Improved yeast strains for organic acid production
A yeast strain and organic acid technology, applied in fermentation, fungi, etc., can solve problems that have not been described
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
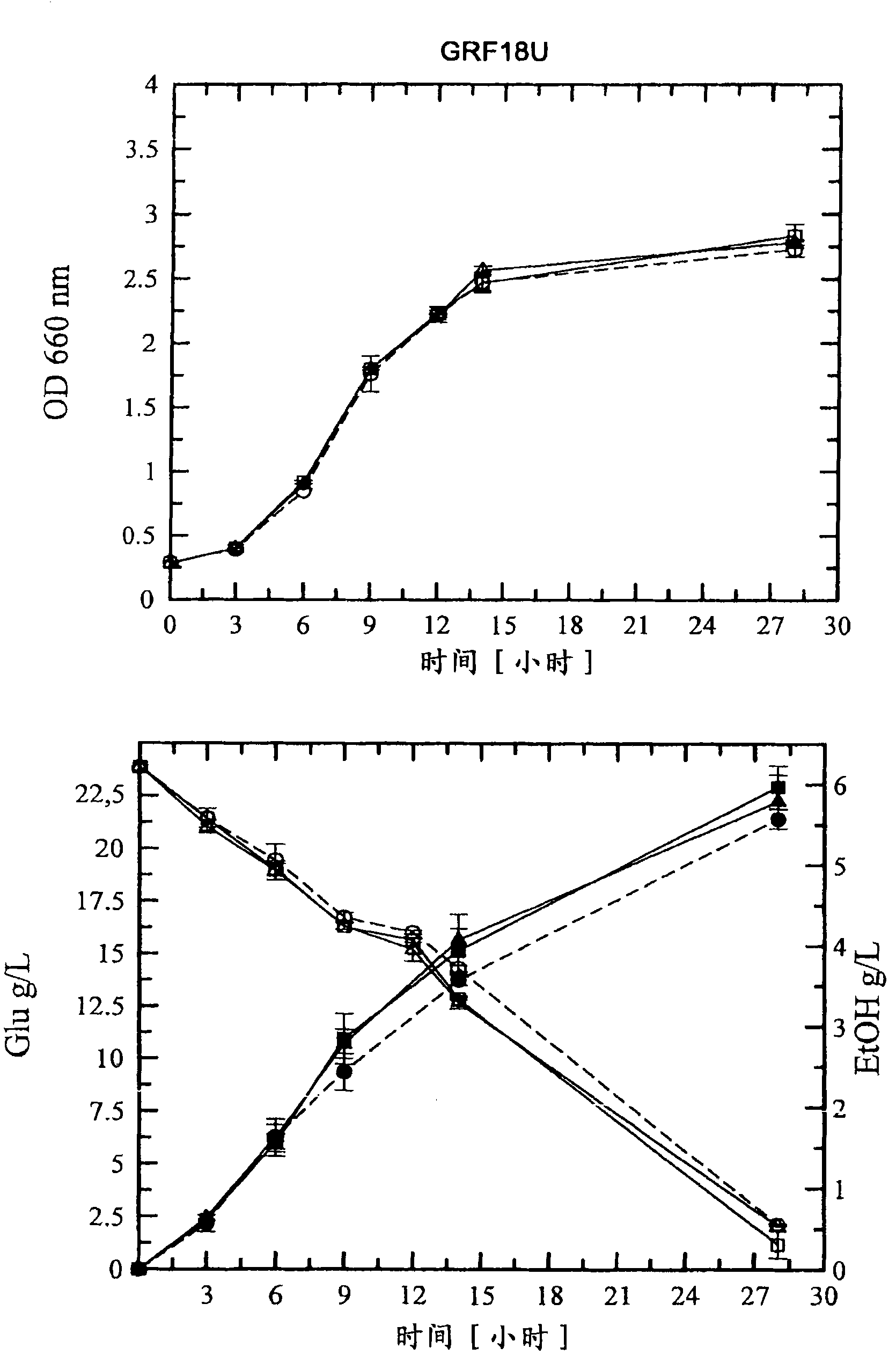
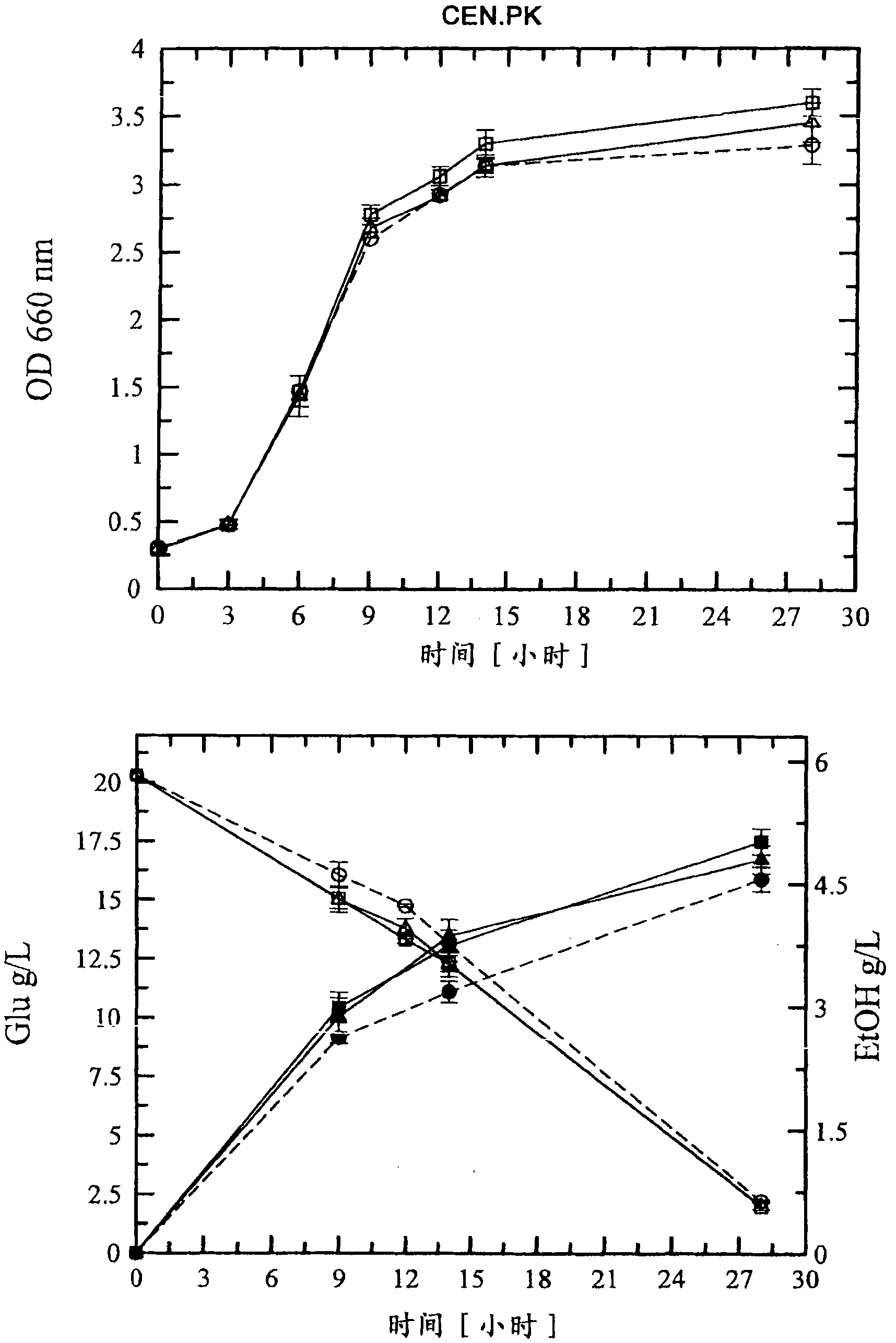
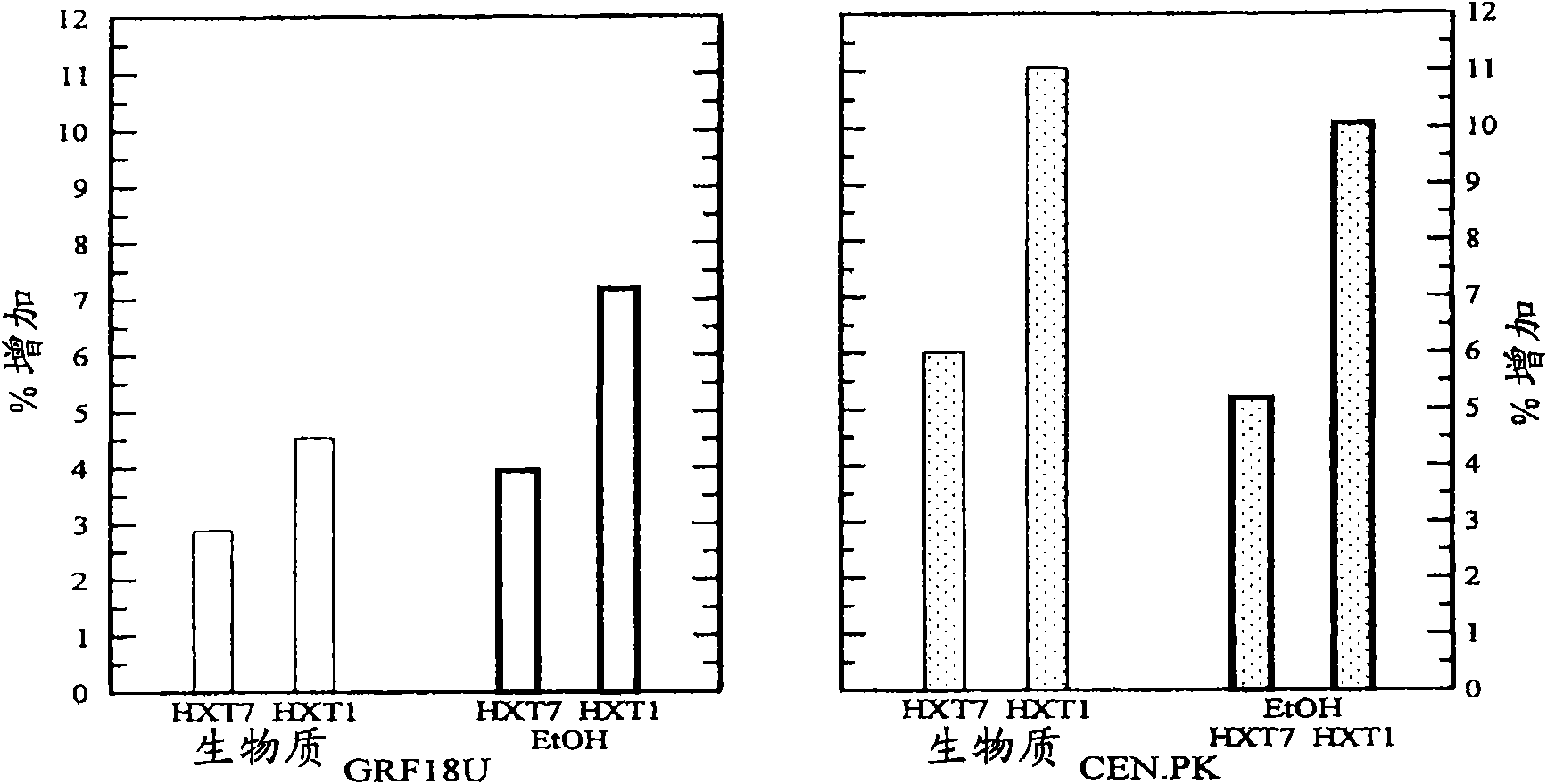
[0132] Example 1: Construction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae (GRF18U and CEN.PK) strains expressing (over)expressing HXT1 or HXT7 genes: Cell growth, glucose consumption and ethanol production of transformants and control strains.
[0133] Saccharomyces cerevisiae HXT1 and HXT7 genes were PCR amplified using genomic DNA extracted from the GRF18U strain as a template.
[0134] The oligonucleotides used for amplification were as follows:
[0135] 5'HXT1 (SEQ ID NO.: 1)
[0136] 5′-AAA ATC ATG AAT TCA ACT CCC GAT CTA-3’Tm: 58.9
[0137] 3'HXT1 (SEQ ID NO.: 2)
[0138] 5′-AGC TTG TTT AGT TTA TTT CCT GCTG AAA-3′Tm: 59.3
[0139] 5'HXT7 (SEQ ID NO.: 3)
[0140] 5′-A AAA ATG TCA CAA GAC GCT GCT ATT GCA-3′Tm: 62.4
[0141] 3'HXT7 exit (SEQ ID NO.: 4)
[0142] 5′-ATA TAT TAA AAA CGT ATT TAC TTT TCA AGT-3′Tm: 54.2
[0143] 3'HXT7 (SEQ ID NO.: 5)
[0144] 5′-AGT GTC GAC AAA TAA TTT GGT GCT GAA CAT-3′ Tm: 61.0
[0145] All amplifications use the following procedure:
[0146]
...
Embodiment 2
[0155] Example 2: Construction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae (GRF18U and CEN.PK) strains expressing heterologous LDH activity from Lactobacillus plantarum and (over)expressing HXT1 or HXT7 genes: cell growth, glucose consumption, lactic acid and ethanol production.
[0156] S. cerevisiae strains (GRF18U and CEN.PK) that had been transformed with p022HXT1 and p022HXT7 expression vectors were further transformed with a plasmid called Ycp111bTLDH. The plasmid was obtained by inserting the LDH gene under the control of the Z. bayeria TPI promoter in the basic S. cerevisiae centromeric plasmid Ycplac111 (LEU2 marker, ACX75457). In order to obtain the plasmid, the Lactobacillus plantarum LDH gene was PCR-amplified in advance and subcloned into the Escherichia coli vector pSTBlue to obtain the pSTplLDH plasmid (Microb Cell Fact. January 30, 2006; 5:4.Lactate production yield from engineered yeasts is dependent from the host background, the lactate dehydrogenase source and the lactate ...
Embodiment 3
[0159] Example 3: Construction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae (CEN.PK) strains expressing heterologous LDH activity from Lactobacillus plantarum and (over)expressing HXT1 or HXT7 genes; cell growth, glucose consumption, lactic acid and ethanol production of transformants and control strains .
[0160] In this example, the lactic acid and ethanol production of the CEN.PK strain transformed with multiple copies of L. plantarum LDH was compared to that obtained with one extra copy of the HXT1 or HXT7 gene.
[0161] Bacterial lactate dehydrogenase was excised from the aforementioned pSTplLDH with EcoRI and inserted into similarly cleaved and dephosphorylated plasmid pYX212 (basic Saccharomyces cerevisiae multicopy expression plasmid pYX212, LEU2 marker, R&D Systems, Inc., Wiesbaden , D), the expression plasmid p212lpLDH was obtained. Independent transformants derived from yeast transformation were cultured in shake flasks in minimal medium (YNB, 1.34% w / V YNB from Difco Laboratories...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com