Method for producing hydrogen by compounding facultative hydrogenogen with anaerobic bacteria
A technology of anaerobic bacteria and fermentation method, which is applied in the field of hydrogen production by compounding facultative hydrogen-producing bacteria and anaerobic bacteria, and can solve the problems of less research on the combination of high-efficiency hydrogen-producing bacteria and less research on single substrates.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] The fermentation method of this example is batch fermentation, the substrate glucose is added to the hydrogen production medium, the glucose concentration is 20 g / L, and the initial pH=6.0-7.0. Put an effective volume of 6L hydrogen-producing medium into a 10L fermenter, and sterilize at 115°C for 25min. Inoculate the prepared high-concentration bacterial liquid into the hydrogen-producing medium at a ratio of 1:1, and the inoculum amount of the high-concentration bacterial liquid is 10%, that is, the inoculation volume of the high-concentration bacterial solution is 10% of the medium volume.
[0022] Fermentative hydrogen production process conditions:
[0023] to N 2 Purge the culture medium for 5 minutes to make the fermentation environment close to anaerobic, monitor the pH, temperature and stirring rate of the fermentation liquid phase online, adjust the pH of the fermentation process to maintain 6.0~7.0 by adding dilute NaOH, adjust the stirring rate of the ferm...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Example 2: The difference between this example and Example 1 is that the compounding scheme is facultative hydrogen-producing bacteria Bacteria.E and anaerobic hydrogen-producing bacteria Bacteria.B. The inoculation ratio of high-concentration bacteria solution is 1:1, and the rest are the same Embodiment one.
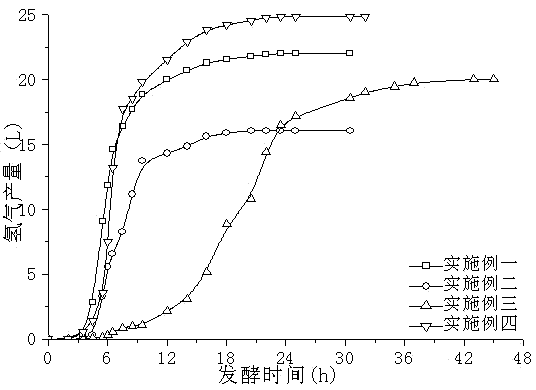
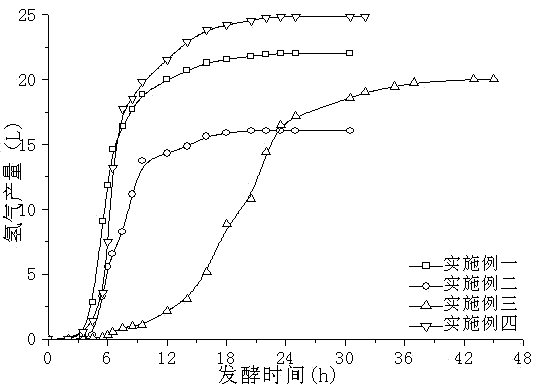
[0028] Obtain the dynamic hydrogen production curve of embodiment two and refer to the appendix of the description figure 1 , the fermentation hydrogen production cycle is 24h, the cumulative gas production is 29.3L, the fermentation gas phase is composed of two gases, hydrogen and carbon dioxide, of which the hydrogen gas fraction is 54.80%, and the final cumulative hydrogen production is 16.1L; the average hydrogen production rate of the fermentation process is up to 167.25mL / (h L), the decomposition rate of glucose in the liquid phase is 92.00%, and the final hydrogen production per unit substrate is 1.290molH 2 / mol glucose.
Embodiment 3
[0029] Example 3: Two strains of anaerobic hydrogen-producing bacteria Bacteria.P and Bacteria.B were compounded, and the high-concentration bacterial solution was inoculated into the hydrogen-producing medium at a ratio of 1:1, and the rest were the same as in Example 1.
[0030] The dynamic hydrogen production curve obtained in Example 3 is shown in the appendix of the description figure 1 In this example, the fermentative hydrogen production period is 50 hours, and the cumulative gas production is 33.3 L. The fermentation gas phase consists of two gases, hydrogen and carbon dioxide, wherein the hydrogen gas fraction is 60.00%, and the final cumulative hydrogen production is 20.0 L; the fermentation process produces an average The hydrogen rate reaches 86.70mL / (h L), the decomposition rate of glucose in the liquid phase is 93.00%, and the final hydrogen production per unit substrate is 1.604molH 2 / mol glucose. Compared with Example 1 and Example 2, Example 3 has a longer ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com