Martensitic stainless steel and manufacturing method thereof
A kind of martensitic stainless steel, an unavoidable technology, applied in the field of martensitic stainless steel, can solve the problems that cannot meet the needs of ocean transportation, poor low-temperature impact toughness, and limit popularization and application, so as to improve the overall stability, improve strong plasticity and impact Toughness, effect of reducing nickel content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
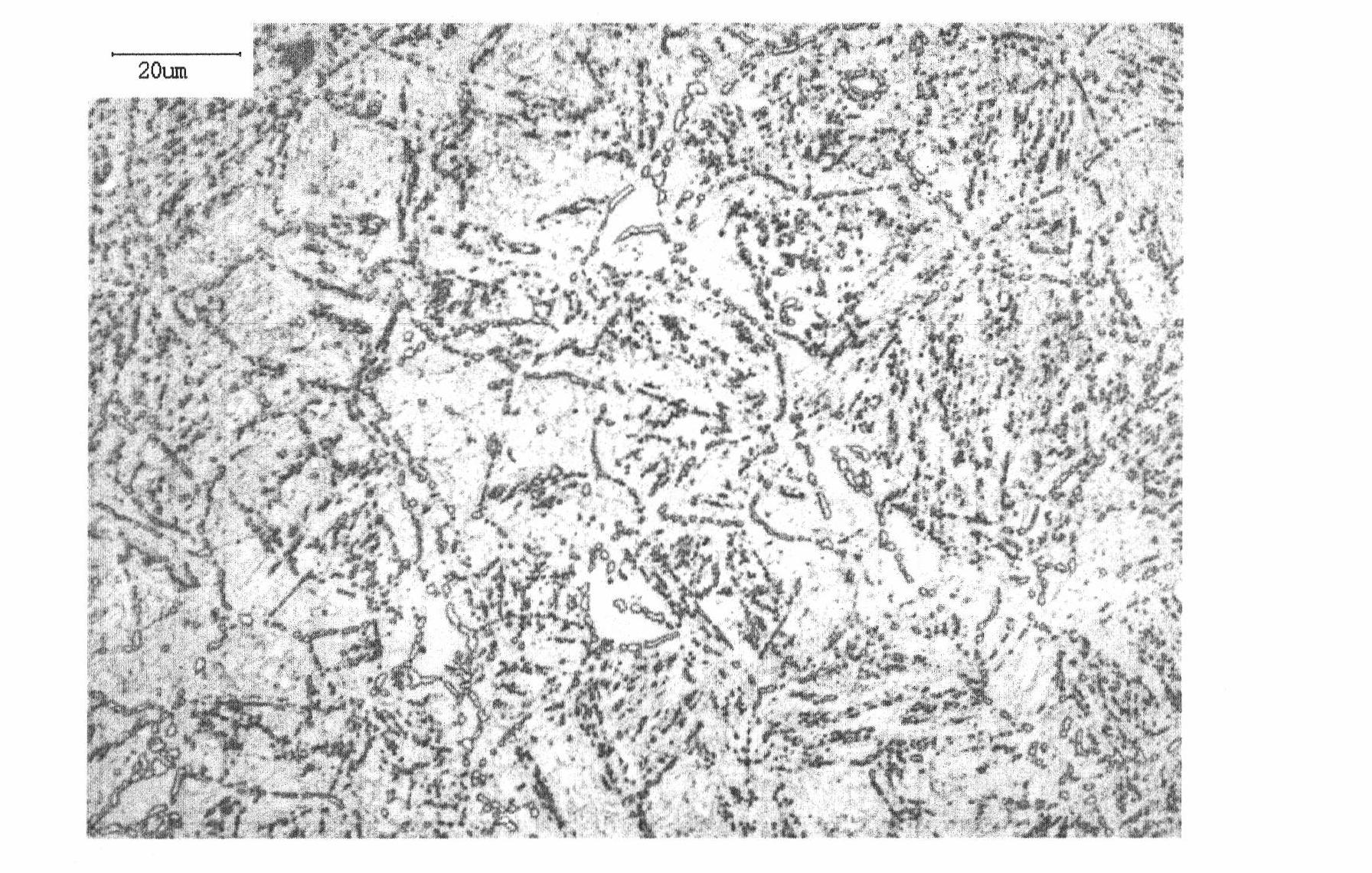
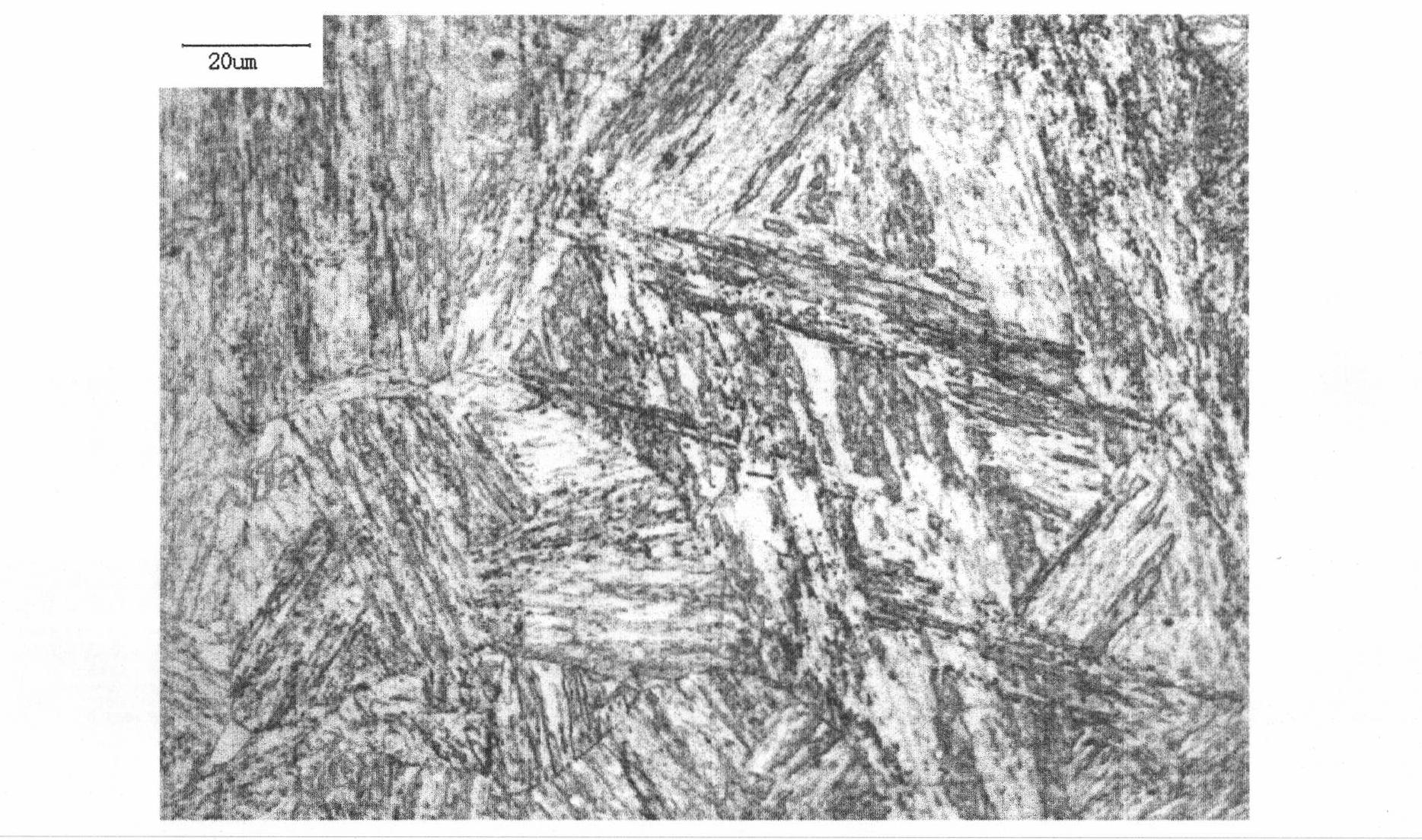
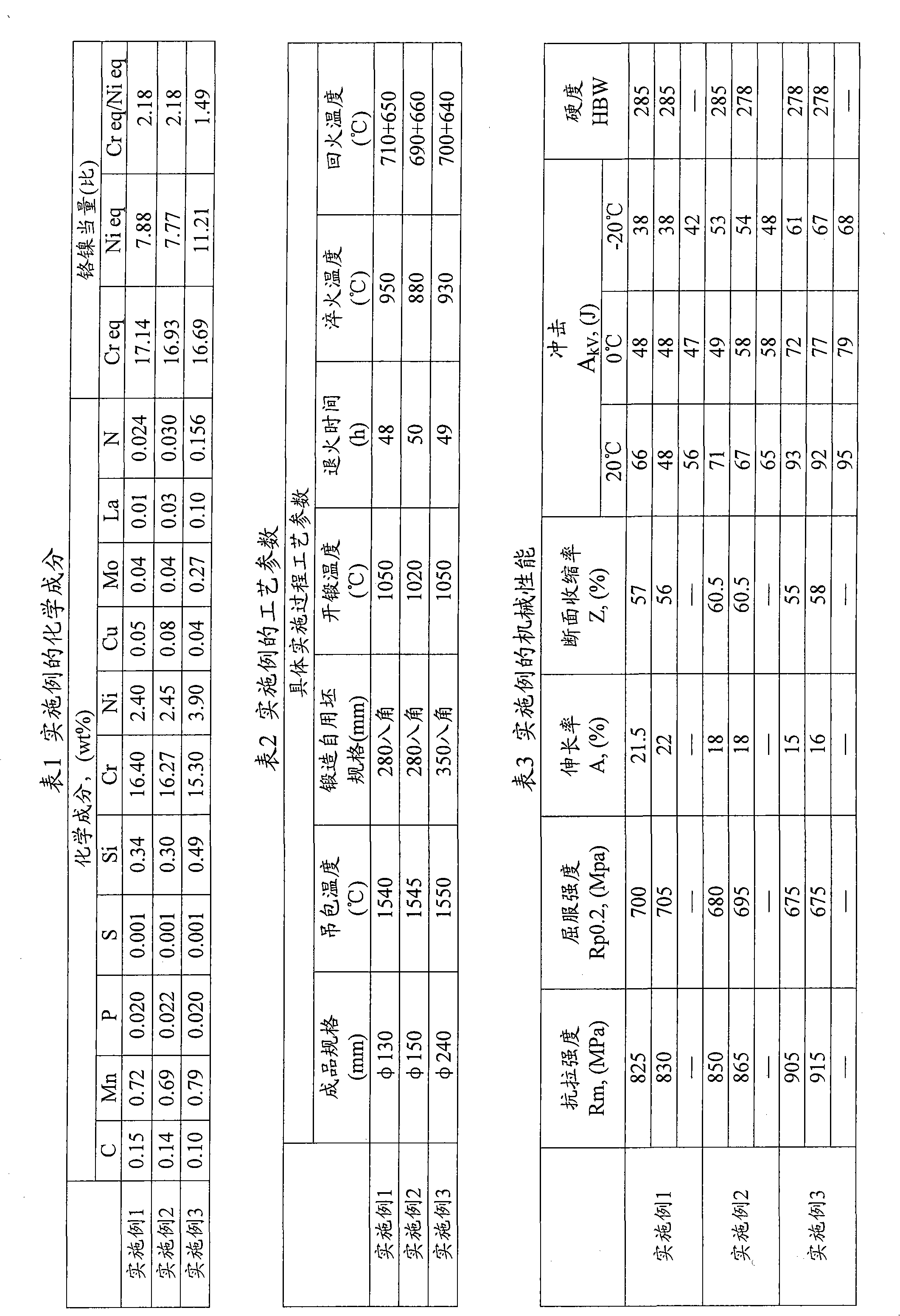
[0057] Examples The chemical composition is shown in Table 1, the preparation process parameters are shown in Table 2, and the mechanical properties are shown in Table 3. The preparation process is as follows. See Table 4 for a comparison of the chemical composition and mechanical properties of the examples and X17CrNi16-2.
[0058] Step 1: Smelting
[0059] Initial smelting in 40-ton EAF electric arc furnace, the bottom stirring mode uses nitrogen, and the reducing agent of electric furnace uses silicon carbide and silicon balls; after the initial smelting, turn to 40-ton AOD / LF furnace for refining, remove the reducing slag before tapping, and add alloy at 1680 °C , when decarburization by oxygen blowing to 0.30%, add 800kg of lime, and when decarburization by oxygen blowing to 0.10%, add 800kg of lime. End point carbon control <0.03%, hanging bag temperature 1540-1550°C; die casting 2.3 tons of steel ingots are hoisted 120 minutes after pouring; 30 minutes after the steel ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com