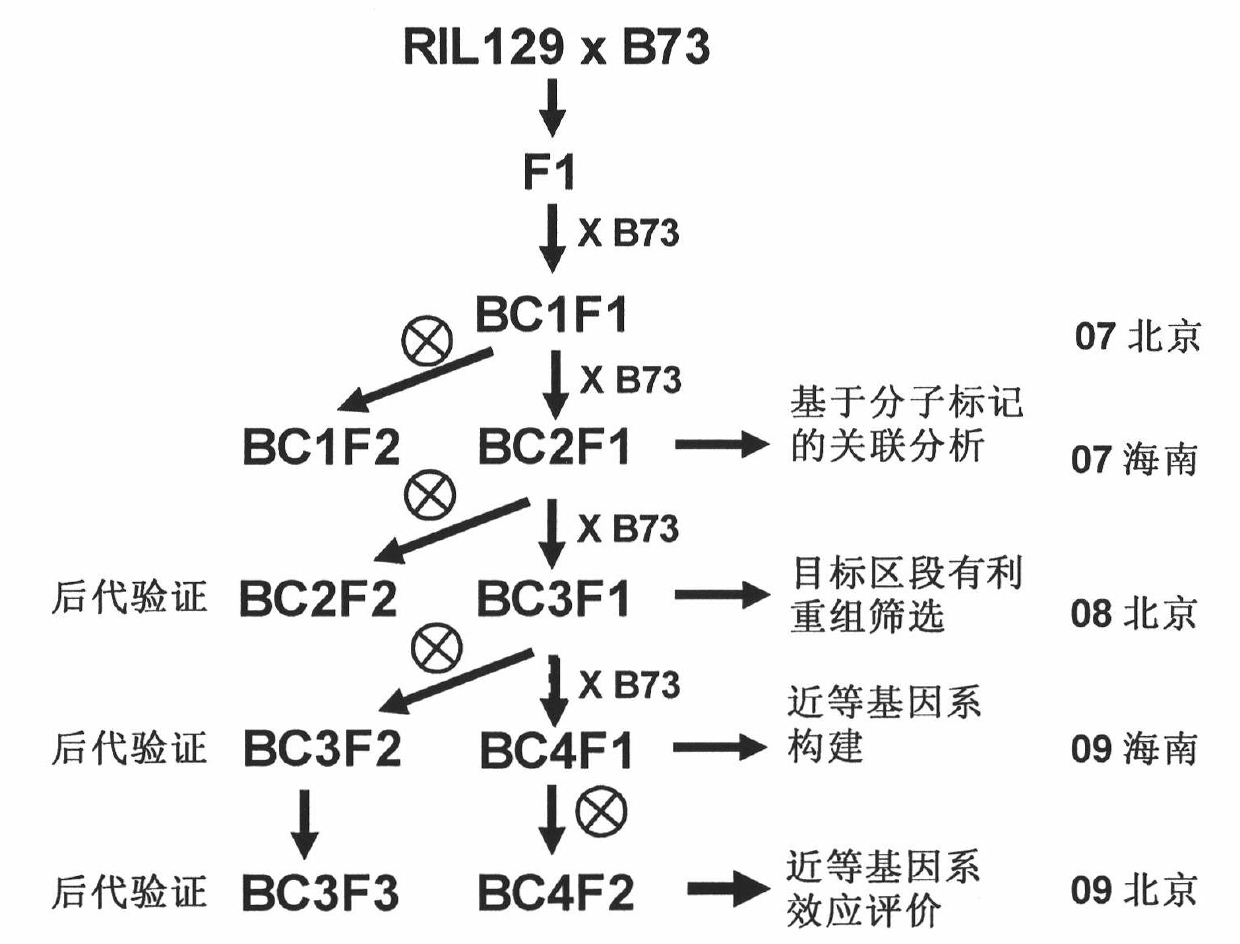
Patents
Literature
93 results about "Recombinant inbred strain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
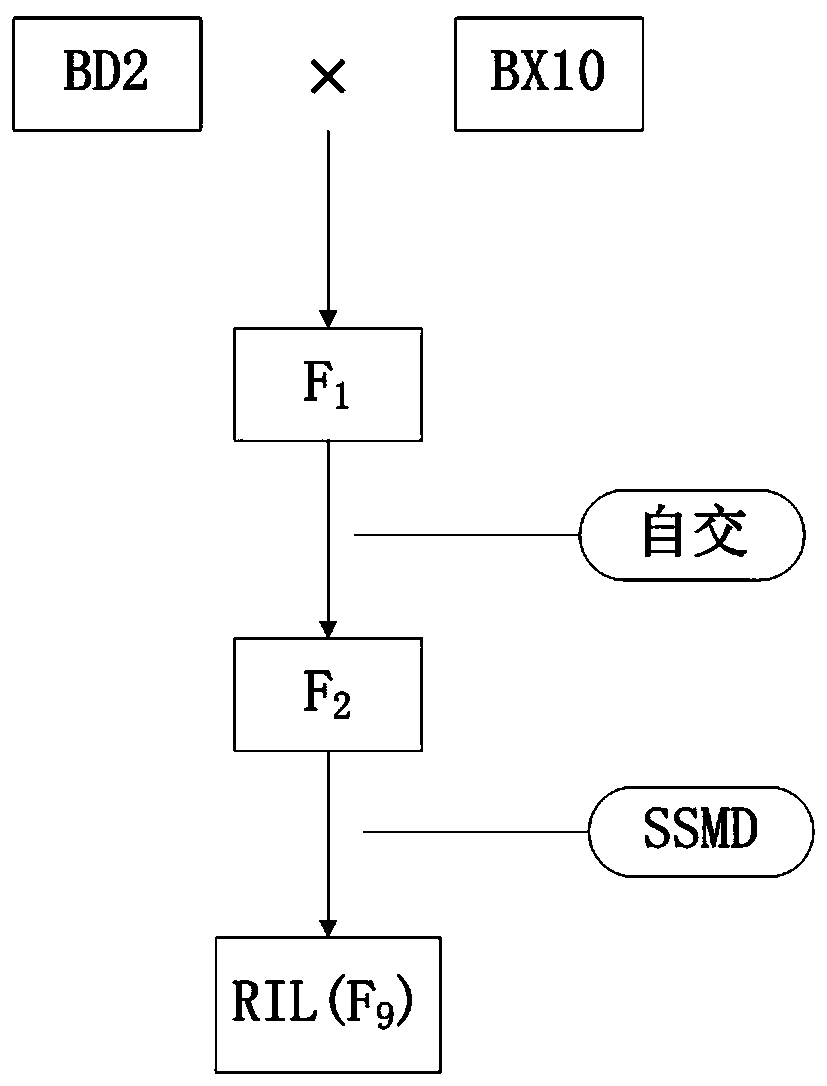
A recombinant inbred strain (or recombinant inbred line) is an organism with chromosomes that incorporate an essentially permanent set of recombination events between chromosomes inherited from two or more inbred strains. F1 and F2 generations are produced by intercrossing the inbred strains; pairs of the F2 progeny are then mated to establish inbred strains through long-term inbreeding.
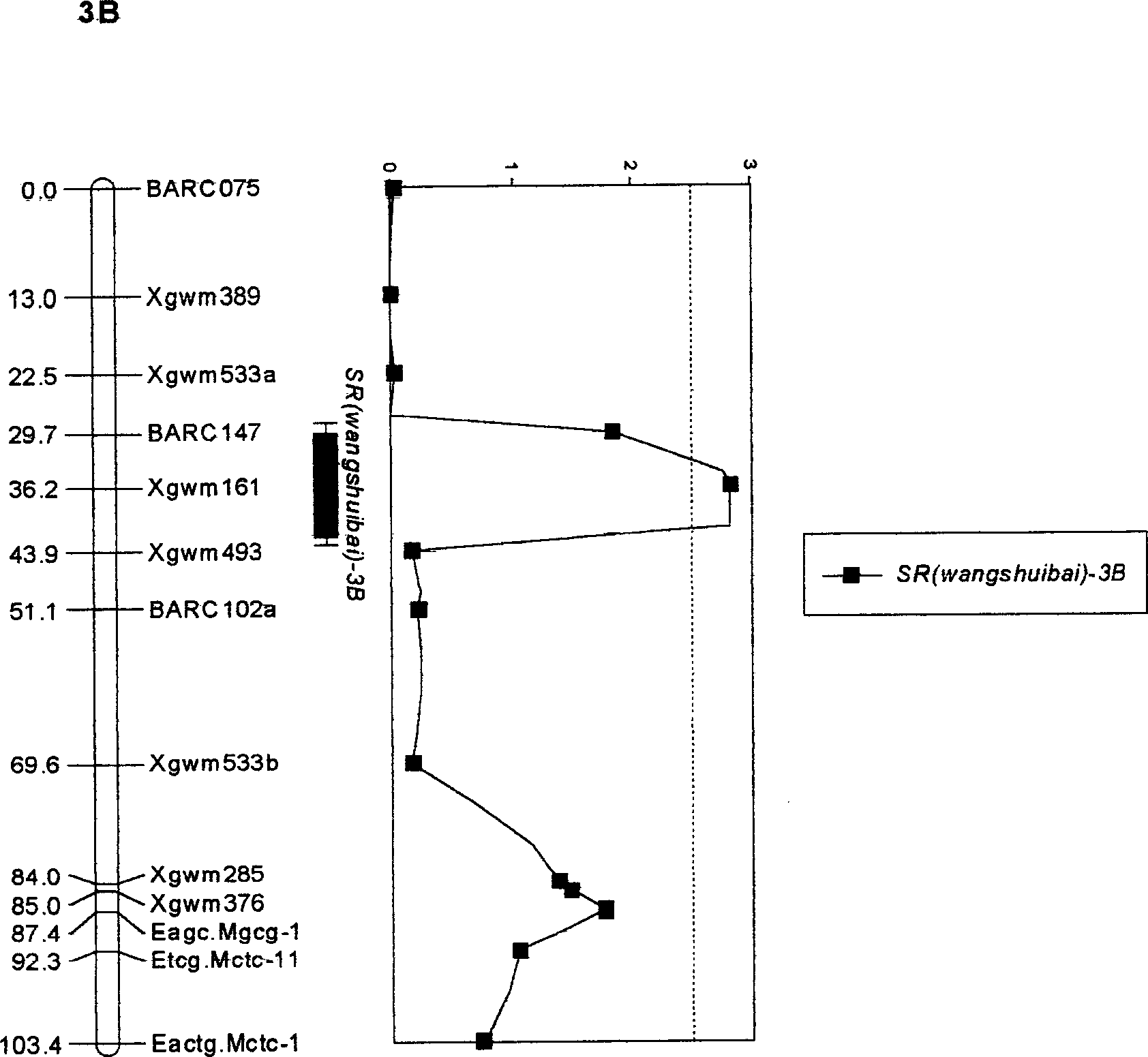
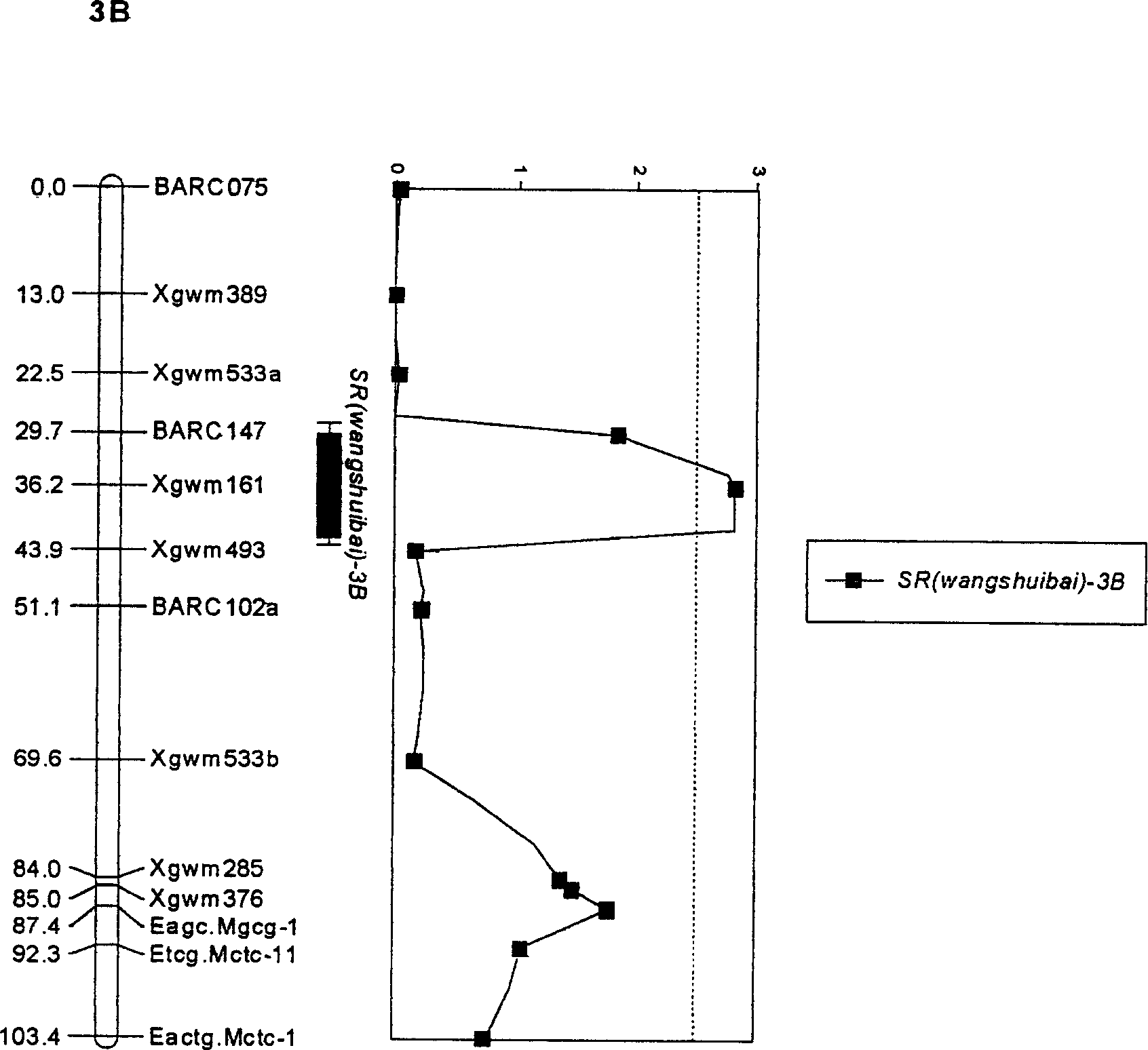
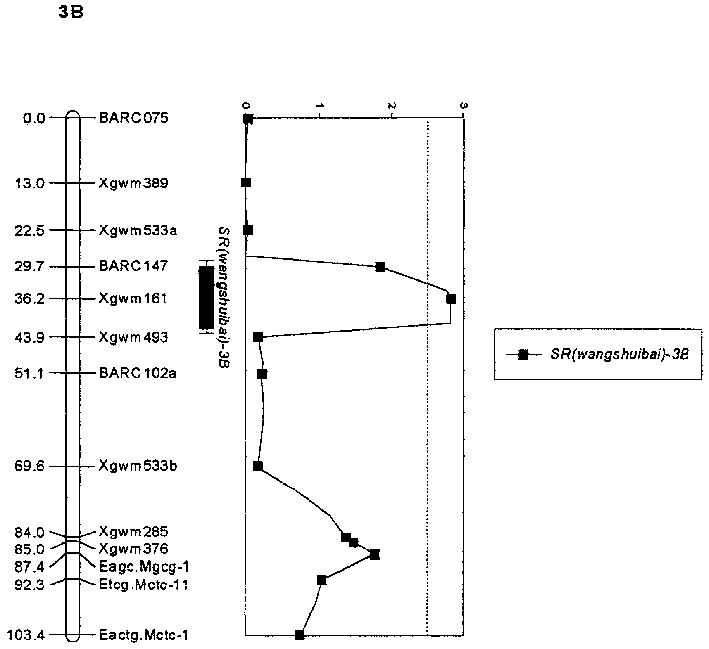
Molecular label closely linked with wheat gibberellin resistance main effect QTL and its application
InactiveCN1442039AReduce the waste of manpower and material resourcesImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDiseaseAgricultural science
The molecular label closely linked with the active QTL of wheat fusarium blight resistance is prepared through hybridizing the disease-resistant wheat with the disease-sensitive wheat to obtain recombinant selfing line, and performing QTL and genetic linkage analysis to obtain the said molecular labels Xgwin 161, BARC 147 and Xgwin 493. They can be used to predict the level of the resistance to fusarium blight by detecting whether the DNA of wheat contains the said molecular labels or not.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Quantitative character gene site locating method based genomic exon chip
The new quantitative character gene site locating method based on genome exon chip is to utilize exon sequence as one kind of molecular mark and utilize the detected data of human, rice and other allgenome or exon sequence chip of partial chromosome as colony locating molecular mark data for gene location via statistic location method. The present invention can obtain located functional gene sequence directly, and is suitable for all the quantitative character and complicated character of life. The research colonies include plant DH colony, F2 colony, near isogenic line, near isogenic introduction line, recombinant idiogamy line, animal family, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Supergrade hybrid rice breeding parent matching method
The present invention uses rice intermedium type sterile line as female parent, uses intermedius type restoring line as male parent for cross breeding rice hybrid species. Said invention also includes that uses hsien rice sterile line and intermedius sterile line as female parent and uses rice hsien-keng crossed duplex haploid (DH) population and hsien-keng crossed recombinant inbred line (RIL) population as male parent to make test cross to obtain four hybrid populations of hybrid F1 generation. By detecting character of F1 and using hisen-keng molecule specific probe to detect keng-type index of F1 correspondent to male parent DH and RIL the F1 character-male-type keng-type index correlation can be obtained.
Owner:程式华
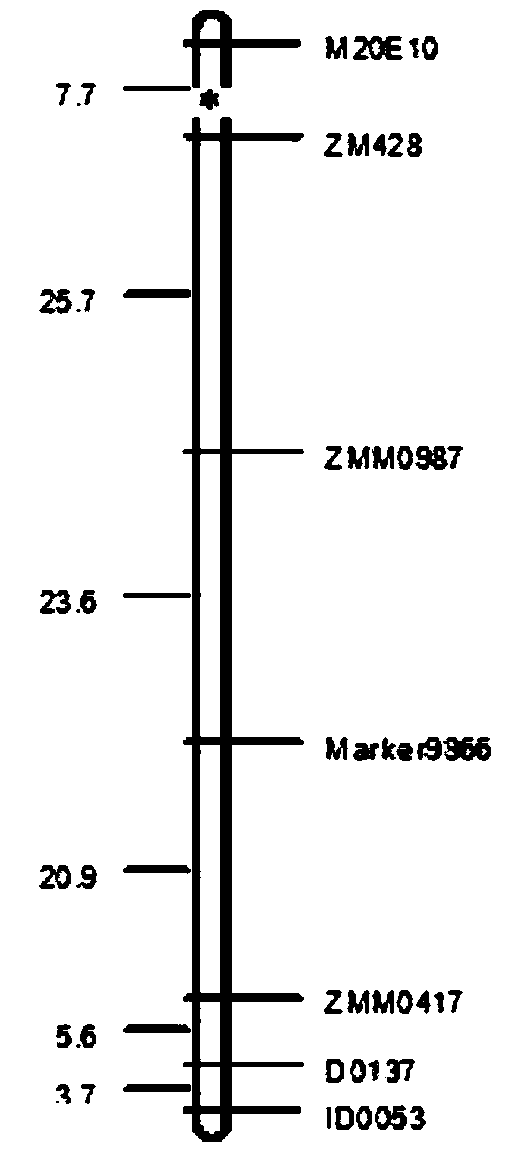
Molecular marker tightly linked with main effective genetic locus embodying sesame dampness resistance and application thereof
ActiveCN103525919AChoose a clear goalLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationEarly predictionGermplasm
The invention relates to a molecular marker tightly linked with a main effective genetic locus embodying sesame dampness resistance and application thereof. The main effective genetic locus qWHCHL09 is located on the 9th linkage group, and the molecular marker tightly linked with the main effective genetic locus is ZM428 whose sequences are as follows: ZM428F: AGGATGATGATGTGATGAGAG (5'-3') and ZM428R: CTGCTACTCCTTTTGTCTCTG (5'-3'). The molecular marker is obtained by hybridizing sesame 13 in sesame dampness-resistant varieties and a sensitive germplasm Yiyangbai to obtain F6-generation segregation population, namely a recombinant inbred line (RIL) population, and performing molecular genetic linkage analysis on the F6-generation segregation population. The molecular marker tightly linked with the main effective genetic locus embodying the sesame dampness resistance is applied to breeding of the sesame dampness-resistant varieties and screening of dampness-resistant traits of the sesame germplasm as well as early prediction; the auxiliary dampness resistance choosing target is clear; and the cost is relatively low.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cucumber powdery mildew resistance main effect QTL compact linkage molecule labeling method and applying method
InactiveCN101240342AReduce manpowerReduce the waste of equipment and material resourcesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyEarly generation
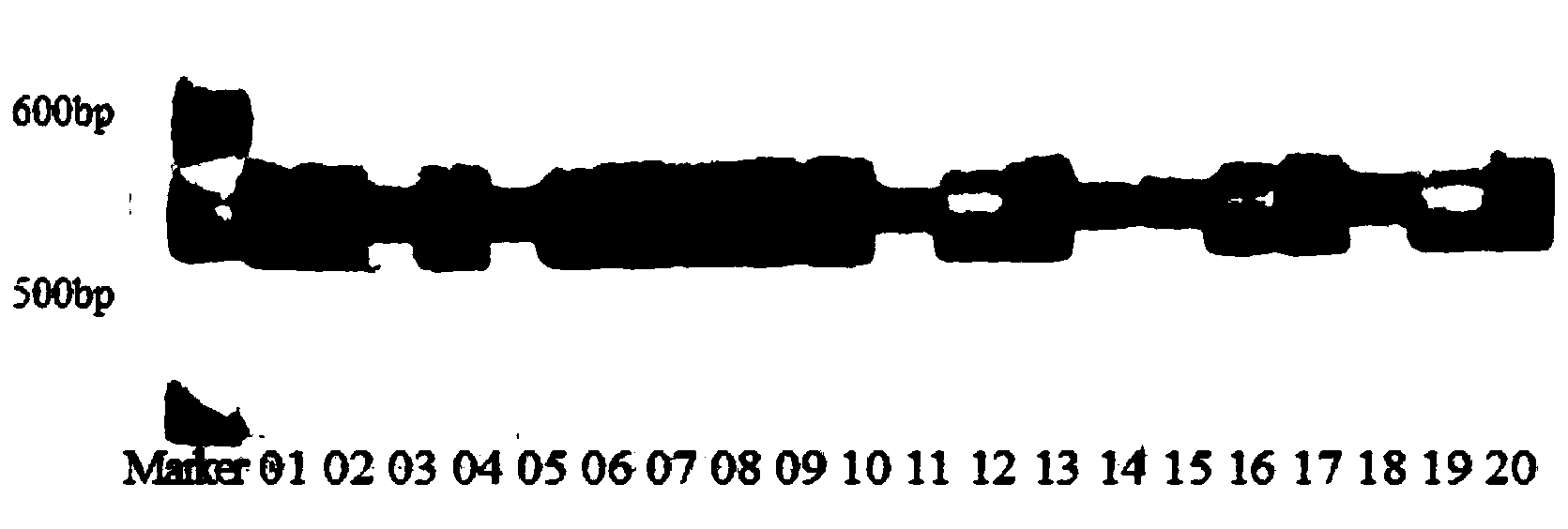
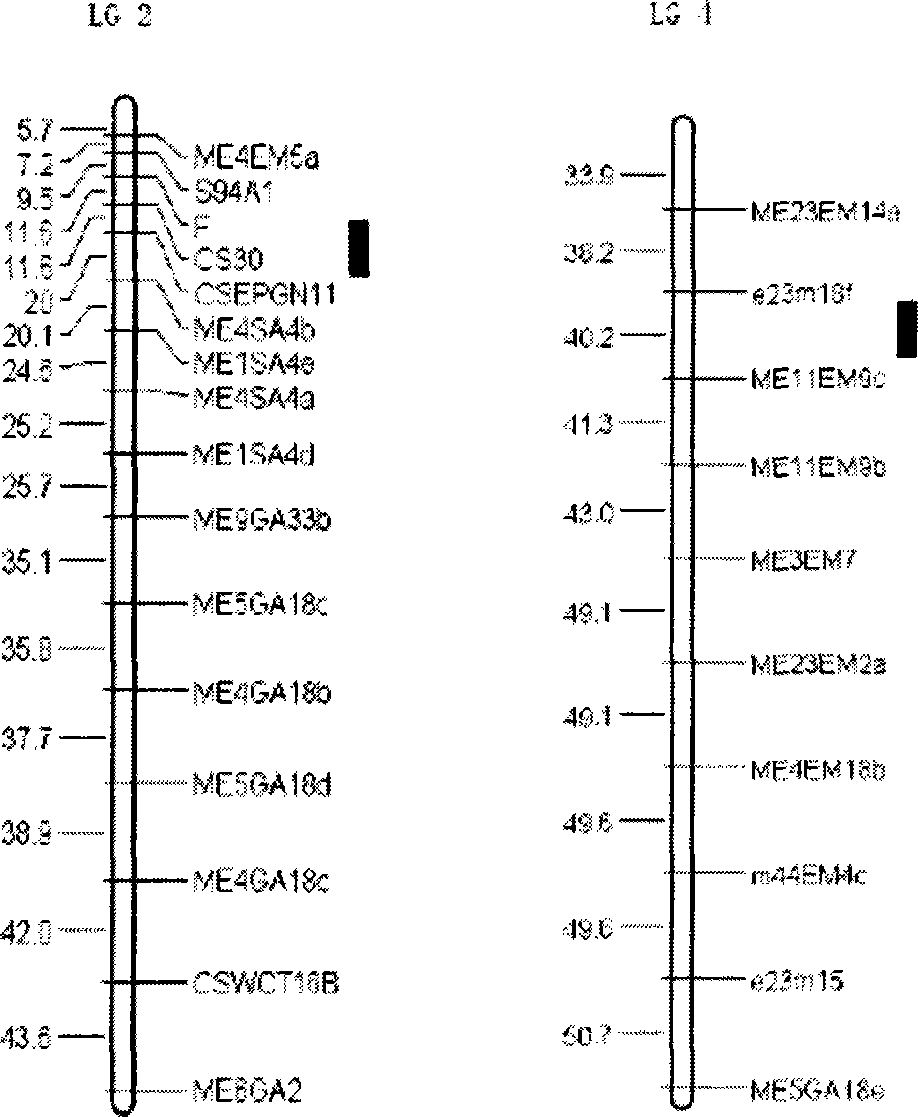
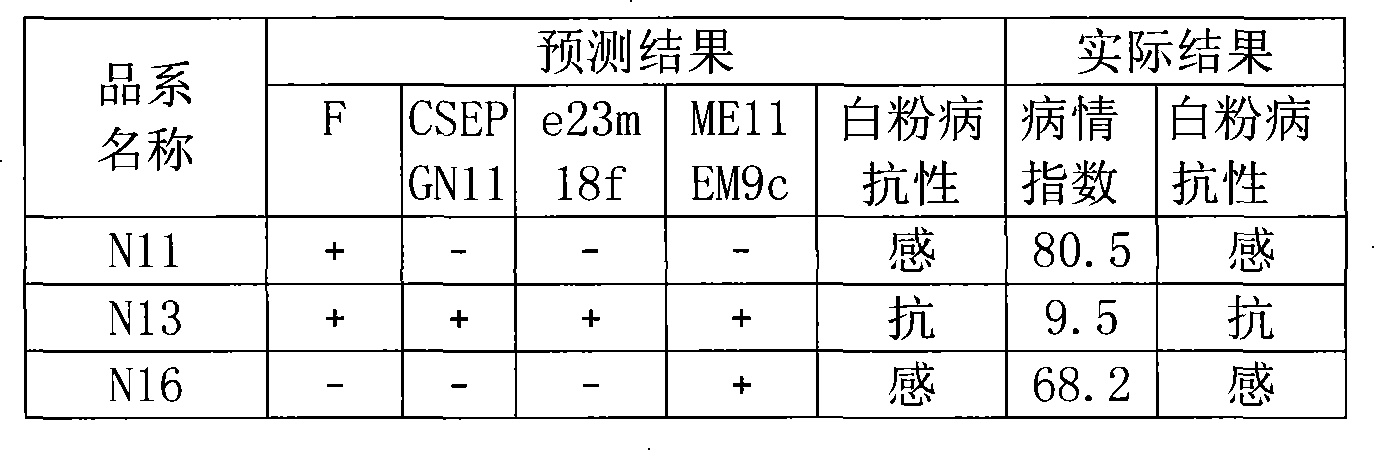
The present invention relates to a molecular marker method closely linked with major QTL for powdery mildew of cucumber resistance, belonging to the field of biological technology. The invention comprises the following steps: hybridizing susceptible variety S94 of powdery mildew of cucumber with susceptible variety S06 of powdery mildew of cucumber, getting hybrid F1; acquiring F7 generation recombinant inbred lines by filial generation single seed descent method; separating DNA of individual cucumber leaves and performing PCR amplification; analyzing data and constructing cucumber genetic linkage map for molecular marker; applying to statistical analysis and QTL location; and determining molecular markers F, CSEPGN11, e23m18f and ME11EM9c linked with major QTL for resistance source S06 powdery mildew. The coincidence rate between the identification result of the invention and the field resistance has improved from 94 percent to 100 percent. By the molecular markers linked with major QTL for resistance source S06 powdery mildew, progeny and derived varieties thereof for the specific resistant source can be selected in early generation seedling without the influence of environment condition, saving cost and improving breeding and selection efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
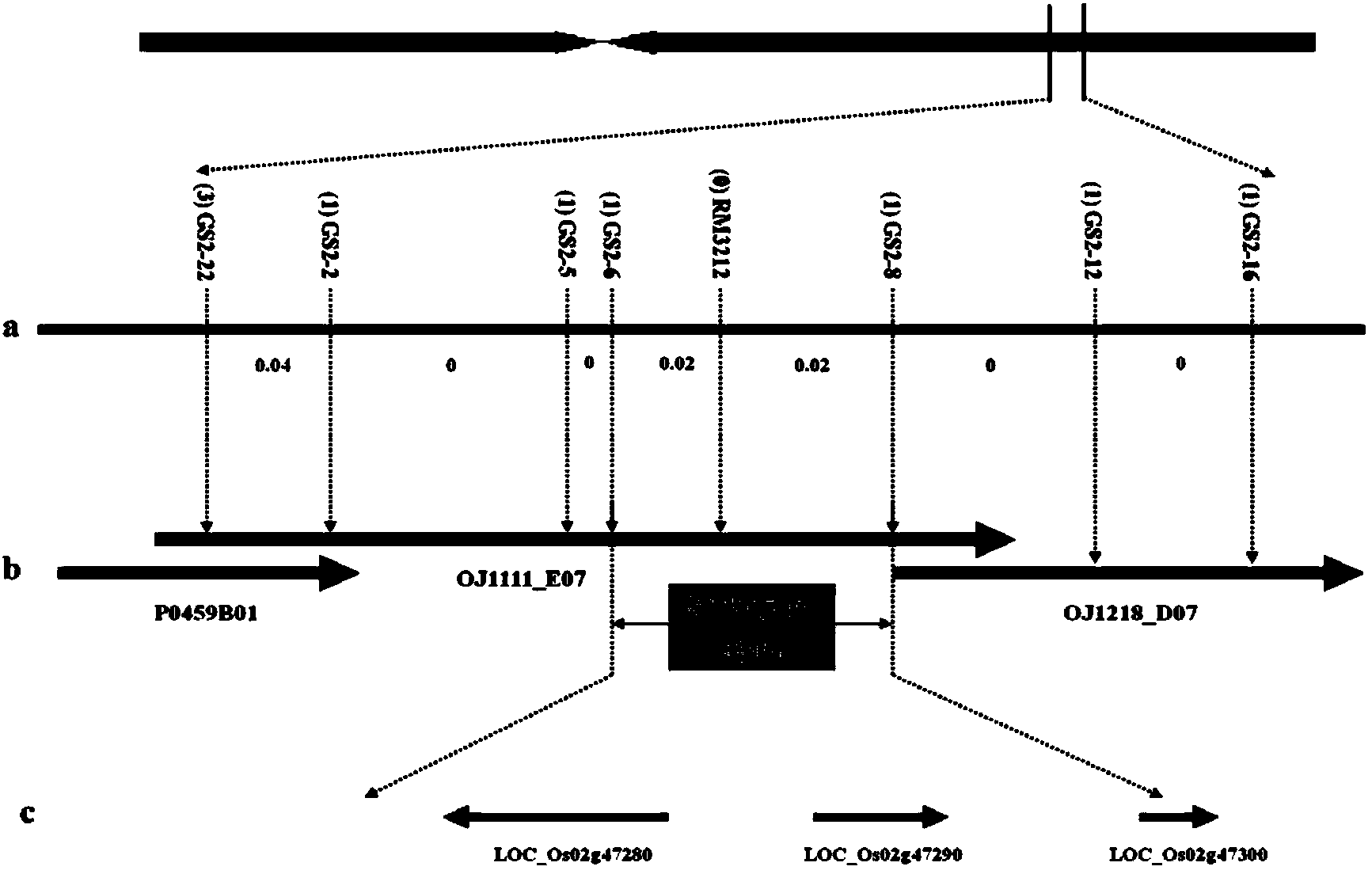
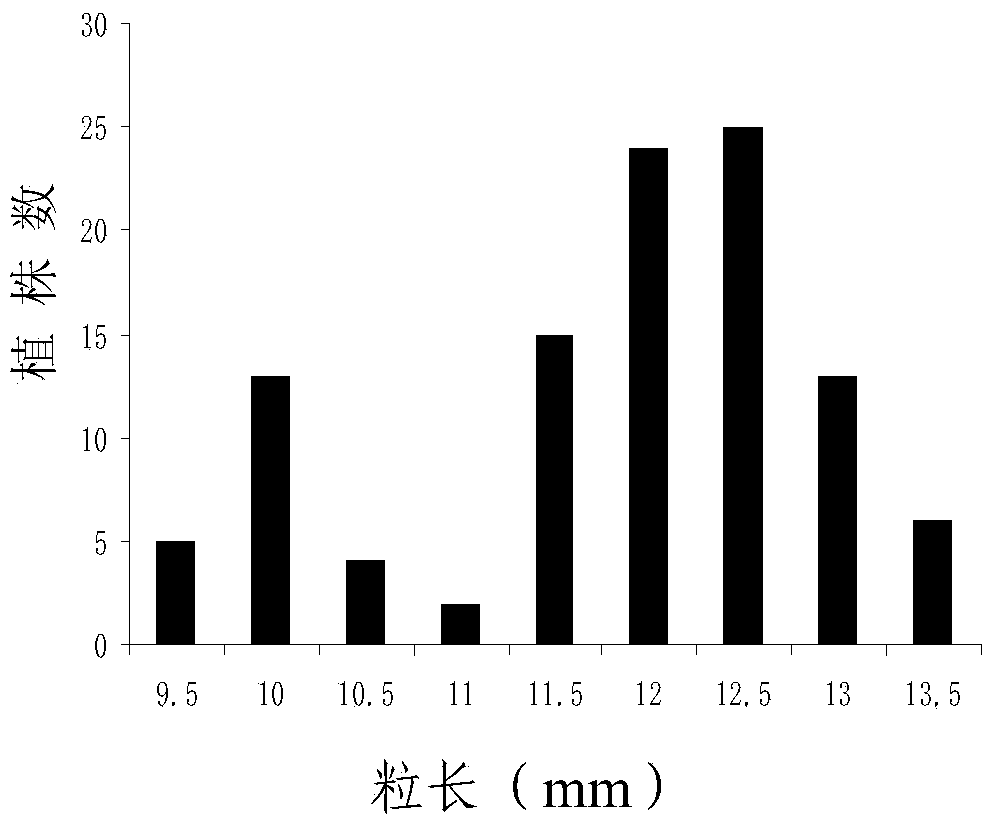
Molecular markers in close linkage with large grain gene GS2 of rice and application thereof
ActiveCN103409418AInhibition of grain width effectLittle or no grain width effectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceMolecular marker
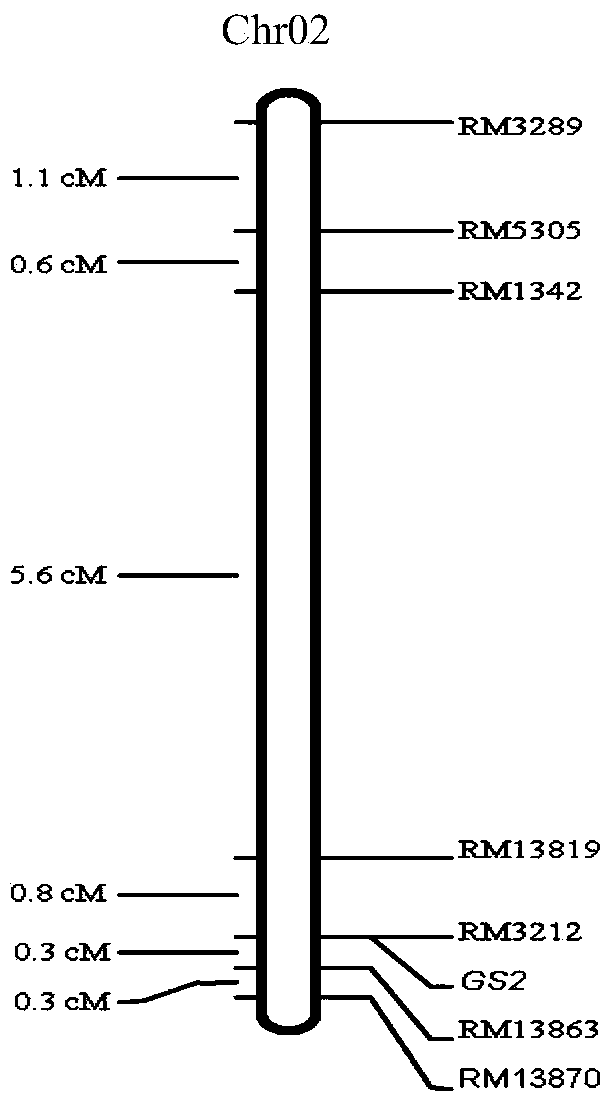
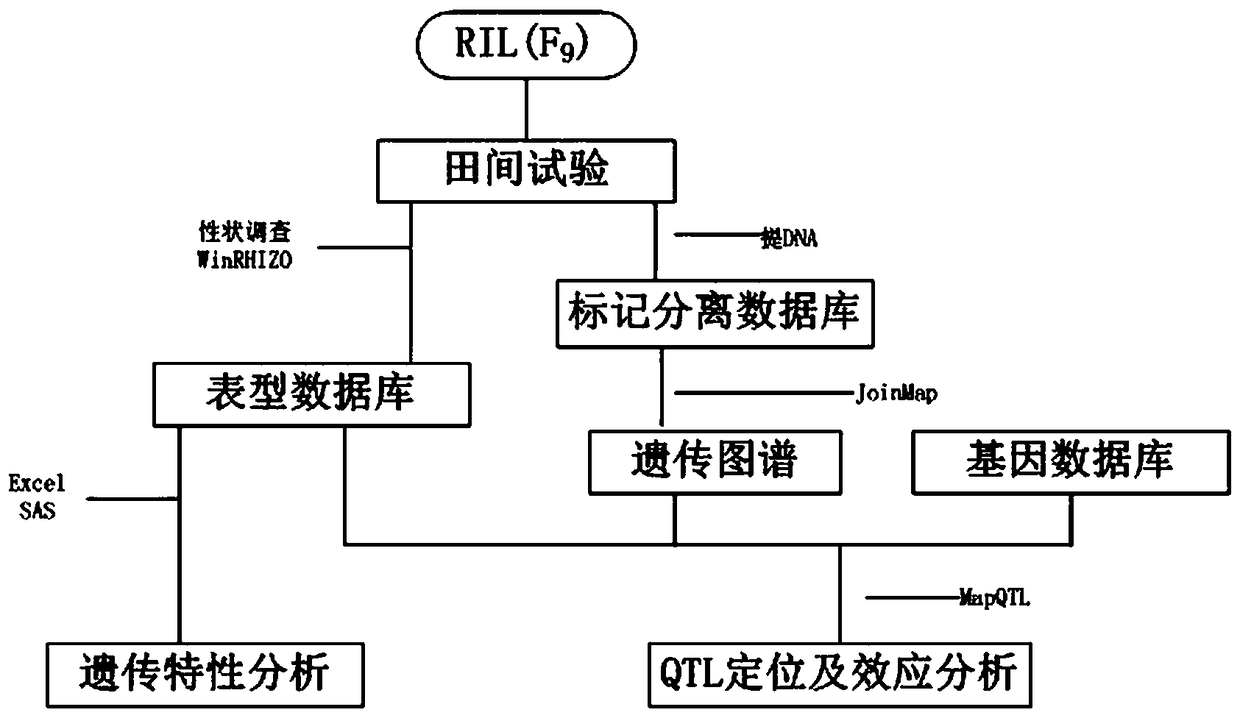
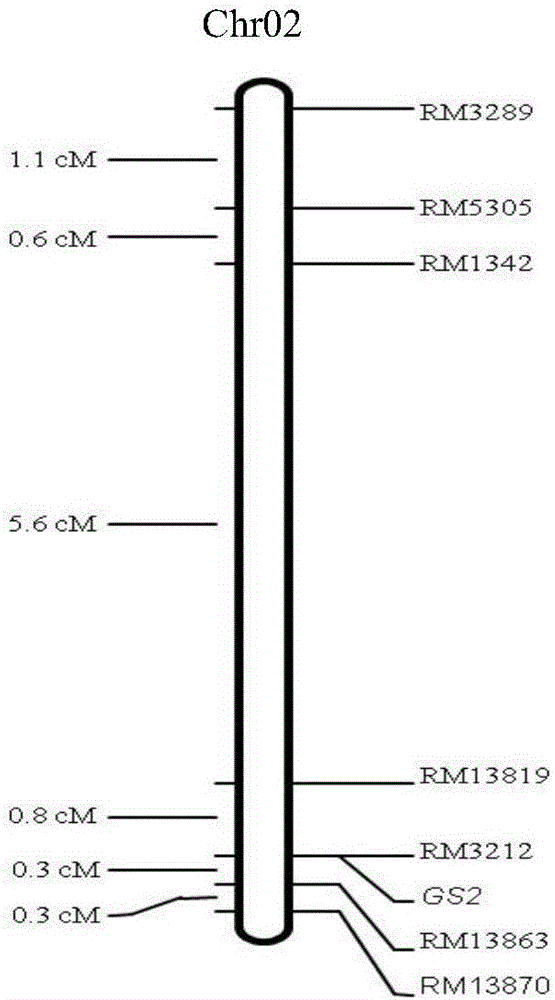
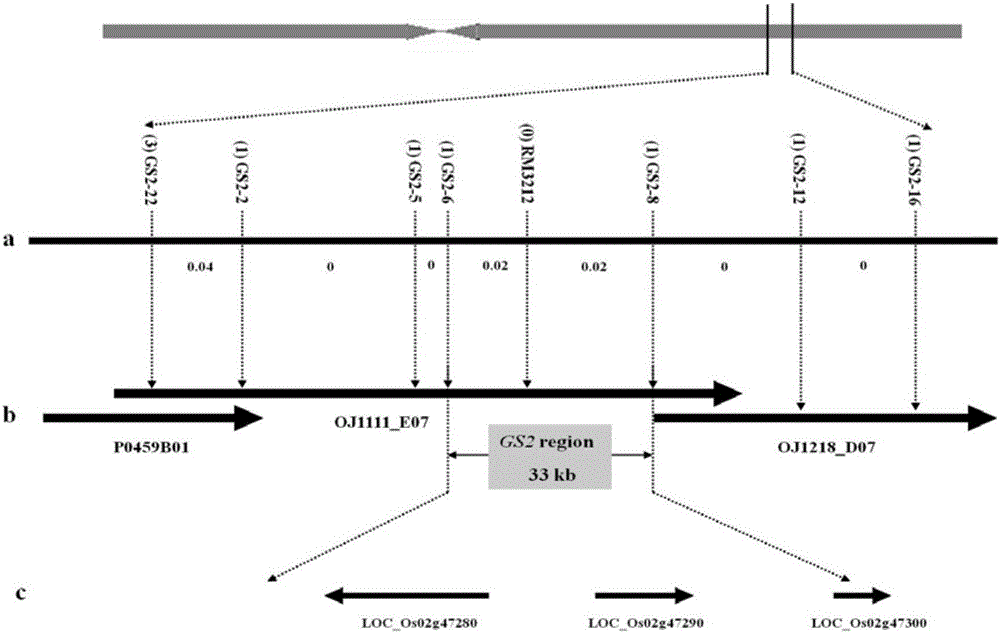
The invention provides molecular markers in close linkage with a large grain gene GS2 of rice and an application of the molecular markers. Through a recombinant inbred line (RIL) advanced grain shape segregation population, the grain shape major gene GS2 is finely located on a second chromosome and within a range of 33.2kb from GS2-6 to GS2-8, so as to obtain a series of molecular markers in close linkage with GS2. The molecular markers include a common data base marker RM3212 and 22 self-developed InDel markers (from GS2-1 to GS2-22). The molecular markers can be used for effectively detecting the GS2 genetic locus and further improving the breeding efficiency of large grain varieties (or parents).
Owner:HUNAN HYBRID RICE RES CENT
Cucumber downy mildew resistance main effect QTL linkage molecule labeling method and applying method
InactiveCN101240343AReduce workloadImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementSelf-pollinationGenotype
The present invention relates to a molecular marker method linked with major QTL for cucumber downy mildew resistance and an application method, belonging to the field of biological technology. The molecular marker method: getting F2 filial generation by self-pollination of hybrid F1; acquiring F7 generation recombinant inbred lines by filial generation single seed descent method; describing the gene type of each strain of the recombinant inbred lines; constructing genetic linkage map for molecular marker; testing the downy mildew resistance of each strain of the recombinant inbred lines; and composite interval mapping for interval possible located in QTL. The application method: hybridizing S94 and derive verities thereof with other cucumbers and multiplying to F2 generation; separating genome DNA of single cucumber plant, and testing whether each cucumber plant has molecular marker method linked with major QTL for cucumber downy mildew resistance. The invention develops an efficient, rapid breeding technology, selects breeding variety with conventional downy mildew, reduces workload of breeder, and improves precise of selection and breeding efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Molecular marker Hf1-Indel related to hardness of watermelon flesh and application of molecular marker Hf1-Indel
ActiveCN106148526ATo achieve the purpose of assisted breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGenome
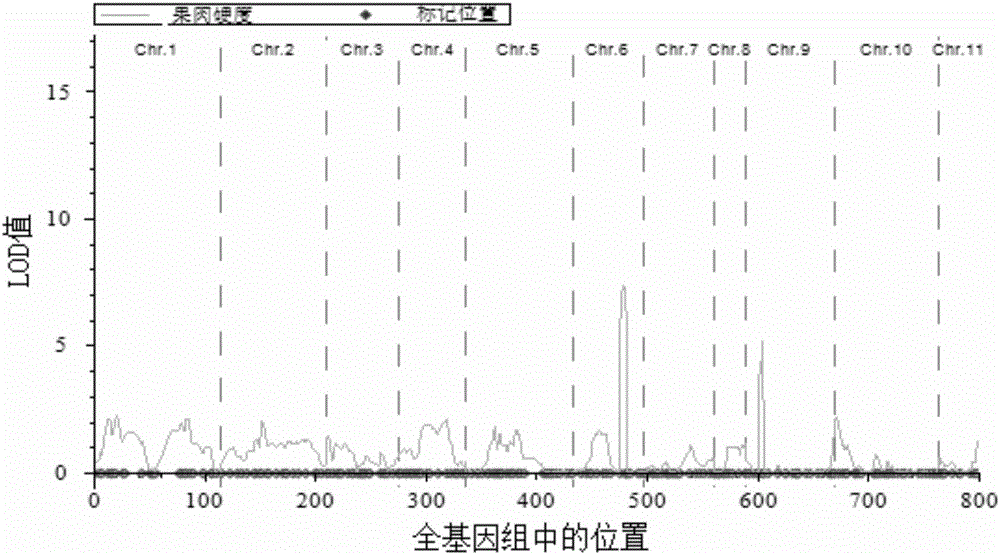
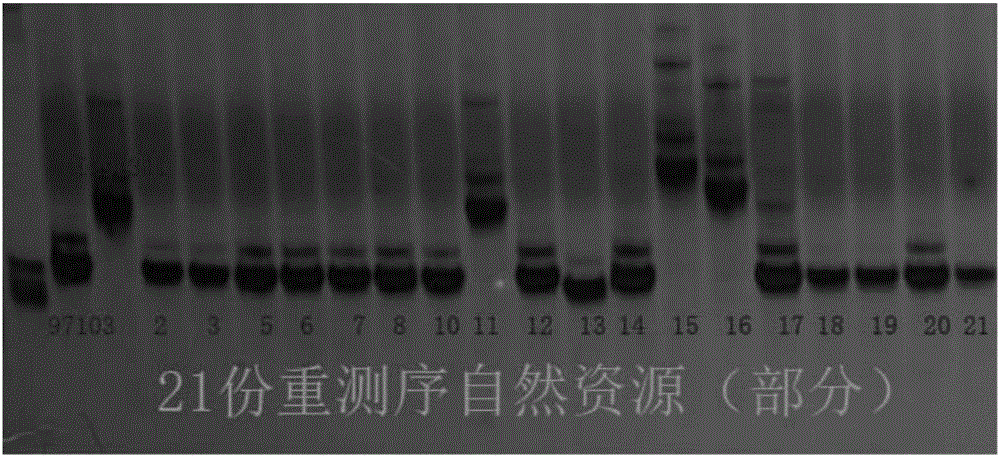
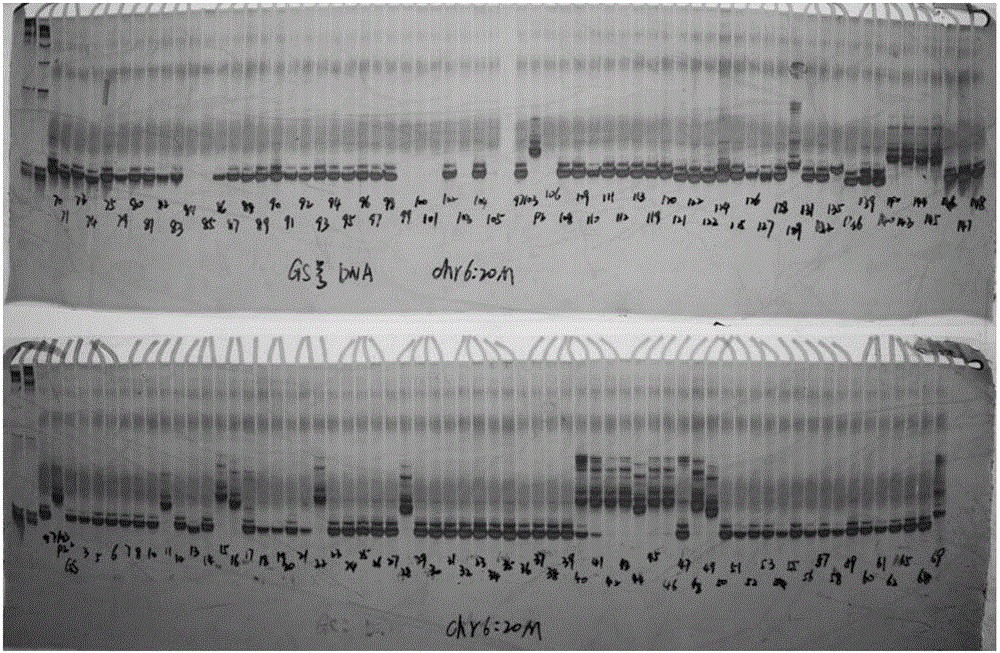
The invention discloses a molecular marker Hf1-Indel related to hardness of watermelon flesh and application of the molecular marker Hf1-Indel. On the basis of a 97103 whole genome sequence and PI296341-FR resequencing information, the molecular marker Hf1-Indel related to hardness of the watermelon flesh is a closely interlocked molecular marker Hf1-Indel which is developed by designing a marker according to sites with alignment gaps or missing, and finely positioning hard flesh genes of watermelons by recombinant inbred line offspring target groups after hybridization of hard-flesh watermelons PI296341-FR and cultivated watermelon 97103. Experiments prove that the molecular marker Hf1-Indel can be used for preliminarily screening watermelon flesh hardness varieties, and the purpose of molecular assisted selection is achieved.
Owner:京研益农(北京)种业科技有限公司
Primers and kit for detecting molecular marker linked to major QTL for controlling corn stalk strength, detection method for detecting corn stalk strength, and applications of primers, kit and detection method
InactiveCN109295248AEasy to operateThe result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates to primers and a kit for detecting a molecular marker linked to major QTL for controlling corn stalk strength, a detection method for detecting corn stalk strength, and applications of the primers, the kit and the detection method, and belongs to the technical field of corn genetic breeding and molecular biology. According to the present invention, a recombinant selfing linepopulation containing 241 families is constructed through Zheng 58*D863F, and genetic linkage map analysis is performed, such that four QTL for controlling corn stalk strength are detected, wherein the high stalk strength major QTL qRPR1.07 is identified simultaneously at the position 1.07 of the chromosome 1 of the corn from Hainan Ledong and Henan Yuanyang Demonstration Base, and is positioned between two SSR markers bnlg1556 and umc2232 so as to explain nearly 20% of genetic variation; and the molecular marker linked to the major QTL for controlling corn stalk strength can directionally andprecisely screen corn materials with high stalk strength at the early stage of growth so as to save the breeding cost and the breeding time, and is used for lodging-resistant breeding of corn.
Owner:河南省农业科学院作物设计中心
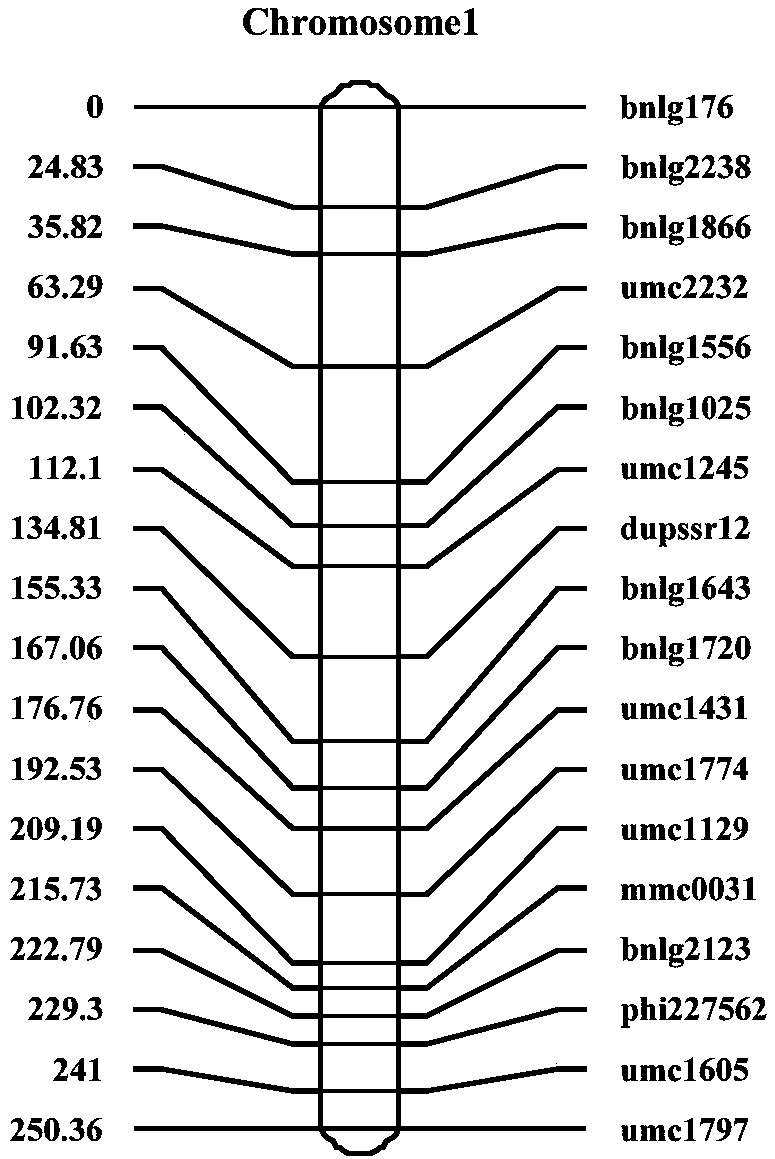
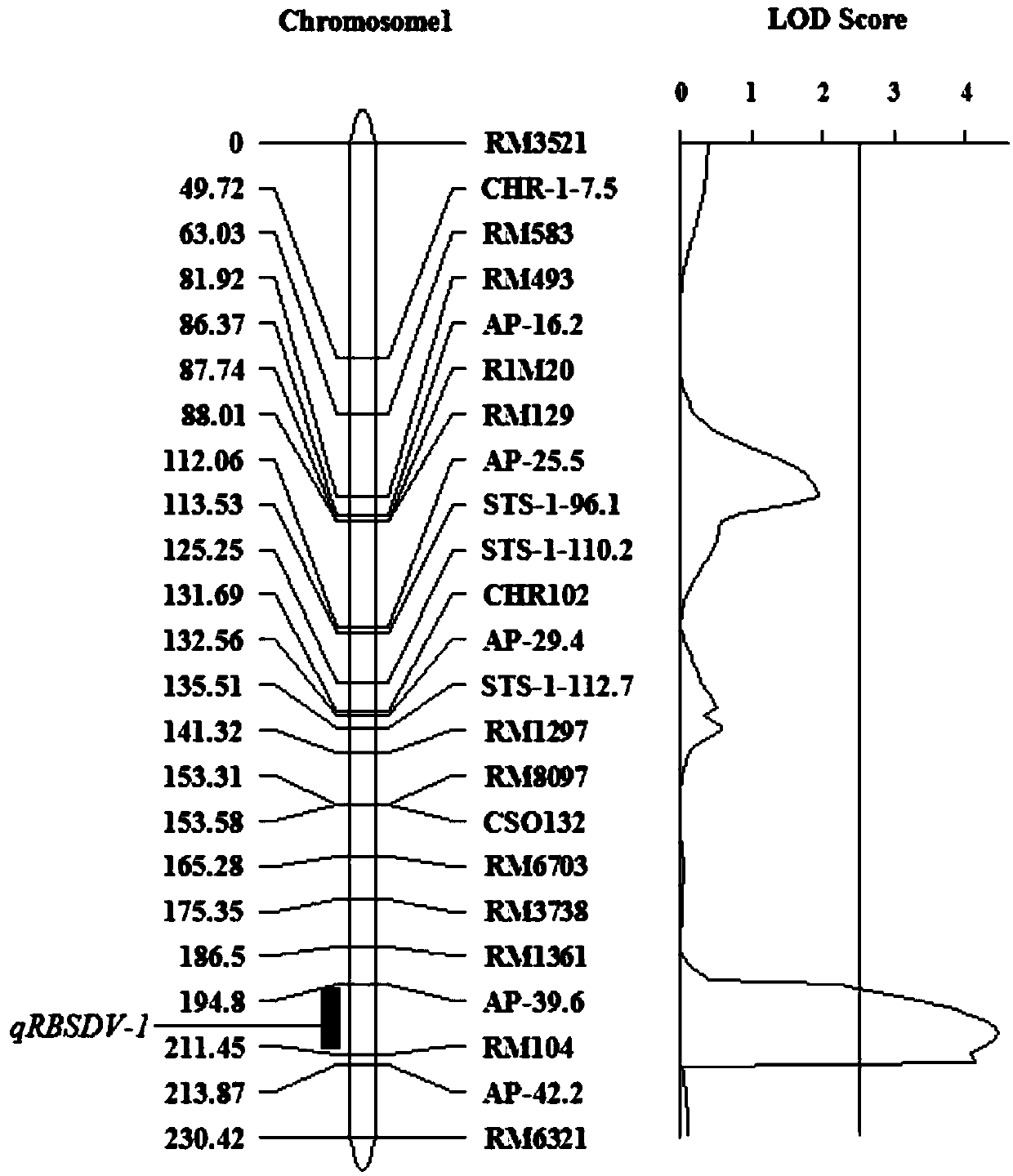
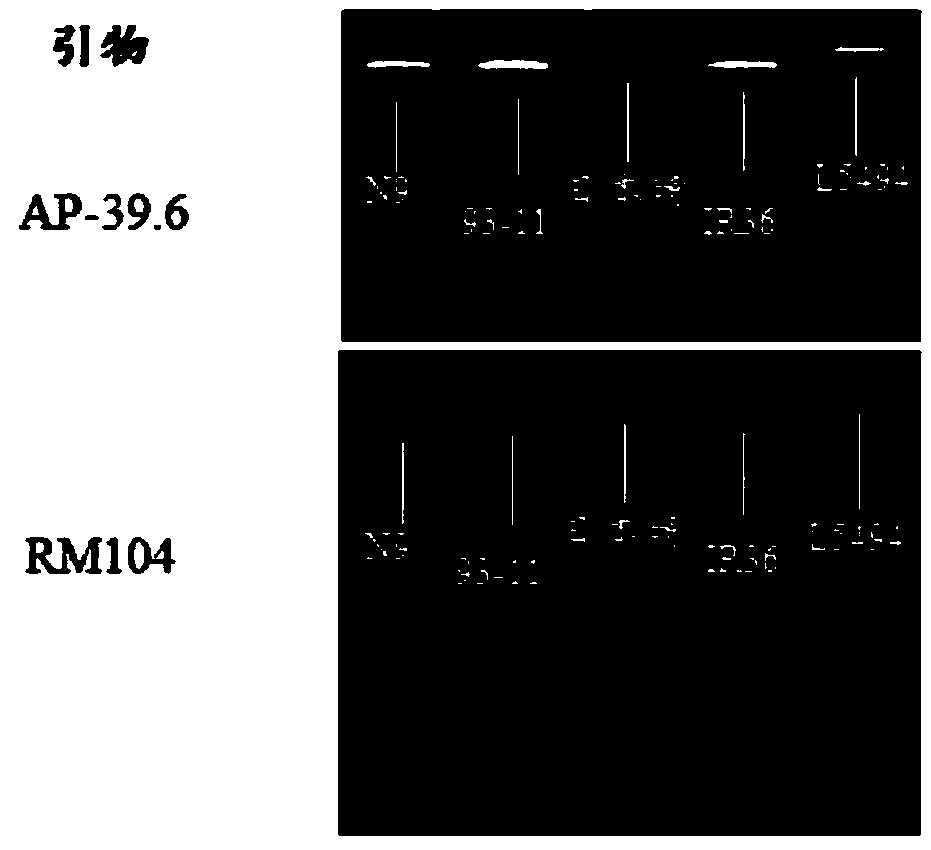
Rice variety IR36 black-streaked dwarf virus resistance site qRBSDV-1 and molecular marking method and application thereof
InactiveCN109652583AImprove selection efficiencyThe location of the resistance gene locus is clearly definedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRice black-streaked dwarf virusMolecular marker
The invention relates to a rice variety IR36 black-streaked dwarf virus resistance site qRBSDV-1 and a molecular marking method and application thereof. According to the invention, a recombinant inbred line population constructed by crossing a rice black-streaked dwarf virus resistance variety IR36 and a black-streaked dwarf virus susceptible variety L5494 is taken as a positioning population, andthe black-streaked dwarf virus resistance identification is carried out by a field natural identification method, a resistance gene site, named qRBSDV-1, from a black-streaked dwarf virus resistancevariety IR36 is obtained, located between the markers AP-39.6 and RM104. The method verifies qRBSDV-1 by performing molecular detection and identification of the incidence of black-streaked dwarf virus by using a substitution line (No. N9) containing 93-11 introduced fragments only in the chromosome segment where qRBSDV-1 is located and parents in a Japanese sunny background. According to the invention, the resistance of the plant to the rice black-streaked dwarf virus can be predicted by detecting the bands at the molecular markers of AP-39.6 and RM104, and the breeding efficiency of the ricevariety resistant to the black-streaked dwarf virus is improved.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Protein, gene and function fragment involved in palmitic acid synthesis and application thereof
InactiveCN101948517AImprove qualityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAgricultural scienceLevel of detail
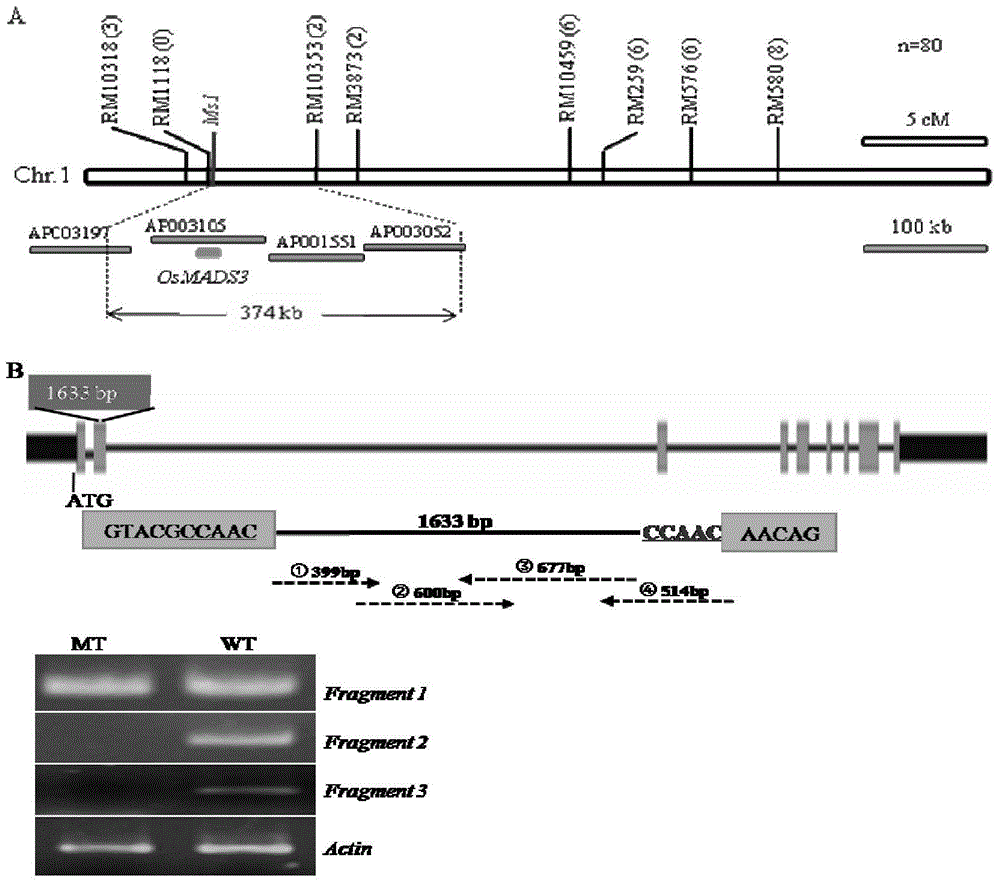
The invention discloses a protein, a gene and a function fragment involved in palmitic acid synthesis and application thereof. The invention provides a protein composed of amino acid sequences shown by a sequence 6, a sequence 4 or a sequence 2 in a sequence table, a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) molecule shown by a sequence 5, a sequence 3 or a sequence 1 in the sequence table, and a DNA fragment shown by a sequence 7. In the invention, a recombinant inbred strain colony is constructed by utilizing a common material B73 and a high oil system By 804, a major QTL-Pa 19 for controlling corn oil palmitic acid is positioned on a ninth chromosome 9.02 Bin, and the LOD (Level of Detail) of the major QTL-Pa can reach 27, and can be used for interpreting 42% of genetic variation. By means of the method of based cloning, the invention accurately positions the major QTL-Pa for controlling the palmitic acid content of corn kernels and the proportion of kernel saturated / unsaturated fatty acid in Beijing high oil, clones the function gene of QTL-Pa 19, probes the functional sites thereof, develops the functional markers, and has great value for improving the quality of corn kernels.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
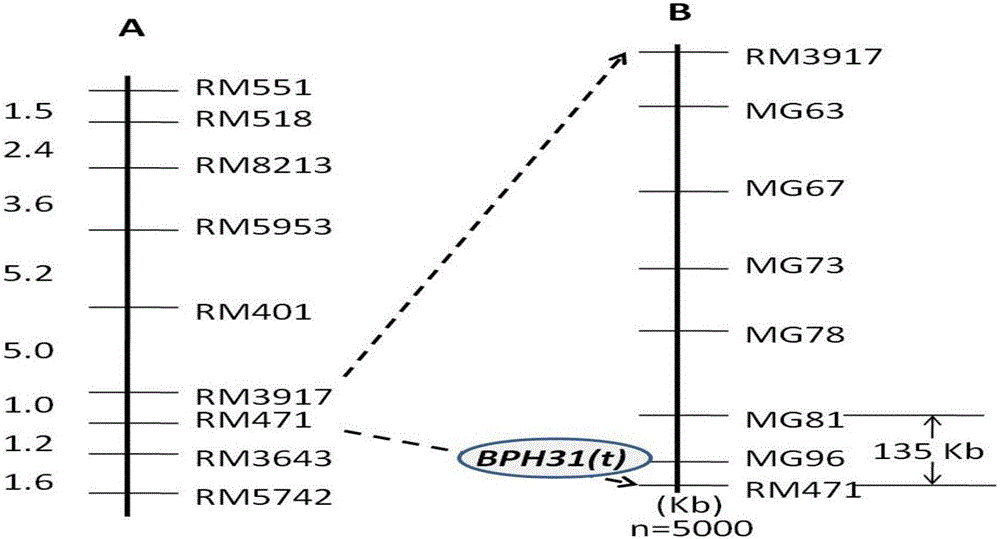
Molecular marker of rice brown-plant-hopper-resistant gene Bph31 (t) and application of molecular marker
InactiveCN106434948AIncrease resistance levelTimely crossbreedingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceResistant genes
The invention discloses a molecular marker of a rice brown-plant-hopper-resistant gene Bph31 (t) and application of the molecular marker. Varieties K41 with high brown-plant-hopper resistance and varieties Gui1025 with high brown-plant-hopper sensitivity are hybridized to obtain F2:3 family population and recombinant selfing line population by the aid of heredity linkage analysis, the rice brown-plant-hopper-resistant gene Bph31 (t) on a fourth chromosome of rice is precisely positioned and is positioned in an interval between molecular markers MG81 and RM471, and the individual resistant plant selection efficiency of a single molecular marker MG96 in the interval is 97% approximately. The molecular marker which is in linkage with the gene further comprises the molecular markers MG81 and RM471. The molecular marker and the application have the advantages that the molecular marker can be used for detecting the insect-resistant varieties K41 and derived varieties (lines) of the insect-resistant varieties K41 to determine whether the insect-resistant varieties K41 and the derived varieties (lines) contain the gene or not, and accordingly brown-plant-hopper-resistant rice varieties with the brown-plant-hopper-resistant gene Bph31 (t) can be screened.
Owner:南宁维尔凯生物科技有限公司
Watermelon flesh harness-related molecular marker Hf2-Indel and application thereof
ActiveCN106011284ATo achieve the purpose of assisted breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementRe sequencingIndel
The invention relates to a watermelon flesh hardness-related molecular marker Hf2-Indel and application thereof. A marker is designed on the basis of a whole-genome sequence of 97103 and re-sequencing information of PI296341-FR according to an insertion / deletion locus, and the closely linked molecular marker Hf2-Indel is developed by accurately mapping hard flesh genes by virtue of a recombinant inbred line progeny mapping population obtained after hybridization of wild hard-flesh watermelons PI296341-FR and cultivated watermelons 97103. Experiments show that the molecular marker Hf2-Indel can be used for preliminarily screening watermelon flesh hardness varieties to fulfill the aim of molecular assisted selection.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES +1
Molecular marker of rice long and slender grain gene, and application thereof
PendingCN110684858AImprove breeding efficiencySave time and costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyCandidate Gene Association Study
The invention discloses a molecular marker of rice long and slender grain gene as well as application thereof. The molecular marker of the rice long and slender grain gene is prepared by the followingsteps: carrying out hybridization by taking a long and slender grain variety, namely Tai-feng B, as a female parent and a short grain variety, namely Te-san-ai No. 2, as a male parent so as to obtainF1; allowing bagged self-pollination of the F1 so as to obtain F2 seeds; planting F2 population, and adopting a single seed descend method so as to obtain recombinant inbred populations composed of 170 families; performing investigation and statistics on grain lengths, grain widths and length-width ratio phenotypes of segregated populations so as to select characteristic plants containing SG7 from the recombinant inbred populations; and then, developing a molecular marker SG7-18 on basis of SG7 candidate genes according to sequence differences of 18 bp insertion / deletion of LOC_Os07g41200 gene between the long and slender grain variety Tai-feng B and the short grain variety Te-san-ai No. 2, thereby obtaining the molecular marker SG7-18 of the rice long and slender grain gene. The molecular marker of the rice long and slender grain gene is used for detecting SG7 genotype in rice varieties; and the rice long and slender grain gene is further used for marking and cultivating long-and-slender-grain-type rice varieties.
Owner:RICE RES INST GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
SNP molecular marker derived from single-boll weight major gene of Xinluzao 24
ActiveCN110607382AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceGossypium hirsutum
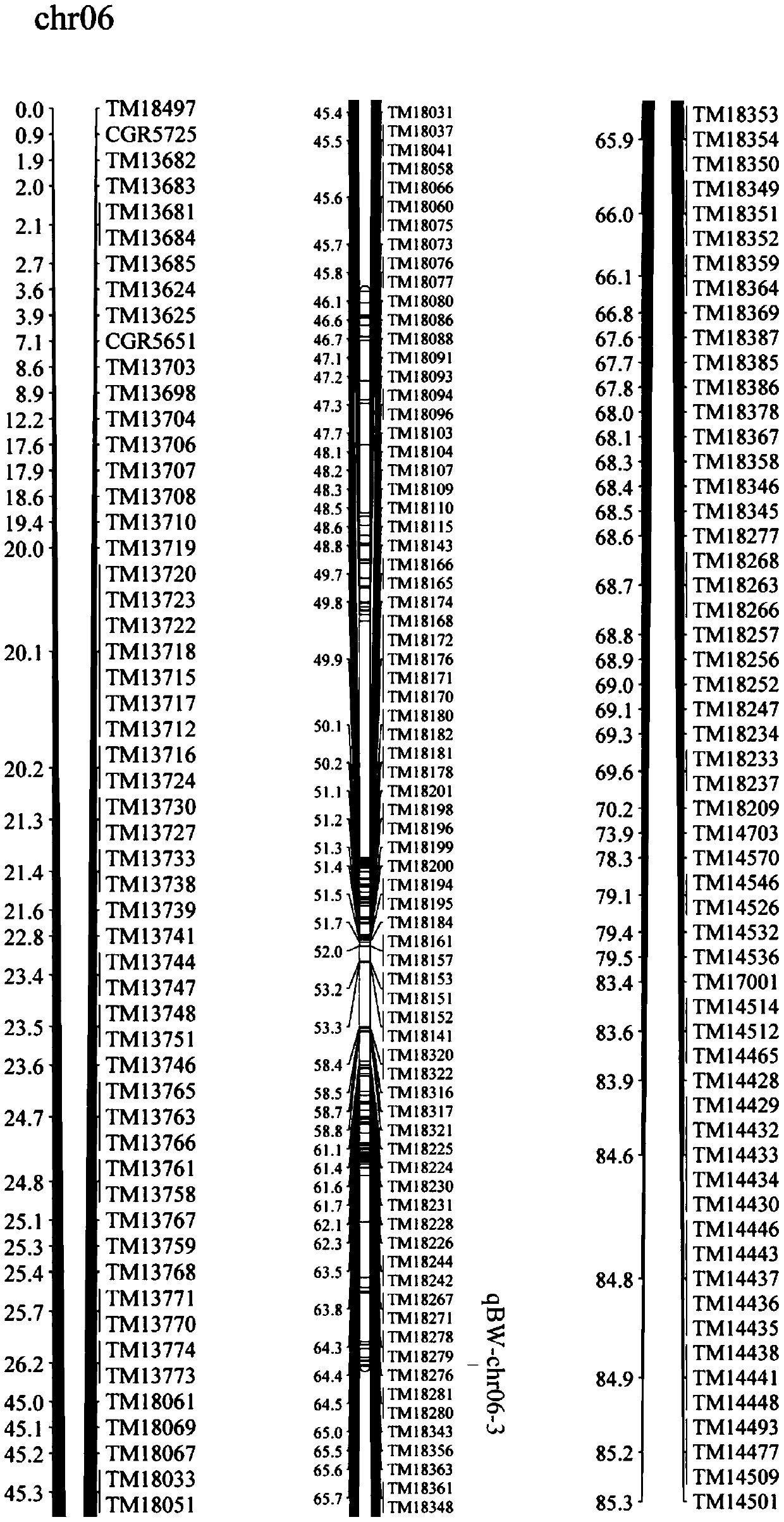
The invention discloses a molecular marker closely linked with major QTL sites qBW-chr04-2, qBW-chr05-5, qBW-chr06-3, qBW-chr21-4 and qBW-chr24-1 of the single boll weight of upland cotton. Accordingto the method, a upland cotton intraspecific recombinant inbred line group constructed by hybridizing Shandong cotton research 28*Xinluozao 24 is utilized, and phenotypic evaluation and identificationare carried out on the cotton yield main constituent factor-the single boll weight of the recombinant inbred line group in a multi-year multi-point environment of a northwest inland cotton area and aYellow River basin cotton area. The genotyping and genetic linkage map construction are carried out on the population by utilizing a cotton SNP80K chip. The major sites influencing the single boll weight of cotton and SNP molecular markers closely linked with the sites are obtained through QTL positioning. In the cotton breeding process, the molecular markers are used for auxiliary selection, thesingle boll weight of a new upland cotton variety can be effectively improved in a targeted mode, and therefore the high-yield and high-quality breeding efficiency is improved.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Identifying and utilizing method of rice wide-compatibility recessive male nuclear sterile line
InactiveCN105986019ASamsara chooses intermediate materialsEliminate the cumbersomeness of manual castrationMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyNormal growth
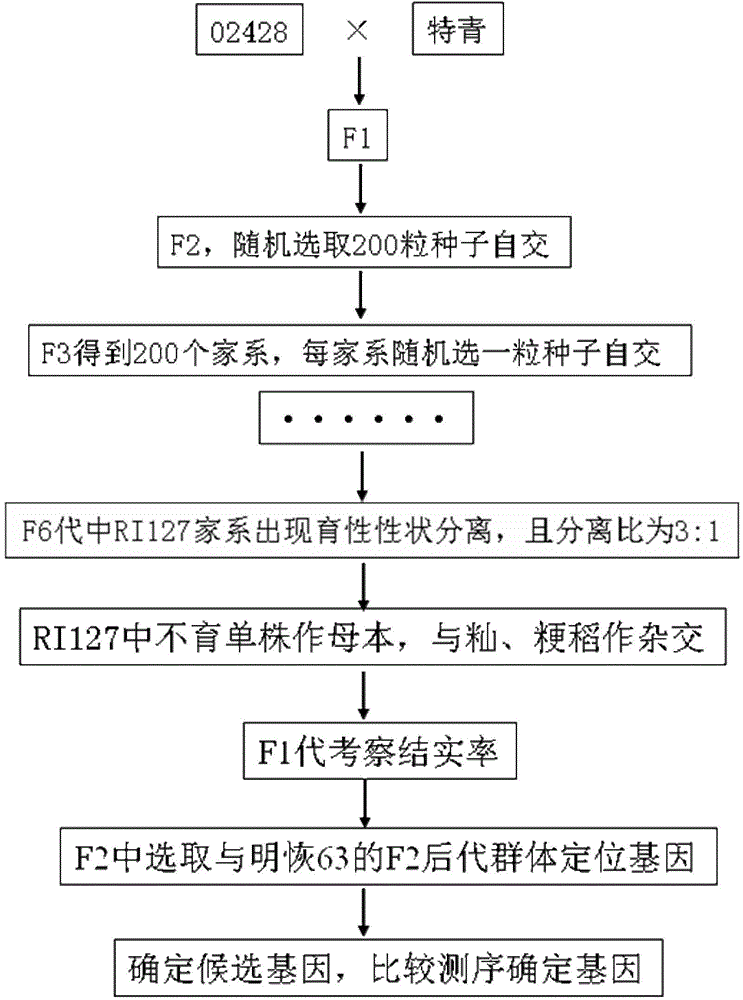
The invention belongs to the field of molecular breeding of crops, and relates to an identifying and utilizing method of a rice wide-compatibility recessive male nuclear sterile line. Nonglutinous rice 'Teqing' and the wide-compatibility variety '02428' are adopted for constructing a recombinant inbred line (RIL), a selfing line with the fertility feature is selected, a novel sterile line RI127S is cultivated and screened, and the sterile line can be used as an intermediate material for rice rotational breeding. The identifying and utilizing method has the advantages that (1) the sterility of the male sterile line is controlled by recessive genes, and is not influenced by length of illumination and temperature under the normal growth condition, and the male sterile line is an ideal recurrent selection intermediate material for rice; (2) the sterile line RI127S contains wide-compatibility genes, the genome of the sterile line RI127S is a mixture of nonglutinous rice and japonica rice varieties, after hybridization with nonglutinous rice and japonica rice, the hybridization seeds are fertile, the F1 fruitage rate of nonglutinous rice is 85%, and the F1 fruitage rate of japonica rice is 80%; (3) the inbred line RI127 has the high yield property intrinsically, and can be taken as a parent of the good stock, and when the RI127 is taken as the sterile line, the process of artificial emasculation for hybridization can be saved.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for constructing QTL positioned new-group-linkage F2 group
InactiveCN105706909AThe analysis result is accurateSolve the inability to carry out cooperative experimentsPlant genotype modificationBiologyLinkage concept
The invention discloses a method for constructing a QTL positioned new-group-linkage F2 group.The method comprises the steps of selecting three selfing lines which are from different sources and have great genetic background differences, utilizing the three selfing lines for hybridization to obtain three hybrids, adopting a single-grain genetic method for performing selfing on the three hybrids for seven generations or more till all the lines in the group are purified, and selecting and breeding three recombination selfing lines; constructing a linkage F2 group, performing recombination on every two selfing lines, and performing hybridization on every two extracted lines randomly to obtain n combinations; finally, obtaining three F2 groups, and forming a linkage F2 group, wherein the number of the hybridization combinations of the obtained linkage F2 group is 3n.According to the constructed linkage F2 group, QTL positioning is researched, the advantages of a temporary group and the advantages of a permanent group are synthesized, meanwhile, the defect existing in QTL positioning of the permanent F2 group is overcome, the accuracy of QTL positioning tests is improved, and the group is novel and can precisely position QTL and promote forward development of hybrid advantage theory research.
Owner:FOOD CROPS RES INST YUNNAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Molecular marker closely linked with bacterial wilt resistance of cultivated peanuts and application of molecular marker
ActiveCN113564161AImprove stabilityHigh contribution rateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyMolecular breeding
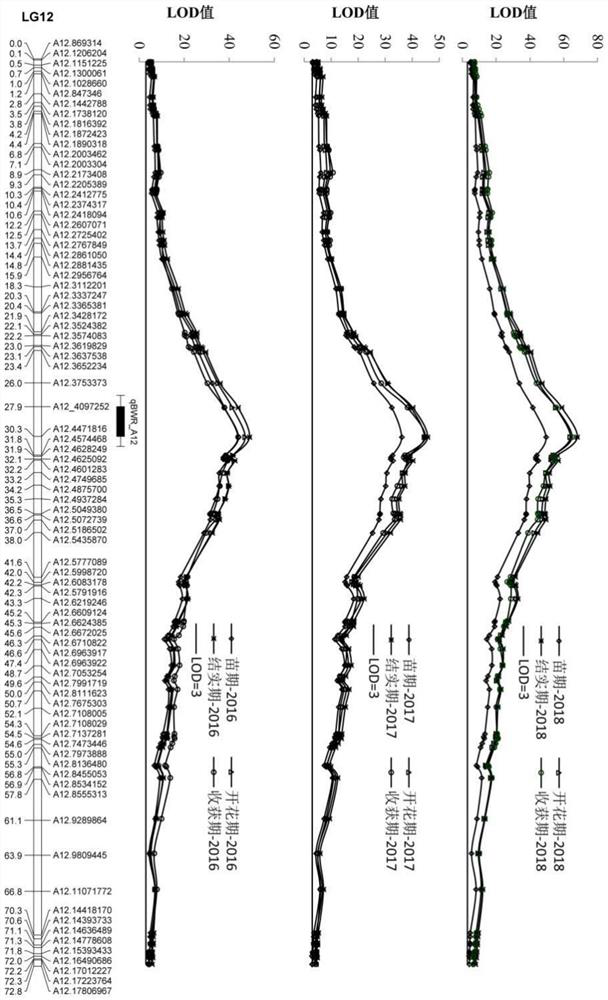
The invention relates to a molecular marker closely linked with bacterial wilt resistance of cultivated peanuts and application of the molecular marker. A recombinant inbred line group taking far-hybrid 9102 and wt09-0023 as parents is utilized to construct a high-density linkage map, and a resistance major QTL (qBWR-A12) which can be repeated in a plurality of growth periods and for many years is positioned. KASP primers are developed according to SNP information of two wings of the major QTL, an SNP molecular marker capable of being applied to far-hybrid 9102 blood-related materials and non-blood-related materials is obtained, the SNP marker is located at the 4097252bp position of the 12th chromosome, and linkage between the marker developed based on the QTL and bacterial wilt resistance is tighter. According to the molecular marker, the step of bacterial wilt inoculation identification or disease nursery identification is omitted, the bacterial wilt resistance information of the material can be rapidly and accurately obtained only by detecting the SNP genotype, and the molecular marker can be applied to molecular breeding of peanut bacterial wilt resistance.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
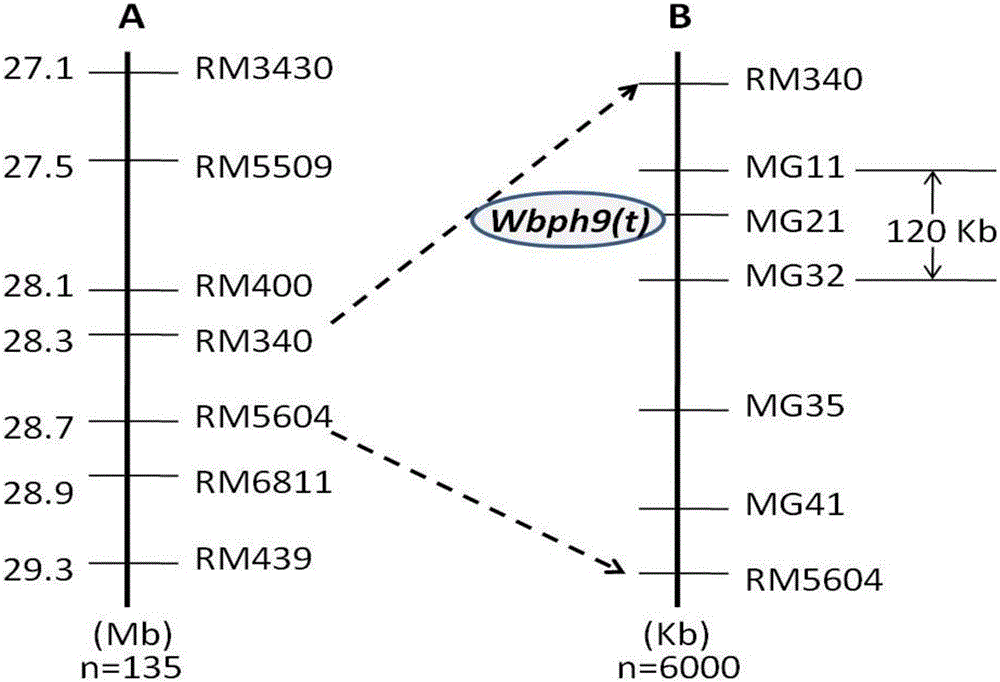
New gene Wbph 9 (t) for resisting rice sogatella furcifera, molecular marking method thereof and application
ActiveCN106480066AIncrease resistance levelEfficient identificationPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyAntigen
The invention discloses a molecular marking method for tight interlocking of new gene Wbph 9 (t) for resisting rice sogatella furcifera, and application thereof. Through genetic linkage analysis, a variety F41 of the high resistant sogatella furcifera and a variety laurel 1025 of high sensitive sogatella furcifera to obtain F2 which consists of 3 family groups and recombinant inbred line groups; a rice resistant sogatella furcifera gene Wbph 9 (t) on the #6 chromosome of the rice is accurately positioned; the gene is positioned in a 120kb zone between the molecular marker MG11 and MG 32; the selecting efficiency of 1 molecular market MG21 of the zone for the antigen single plant is about 98%; the molecular market tightly interlocked by Wbph 9 (t) is applied to detect if the insect resisting variety K41 and its derivative variety (series) contains the gene; thus new material for resisting sogatella furcifera can be selected. The invention is applied to the molecular marking of the rice sogatella furcifera resistance so as to assist the seed breeding and pyramiding breeding, so as to perform the gene type selection on the low generation of breeding material in seedling period; thus the breeding efficiency is improved, and the breeding progress is accelerated.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI SCI
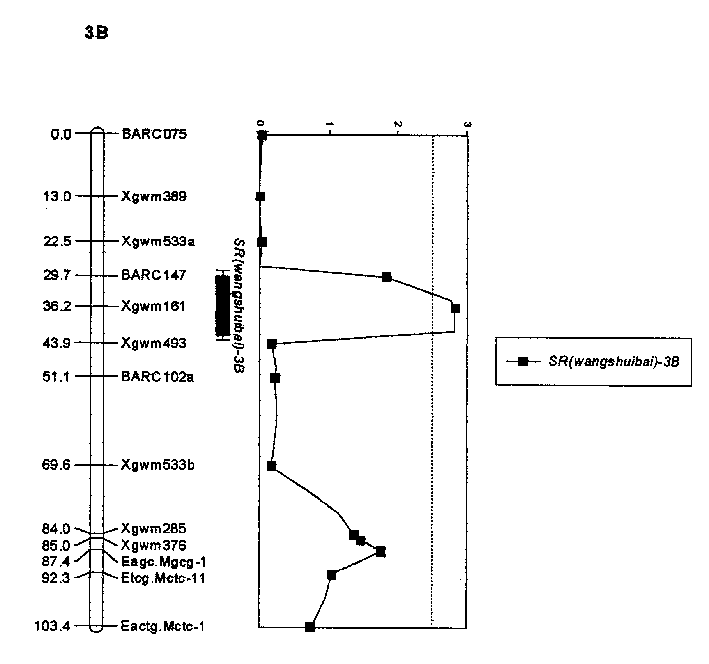
Molecular label closely linked with wangshuibai speces and series wheat tibberellin resistance main efect QTL and its application
InactiveCN1202265CReduce the waste of manpower and material resourcesImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBiotechnologyGenotype
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Technical method of creating parent of polygene type colony heterosis utilization
InactiveCN103155853ASolve the problem of difficult parental selectionWith a clear purposePlant genotype modificationMarker-assisted selectionHeterosis
Owner:隆平优粮(天津)有限公司
Crossbreeding method for pyramiding cotton superior traits
ActiveCN109997682AShorten the improvement periodExpand sourcePlant genotype modificationAgricultural sciencePhenotypic trait
The invention relates to the field of cotton variety breeding, in particular to a crossbreeding method for pyramiding cotton superior traits. The method includes steps: taking a cotton variety authorized in Shandong Province which is a main cotton production region in the Yellow River basin as a female parent, taking two lines with fiber superior traits as male parents, and performing crossbreeding of the female parent with the male parents respectively to obtain a generation F1, wherein at least one of the male parents belongs to chromosome segment substitution lines from gossypium hirsutum and gossypium barbadense or recombinant inbred lines thereof; collecting pollens of stamens of generation F1 plants, mixing, performing pollination backcrossing on the generation F1 plants, and harvesting to obtain a double-cross generation F2; subjecting the generation F2 to continuous selfing for 3-10 times, and screening to obtain cotton superior traits pyramided line. By means of specific multi-parent double-cross pyramiding breeding, the character of high yield of the female parent is kept in the final generation, combining abilities of varieties are explored, pyramiding of superior traitsand certain lines is realized, a superior variety improving term is shortened, and genetic improvement efficiency is improved.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for culturing variety (line) with high phosphorus efficiency by using soybean root configuration near-isogenic line
PendingCN108308018AFast transferEfficiently obtainedMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationTransgenic technologyPhenotype
The invention discloses a method for culturing a variety (line) with high phosphorus efficiency by using a soybean root configuration near-isogenic line, and belongs to the field of genetic improvement and utilization of phosphorus nutrition of crops. The method comprises main steps of building recombination inbred lines (RILs) of traits of phosphorus efficiency related root systems, building near-isogenic lines (NILs) of efficient root configurations, hybridizing, transferring and screening high-phosphorus-efficiency quantitative trait locuses (QTLs), and the like. The method disclosed by theinvention does not need to depend on a gene cloning and transgenosis technology with high time consumption and high cost, avoids phenomena of difficulty in phenotypic selection, linkage drag and thelike which are caused by conventional hybridization and breeding, realizes fast integration of efficient, high-yield and high-quality genes of the phosphorus nutrition, can obtain a soybean variety (line) with good root configurations and high phosphorus efficiency efficiently and accurately, and greatly improves the breeding efficiency of the variety with high phosphorus efficiency.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Molecular marker closely linked to rice large-grain gene gs2 and its application
ActiveCN103409418BInhibition of grain width effectLittle or no grain width effectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceMolecular marker
The invention provides molecular markers in close linkage with a large grain gene GS2 of rice and an application of the molecular markers. Through a recombinant inbred line (RIL) advanced grain shape segregation population, the grain shape major gene GS2 is finely located on a second chromosome and within a range of 33.2kb from GS2-6 to GS2-8, so as to obtain a series of molecular markers in close linkage with GS2. The molecular markers include a common data base marker RM3212 and 22 self-developed InDel markers (from GS2-1 to GS2-22). The molecular markers can be used for effectively detecting the GS2 genetic locus and further improving the breeding efficiency of large grain varieties (or parents).
Owner:HUNAN HYBRID RICE RES CENT
Molecular markers closely linked to major gene loci for moisture resistance traits in sesame and their applications
ActiveCN103525919BChoose a clear goalLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationSesamumEarly prediction
The invention relates to a molecular marker tightly linked with a main effective genetic locus embodying sesame dampness resistance and application thereof. The main effective genetic locus qWHCHL09 is located on the 9th linkage group, and the molecular marker tightly linked with the main effective genetic locus is ZM428 whose sequences are as follows: ZM428F: AGGATGATGATGTGATGAGAG (5'-3') and ZM428R: CTGCTACTCCTTTTGTCTCTG (5'-3'). The molecular marker is obtained by hybridizing sesame 13 in sesame dampness-resistant varieties and a sensitive germplasm Yiyangbai to obtain F6-generation segregation population, namely a recombinant inbred line (RIL) population, and performing molecular genetic linkage analysis on the F6-generation segregation population. The molecular marker tightly linked with the main effective genetic locus embodying the sesame dampness resistance is applied to breeding of the sesame dampness-resistant varieties and screening of dampness-resistant traits of the sesame germplasm as well as early prediction; the auxiliary dampness resistance choosing target is clear; and the cost is relatively low.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for quickly selecting paddy rice with sheath blight resistance and qSBRLEYD2A genes
InactiveCN108070670AMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationOryzaAgricultural science
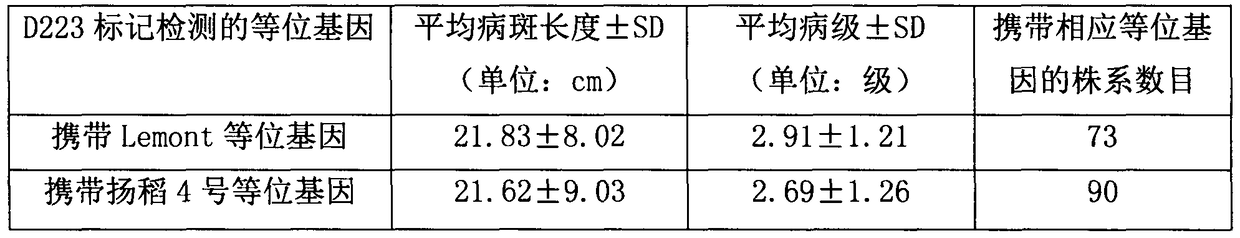
The invention discloses a method for quickly selecting paddy rice with sheath blight resistance and qSBRLEYD2A genes. The method includes carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification ondifferent strains in segregation population of recombinant inbred lines by the aid of D223 labels; selecting strains with banding patterns consistent with No.4 Yangdao which is a parent. Lemont and the No.4 Yangdao are assembled to obtain the segregation population of the recombinant inbred lines. The selected strains are strains with qSBRLEYD2A alleles with sheath blight resistance. Compared withthe traditional field inoculation identification methods, the method has the advantages that the method is simple, convenient and speedy, and stable paddy rice materials with sheath blight resistancecan be selected without inoculation identification; the method is high in selection accuracy as compared with field inoculation methods, and the breeding efficiency can be greatly improved.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
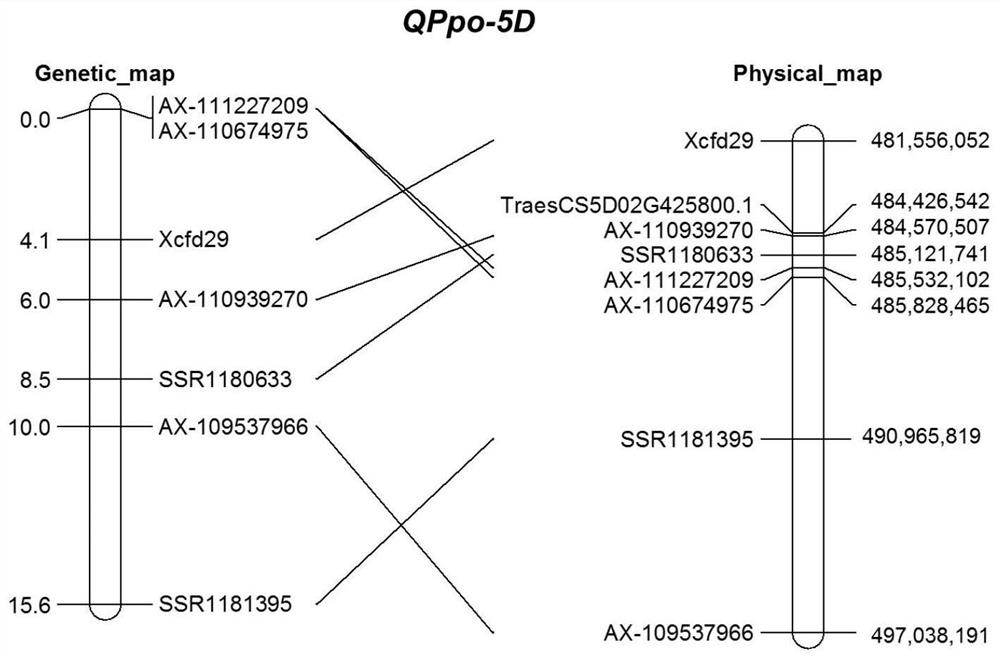
Molecular marker separated from low-polyphenol-oxidase-activity gene QPpo-5D of wheat
ActiveCN112048569ASpeed up the breeding processOvercome the shortcomings of conventional breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyGermplasm
The invention discloses a molecular marker separated from a low-polyphenol-oxidase-activity gene QPpo-5D of wheat and belongs to the technical field of agrobiology. A recombinant inbred line RIL colony is constructed through hybridizing wheat germ plasm with extremely low polyphenol oxidase activity and wheat germ plasm Yangmai with high PPO activity, and a resistant gene is located to a stained 5DL5-0.76-1.00 section through a wheat molecular marker technology. In order to explore novel molecular markers of the low-PPO-activity gene QPpo-5D, a KASP marker AX-110939270 is developed by using anSNP marker conversion method. The marker, as a novel molecular marker of the low-PPO-activity gene QPpo-5D, can be better applied to assisted selecting of low-PPO-activity varieties of the wheat, sothat shortages of conventional breeding are overcome, a selecting method is simplified, the efficiency of breeding is increased, and thus, a breeding progress of high-whiteness and high-quality varieties is accelerated.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Method for polymerizing three banded sclerotial blight resistance genes of Lemont and YangDao No.4
The invention discloses a method for polymerizing three banded sclerotial blight resistance genes of Lemont and YangDao No.4. The method comprises the following steps: respectively carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on different strains in an RIL (Recombinant Inbred Line) segregation population formed by the Lemont and the YangDao No.4 by utilizing three markers of D715, D804 and D1133, naming a banding pattern of the YangDao No.4 amplified by the D715 marker as A and the banding pattern of the Lemont amplified by the D715 marker as D, naming the banding pattern of theYangDao No.4 amplified by the D804 marker as B and the banding pattern of the Lemont amplified by the D804 marker as E, and naming the banding pattern of the Lemont amplified by the D1133 marker as Cand the banding pattern of the YangDao No.4 amplified by the D1133 marker as F; selecting the strains with more banding patterns of A, B and C as banded sclerotial blight-resistant strains, and selecting the strains with more banding patterns of D, E and F as banded sclerotial blight-sensitive strains. According to the method disclosed by the invention, banded sclerotial blight-resistant rice materials can be selected by polymerizing three banded sclerotial blight resistance genes of rice at the same time, so that the breeding efficiency can be greatly increased.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
A SNP Molecular Marker of Jute Anthracnose Resistance Gene Segment
The invention belongs to the technical field of breeding of corchorus spp. and relates to an SNP molecular marker in a corchorus spp. anthracnose resistant gene segment. The SNP molecular marker is realized by the following steps: determining the genetype by extraction of a genome DNA of a corchorus spp. recombinant inbred line (RIL) population, digestion, product purification sequencing, and SNP screening and analysis; identifying the resistant character of the corchorus spp. recombinant inbred line (RIL) population by adopting a single factor randomized block design; and performing genetic linkage map establishment and QTL (quantitative trait loci) positioning on the recombinant inbred line population, wherein the QTL positioning result shows that the phenotypic variation explained by QTL qAR.N10 is 20.13%, the QTL is a major QTL, the QTL segment comprises 26 SNP molecular markers, and the nucleotide sequences and variation sites of the 26 SNP molecular markers are as shown in SEQ ID NO.1-26. The invention provides a new molecular marker for resistance breeding of corchorus spp. anthracnose, which can be used for assisted selection of molecular markers of corchorus spp. anthracnose.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Molecular marker linked with rice cold-tolerant gene qSF12 and application of molecular marker
ActiveCN111635958AStrong reliabilityStrong cold tolerance at booting stageMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyMolecular breeding
The invention discloses a molecular marker linked with a rice cold-tolerant gene qSF12 and application of the molecular marker in identification of rice cold tolerance. According to the invention, a Jileng-1 / Miyang 23 recombinant inbred line group (RIL) is utilized, the invention successfully positions a gene locus qSF12 related to the cold tolerance of rice in the booting stage on the twelfth chromosome of the rice, a cold-tolerant favorable allele of the qSF12 comes from a cold-tolerant parent Jileng-1 and is linked with a molecular marker STS12b, a method for identifying or assisting in identifying the cold resistance of the rice in the booting stage is provided based on the molecular marker STS12b, and the method can be used for identifying and molecular breeding of cold-resistant ricevarieties in the booting stage.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com