Method for producing chlorine-based high phosphorus compound fertilizer by ammoniation method
A technology for compound fertilizers and production methods, applied in fertilizer mixtures, fertilization devices, applications, etc., can solve the problems of poor product color, increased drying load, and low particle strength, and achieve smooth and round particles, reduce drying load, and strength high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Example 1: 15-25-10 products
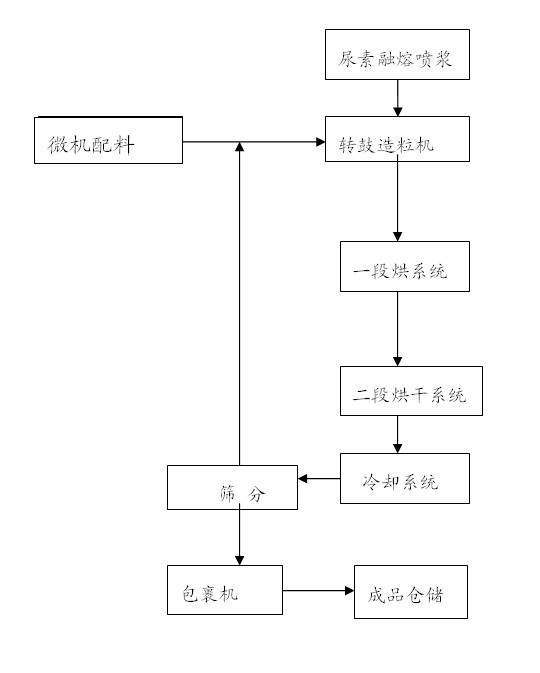
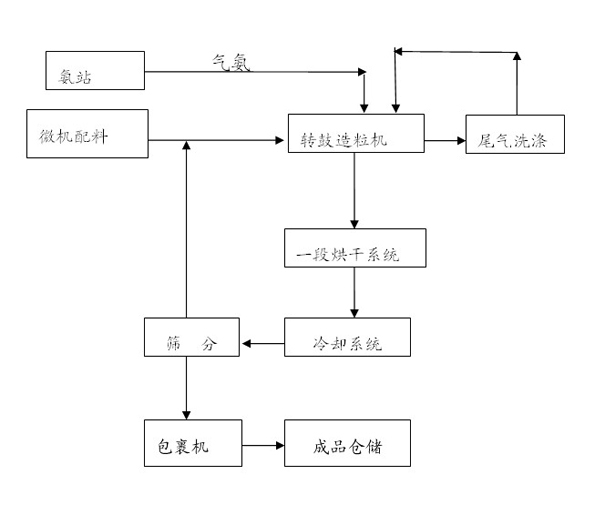
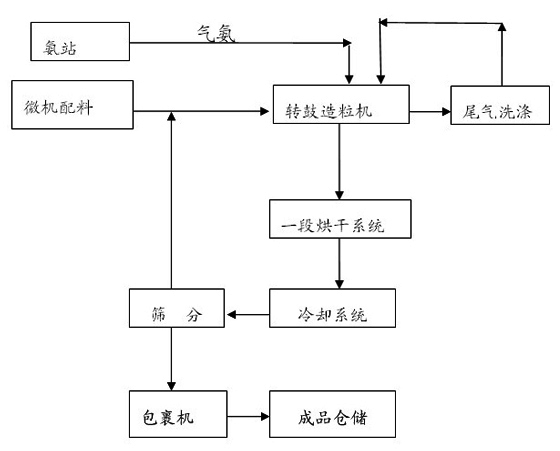
[0049] Gas ammonia (containing N 82.3%, mass percentage, the same below) 35 kg, after being metered, added to the drum granulator material layer, and at the same time, 110 kg of urea (including N46.2, added after crushing) was metered by the computer , Ammonium chloride (containing N23.5) 110 kg, powdered monoammonium phosphate (containing N 11%, P2O5 45%) 380 kg, weight superphosphate 200 kg (containing P2O5 38.5%), potassium chloride (containing K2O56 %) 180 kg, the above powdered material is mixed with gas ammonia in the granulator, and the exothermic reaction of gas ammonia and heavy superphosphate, and the neutralization heat of gas ammonia and monoammonium phosphate are used for heating during the granulation process At the same time, increase the solubility of ammonium phosphate to meet the amount of liquid phase required for granulation, and replace steam with washing water from the granulation tail gas as the amount of liquid phase r...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2: 13-22-10 products
[0051] 30 kg of gaseous ammonia (containing N 82.3%, mass percentage, the same below), after being metered, is added to the drum granulator material layer, and 290 kg of ammonium chloride (including N23.5) is added to the powder 320 kilograms of monoammonium phosphate (containing 11% N, 45% P2O5), 200 kilograms of superphosphate (containing 38.5% P2O5), and 180 kilograms of potassium chloride (containing K2O56%). Mixing in the granulator, the exothermic reaction of gas ammonia and double superphosphate, and the neutralization heat of gas ammonia and monoammonium phosphate reaction are used to heat the material during the granulation process, and the solubility of ammonium phosphate is improved to meet the granulation The required liquid phase quantity, and the granulation tail gas washing water is used to replace steam as the liquid phase quantity required for granulation. The temperature of the material in the drum granulator is controlled a...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3: 17-17-17 High Phosphorus Products
[0053] Ammonia gas (containing N 82.3%, mass percentage, the same below) 30 kg, after being metered, added to the drum granulator material layer, while adding urea (containing N46.2, added after crushing) 200 Kg, 90 kg of ammonium chloride (containing N23.5), 290 kg of powdered monoammonium phosphate (containing N 11%, P2O5 45%), 100 kg of superphosphate (containing P2O5 38.5%), potassium chloride (containing K2O56%) 300 kg, the above-mentioned powdery materials are mixed with gas ammonia in the granulator, and the exothermic reaction of gas ammonia and heavy superphosphate, and the neutralization heat of gas ammonia and monoammonium phosphate are fully utilized in the granulation process. Heat the material while increasing the solubility of ammonium phosphate to meet the liquid phase quantity required for granulation, and replace steam with the granulation tail gas washing water as the liquid phase quantity required for granu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com