Method for preparing thioamide-based chelating nanofiber for adsorbing heavy metal ions
A thioamide-based, heavy metal-adsorbing technology, which is applied in the fields of alkali metal compounds, fiber treatment, and fiber chemical characteristics, can solve the problems of low reusability, few types of adsorbed ions, and low adsorption capacity, and achieve high practical value , good regeneration performance and large adsorption capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
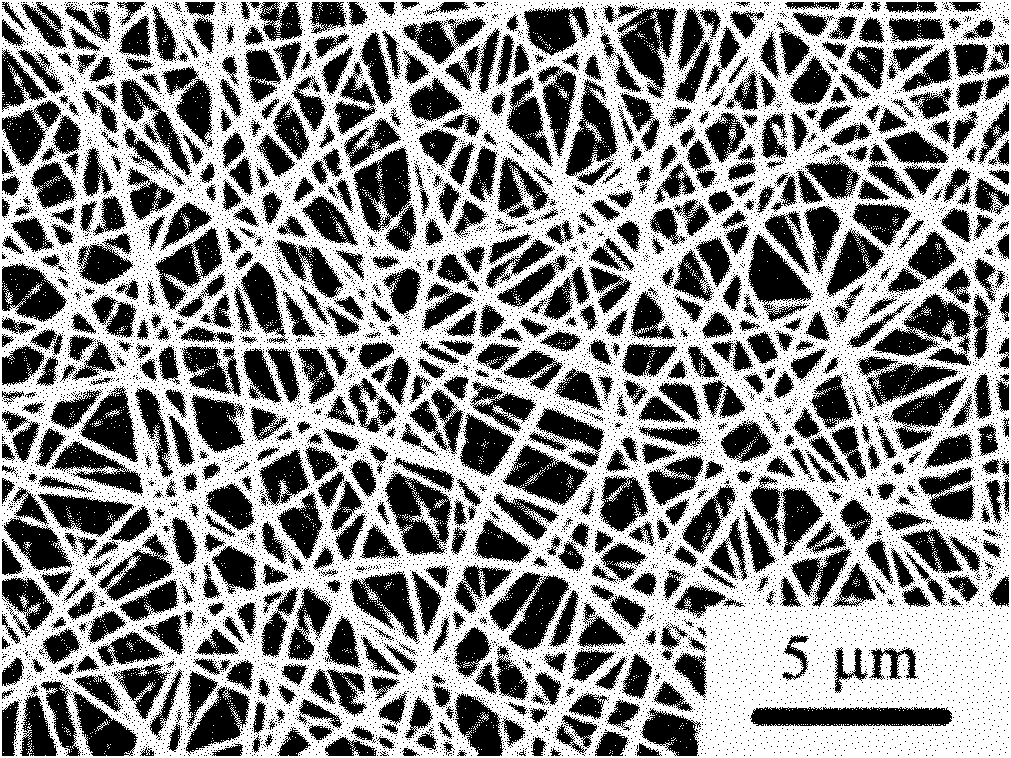
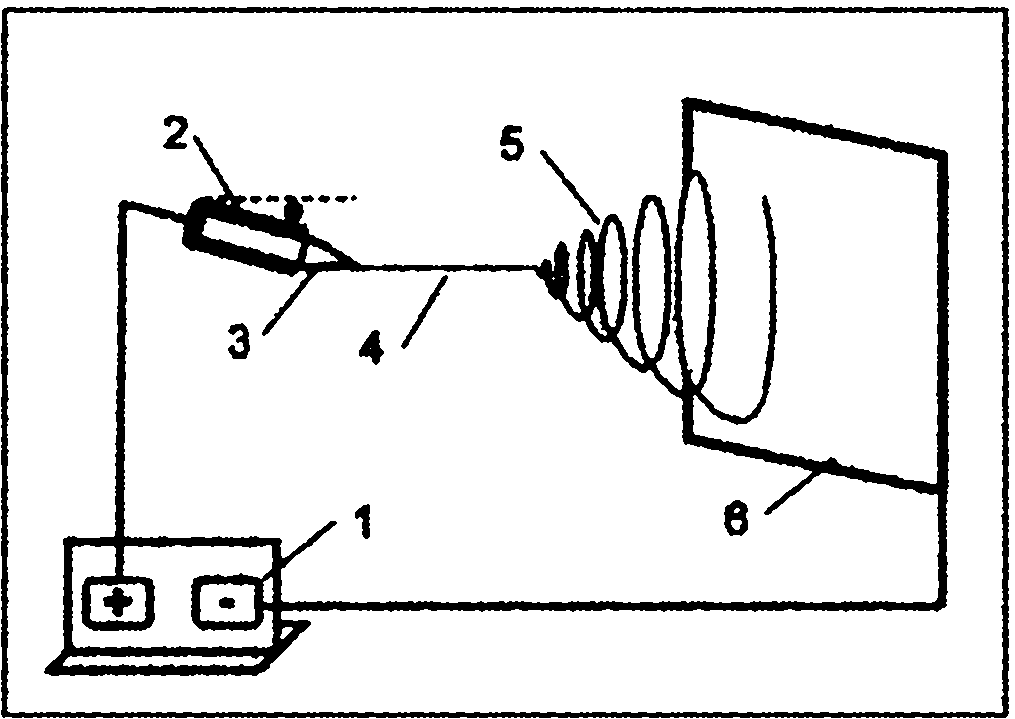
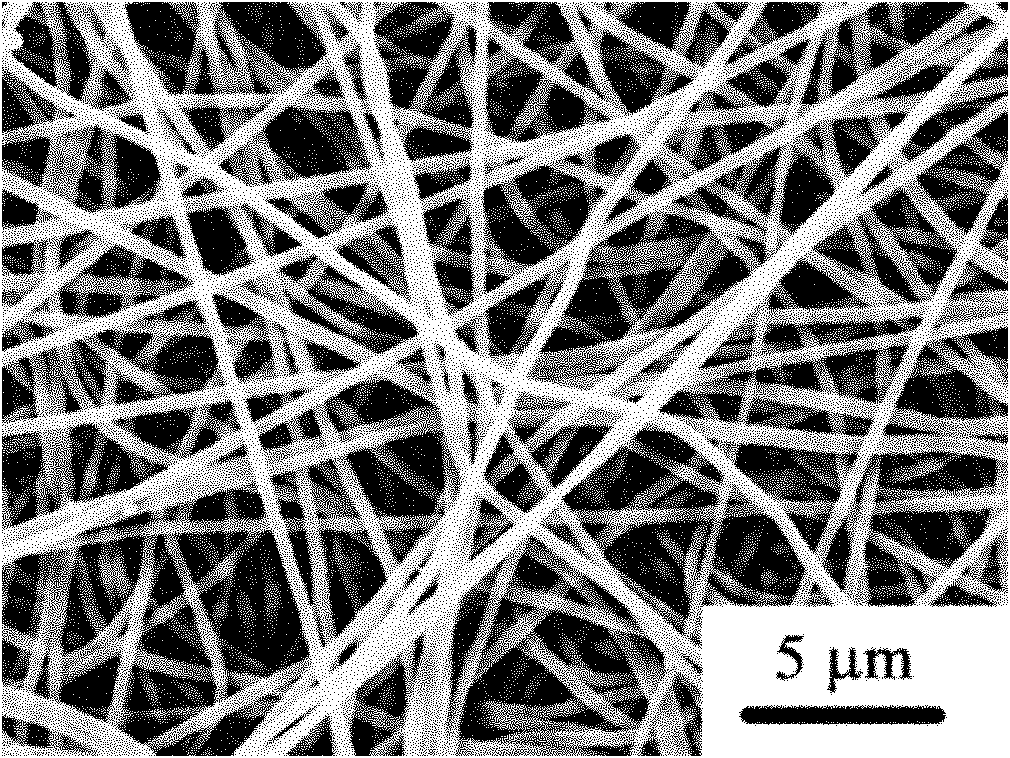
[0025] Add 1.6 g of polyacrylonitrile to 18.4 g of dimethylformamide, heat at 90° C. for 6 hours, until the polyacrylonitrile is completely dissolved and the solution appears yellow-brown, and cool to room temperature. The obtained polymer solution is put into a glass spinneret, the inner diameter of the spinneret head is 1.0 mm, the aluminum sleeve is used as the anode, and the aluminum foil is used as the cathode receiving plate to collect the fiber product. The distance between the two plates is 15 cm, and the applied voltage is Electrospinning was performed at 25kV, and a polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membrane was obtained on the receiving plate after 48 hours, with a fiber diameter of 100-300nm.
Embodiment 2
[0027] Add 1.8 g of polyacrylonitrile to 18.2 g of dimethylformamide, heat at 90° C. for 6 hours, until the polyacrylonitrile is completely dissolved and the solution appears yellow-brown, and cool to room temperature. The obtained polymer solution is put into a glass spinneret, the inner diameter of the spinneret head is 1.0 mm, the aluminum sleeve is used as the anode, and the aluminum foil is used as the cathode receiving plate to collect the fiber product. The distance between the two plates is 15 cm, and the applied voltage is Electrospinning was performed at 25kV, and a polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membrane was obtained on the receiving plate after 48 hours, with a fiber diameter of 200-400nm.
Embodiment 3
[0029] Add 2.0 g of polyacrylonitrile to 18.0 g of dimethylformamide, heat at 90° C. for 6 hours, until the polyacrylonitrile is completely dissolved and the solution turns yellow-brown, then cool to room temperature. The obtained polymer solution is put into a glass spinneret, the inner diameter of the spinneret head is 1.0 mm, the aluminum sleeve is used as the anode, and the aluminum foil is used as the cathode receiving plate to collect the fiber product. The distance between the two plates is 15 cm, and the applied voltage is Electrospinning was performed at 25kV, and a polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membrane was obtained on the receiving plate after 48 hours, with a fiber diameter of 300-500nm.
[0030] Pre-crosslinking of polyacrylonitrile nanofibers
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com