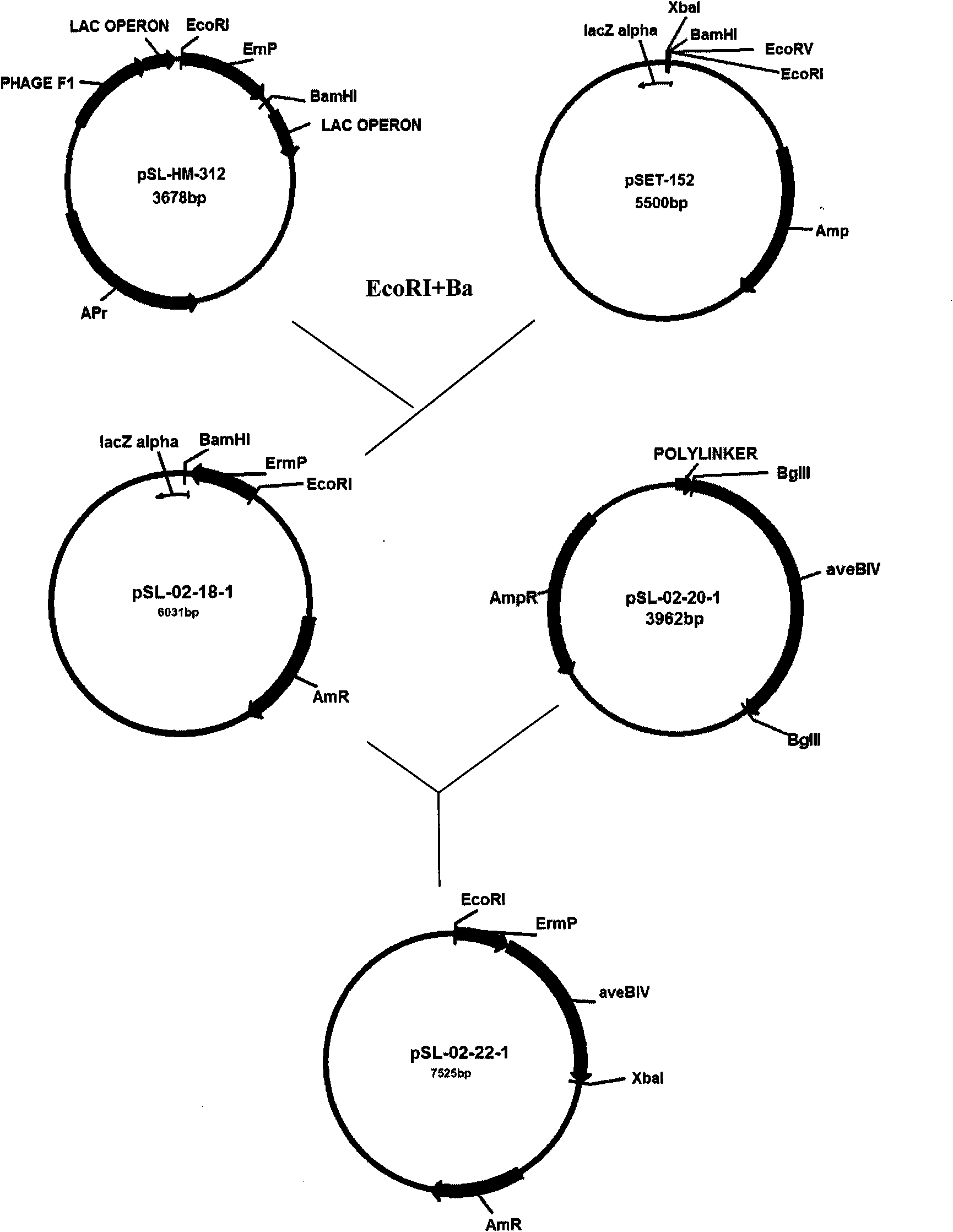
[0033] Example 1 Double exchange of left and right arms and the cloning of aveBIV sequence
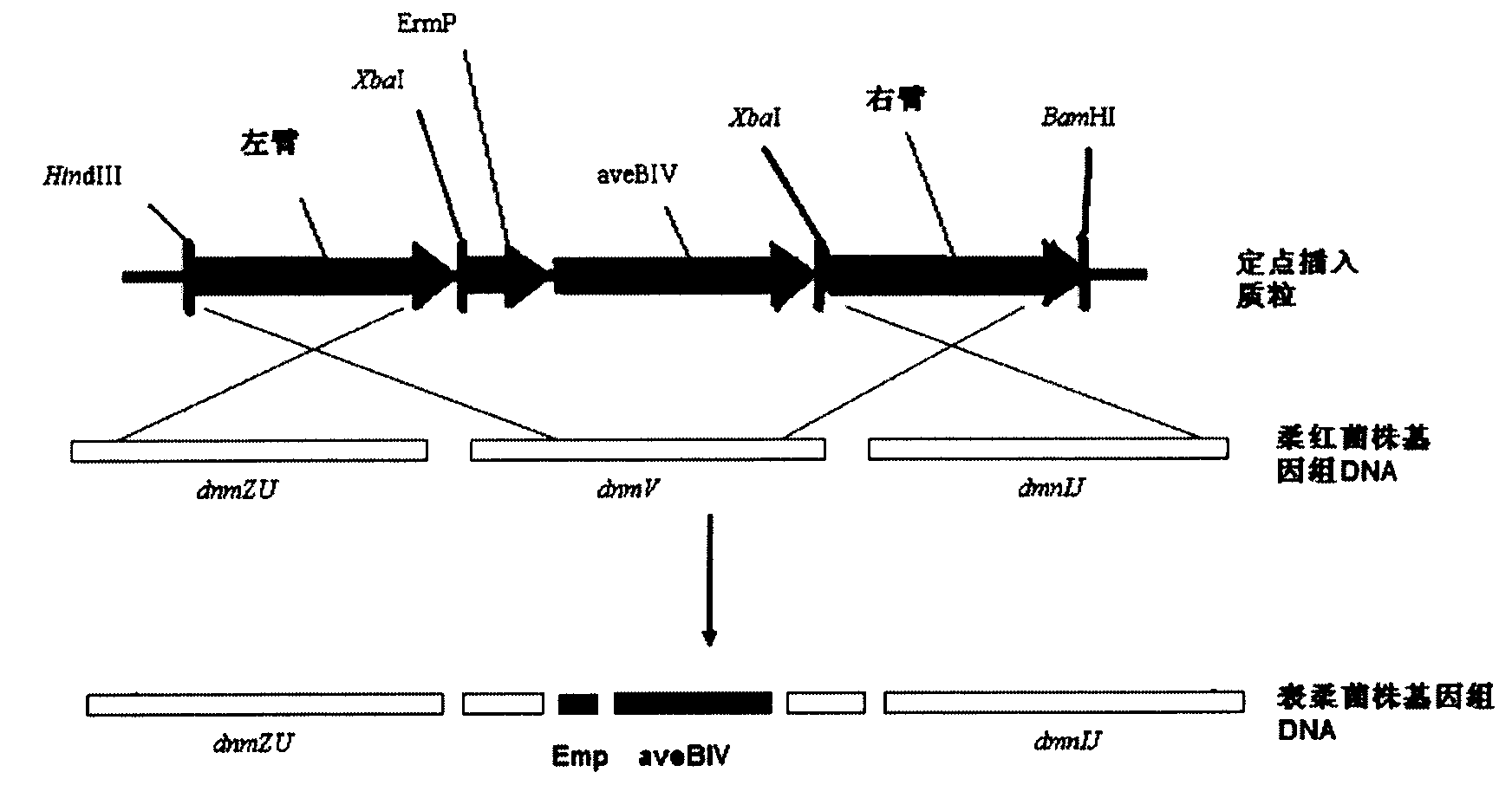
[0034] In Streptomyces coelicolor SIPI-1482, dnmZ and dnmU are sequentially upstream of dnmV, and dnmJ and dnmI are sequentially downstream of dnmV. The present invention takes dnmZ, dmnU plus a part of dmnV as the left arm of the double exchange, and dnmI and dnmJ plus a part dmnV was used as the right arm of the double crossover to construct the double crossover plasmid. Firstly, primers were designed according to the published corresponding sequence of Streptomyces coelicolor SIPI-1482 (GenBank accession number: AF006633):
[0035] The left arm upstream primer is 5'-AAAAAGCTTCTGGGACGGAATGGGC-3',
[0036] The downstream primer of the left arm is 5'-AAATTCGAATCGCACCAGTCGCAGATG-3';
[0037] The upstream primer on the right arm is 5'-AAATCTAGAGGGCTGGTCGTCAACATC-3',
[0038] The downstream primer of the right arm is 5'-AAAGGATCCCATCAAACTCCGCAAGACAT-3'.
[0039] The above primers were...
Embodiment 2
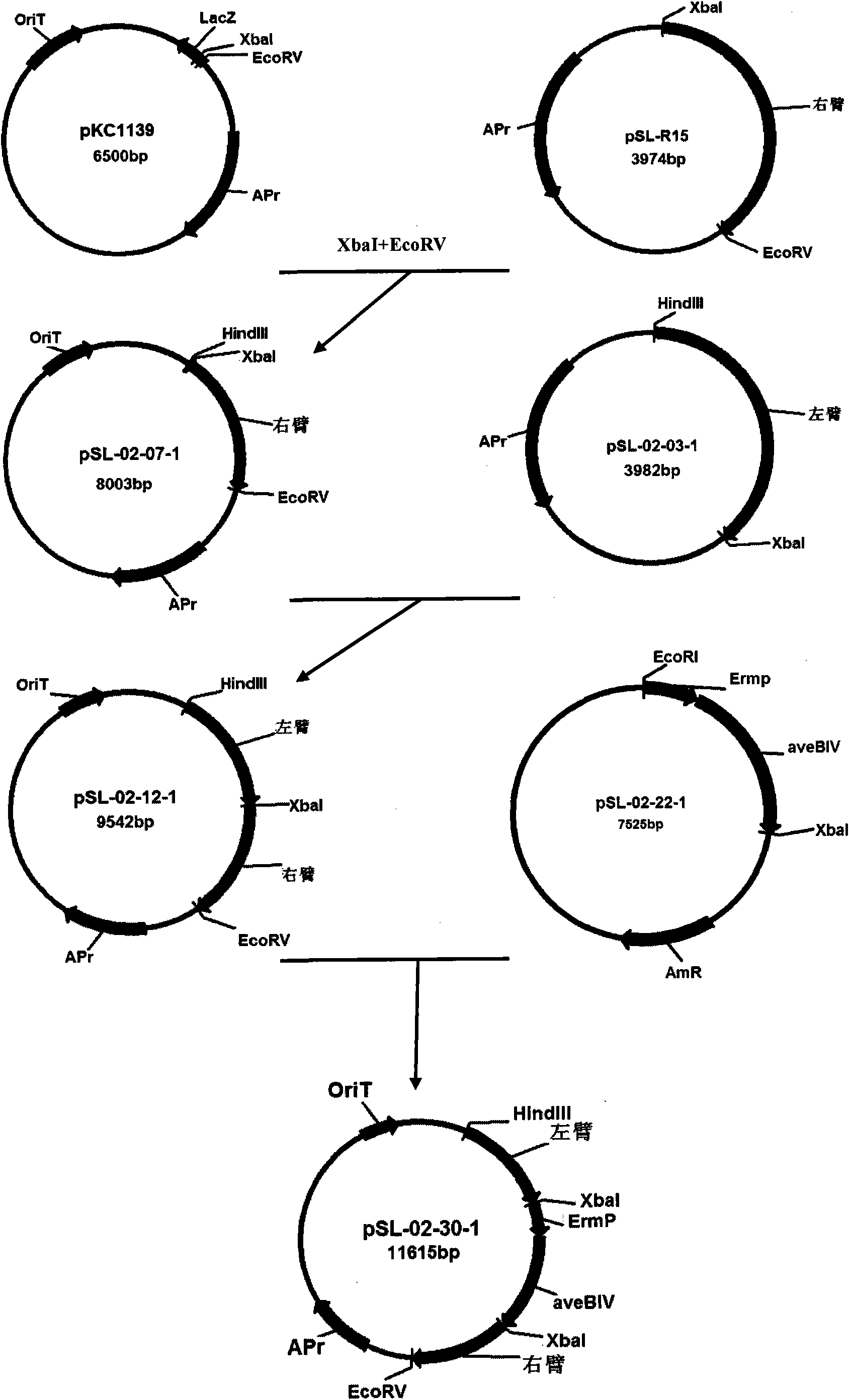
[0042] Example 2 Construction and conjugative transfer of double exchange site-directed insertion plasmids
[0043] The right arm in Example 1 was linked into plasmid pKC1139 (purchased from Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Technology Service Co., Ltd.), and the access sites XbaI and EcoRV were inserted to obtain a plasmid, which was named pSL-02-7-1. The left arm was positively connected to the plasmid pSL-02-7-1, and the access sites HindIII and XbaI were used to obtain the plasmid, which was named pSL-02-12-1. Use the restriction endonuclease XbaI to cut out the ErmEP+aveBIV gene from the pSL-02-26-1 plasmid in Example 1 and insert it forward into pSL-02-12-1. This plasmid is the double exchange knockout dmnV , and at the same time site-specific insertion of the epidaunorubicin expression integration plasmid of aveBIV. This plasmid was used to transform large intestine DH5α, and the transformants were cultured in LB. The plasmid was extracted for enzyme digestion and PCR ver...
Embodiment 3
[0045] The screening of embodiment 3 double exchange engineering bacteria
[0046] The zygotes obtained in Example 2 were picked and placed in a small test tube containing 4 ml of TSB medium (containing Am50 μg / ml, 2 to 3 glass beads with a diameter of 2 to 5 mm were added to the test tube), and cultured with shaking at 30°C. After the bacterial solution was shaken, take 1 μl of the bacterial solution and dilute it in 1 ml of sterile water, mix well, take 100 μl of the Gao No. 1 plate coated with Am 50 μg / ml, and incubate at 37°C. Because the pKC1139 plasmid is a temperature-sensitive plasmid, it can survive only when it is integrated into the chromosome, and all integrants that come out have undergone homologous recombination exchange. After 4 to 5 days, the integrants were picked and cultured in antibiotic-free TSB medium for continuous passage to promote double crossover. Take 1 μl of the third-generation bacterial solution, dilute it in 10ml of sterile water, mix well, ta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com