Protein, gene and function fragment involved in palmitic acid synthesis and application thereof
A palmitic acid and gene technology, applied in the field of proteins involved in palmitic acid synthesis, can solve the problems of slow development of high-oil corn, long innovation time of germplasm resources, slow progress, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Embodiment 1, the discovery of gene and functional fragment
[0042] 1. QTL-Pa19 fine mapping and cloning
[0043] 1. Construction and evaluation of QTL-Pa19 near isogenic line
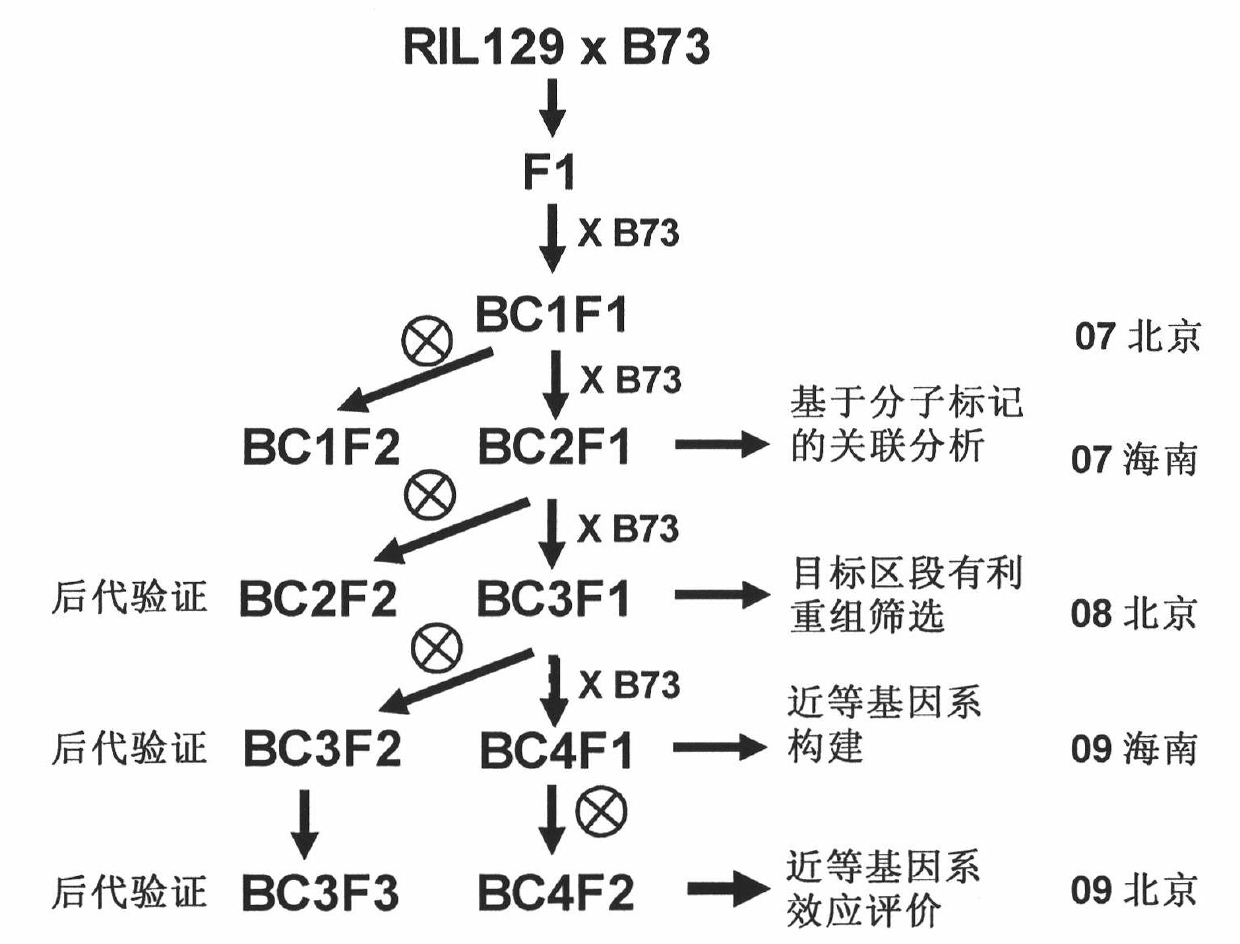
[0044] A near-isogenic line for the target gene of QTL-Pa19 was constructed using a high-generation backcross strategy, such as figure 1 As shown, RIL129 from the recombinant inbred line population obtained from the crossing of B73 and By804 was selected as the donor parent. About 44.5% of the genetic background of this line came from B73, which carried the By804 fragment in the target genome region and had relatively High absolute palmitic acid content and high proportion of palmitic acid; B73, as a recurrent parent, has significant differences in target traits from By804 and RIL129. Each generation uses molecular markers to control the genetic background, and uses association analysis and linkage population progeny verification to evaluate the target traits of the population with favorable re...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Example 2, Functional verification of ZmFatB (prokaryotic expression)
[0087] 1. Basic principles
[0088] The in vivo expression results confirmed that there was no difference in the expression of ZmFatB alleles, so the indel at the 3' end 11bp is very likely to lead to differences in protein activity, resulting in phenotypic variation. There are two alternative outcomes for plastid fatty acid synthesis in plants. Part of the formed acyl carrier protein is directly converted into glycerol lipids in plastids, and palmitic acid in the form of C16:0-ACP can be directly converted into plastids Prokaryotic lipid metabolism is catalyzed by acyltransferase, while the other part is hydrolyzed into free fatty acids and acyl carrier protein (ACP) by acyl-ACP thioesterases (FAT). Free fatty acids enter the cytoplasm and further participate in the "eukaryotic pathway" of lipid metabolism - the Kennedy pathway (Kennedy pathway). Therefore, the FATB gene acts on the plastid and p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com