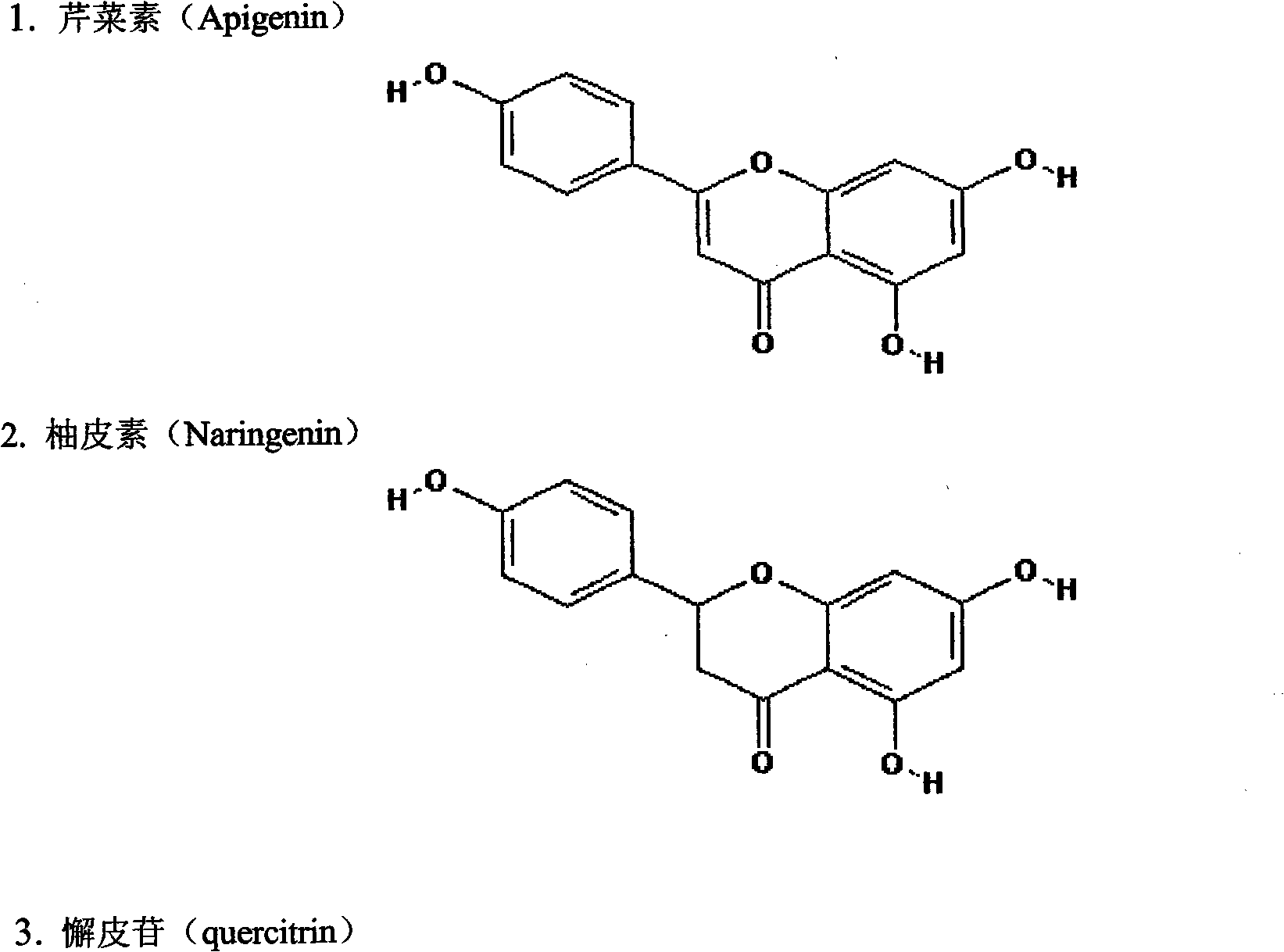
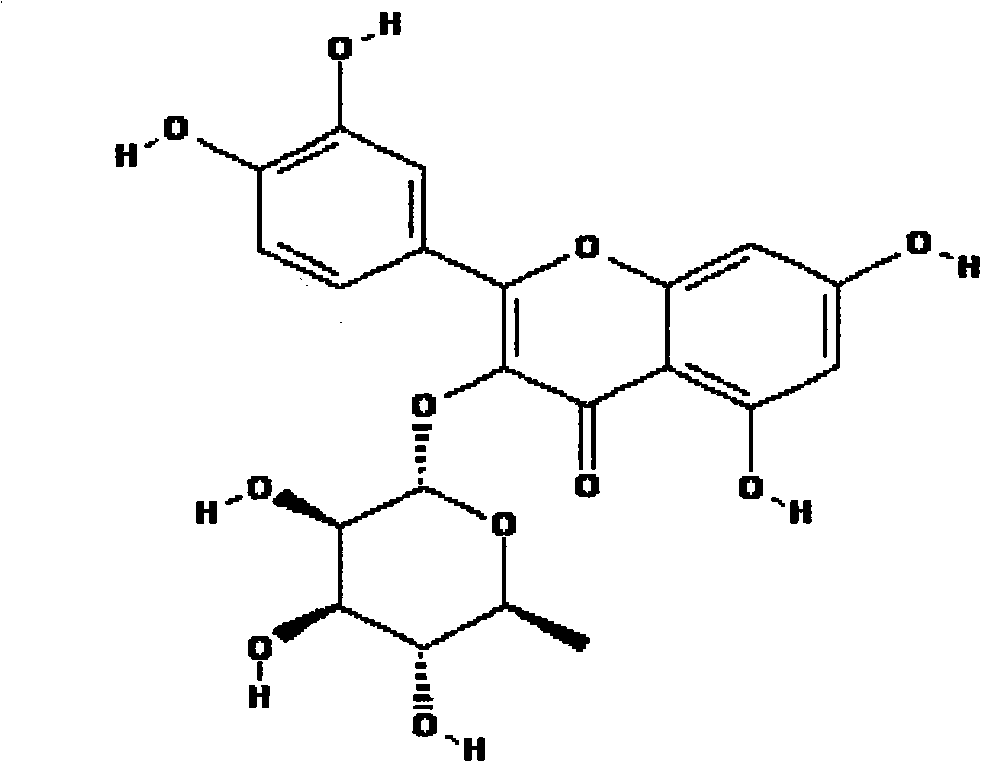
Application of extractive of adinandra nitida leaves to preparation of anti-inflammatory analgesia medicament
An anti-inflammatory and analgesic and extractive technology is applied to the application field of the ethyl acetate part of the leaves of Populus glabrata in the preparation of anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs, which can solve the problems of no anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect and the like, and achieve a good therapeutic effect. , less toxic effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Example 1: The preparation method of the ethyl acetate part of poplar leaf
[0019] Pulverize the leaves of the dried poplar plant, extract 3 times with 50-60% (volume concentration) ethanol reflux by the weight of the material, filter for 3 hours each time, filter, and combine the filtrates to obtain the ethanol solution of poplar leaves . Then, the ethanol solution of poplar leaves ethanol is distilled under reduced pressure to recover ethanol, and the ethanol concentrated ointment of poplar leaves is obtained. Then, the concentrated ointment of poplar leaves of bright leaves was centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 10-15 minutes to separate it into supernatant and sediment. Extract the supernatant with an equal amount of ethyl acetate to obtain an ethyl acetate extract of Poplaria radiata leaves; extract the precipitate with 3 times the amount of ethyl acetate at room temperature, and centrifuge to obtain an ethyl acetate extract of Populus radix leaves. Finally, the extrac...
Embodiment 2
[0020] Example 2: Acute Toxicity Test of Ethyl Acetate Parts of Populus radiata Leaf
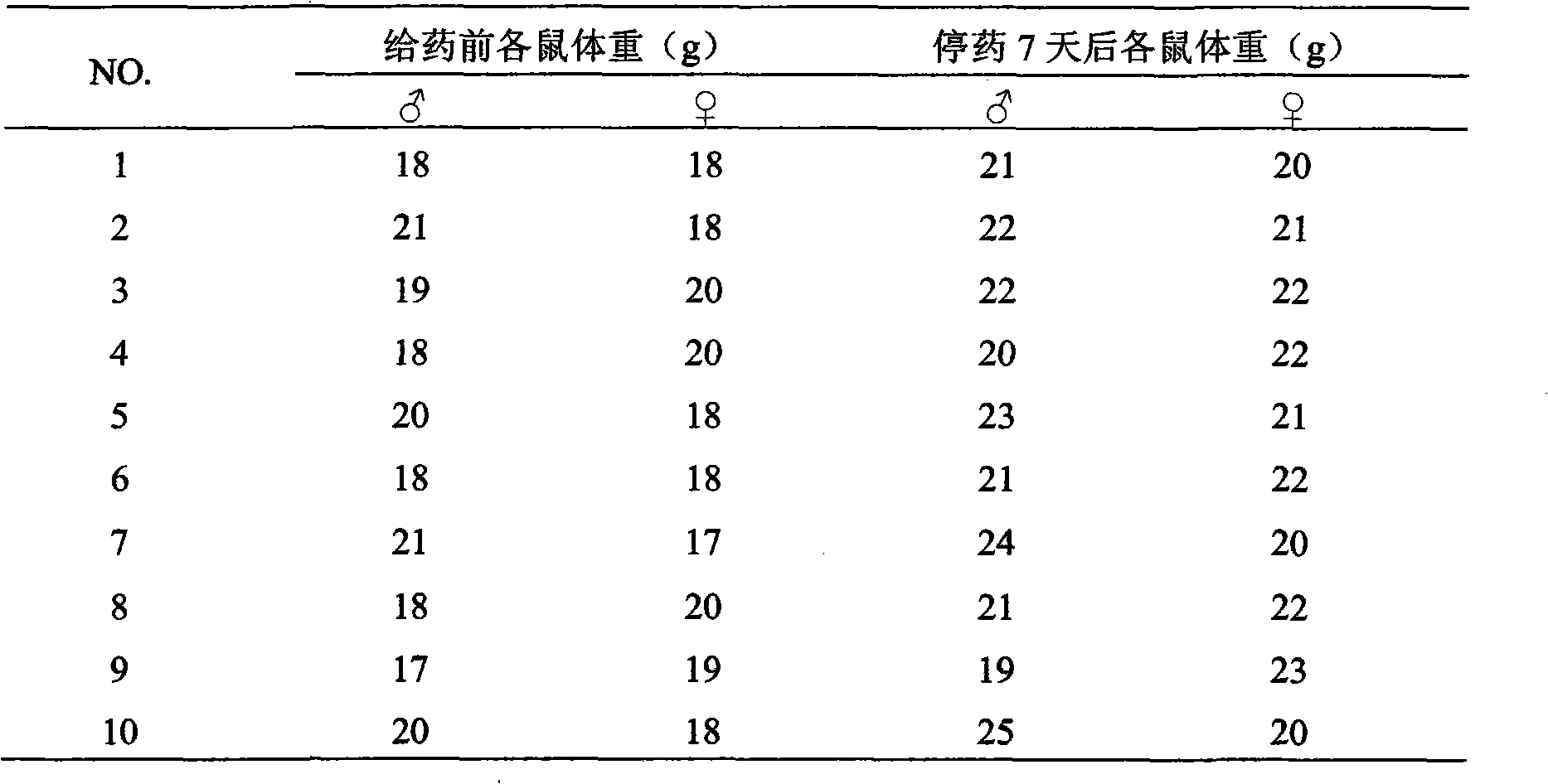
[0021] Choose 20 mice with a body weight of 18-22g, half male and half male, fasting without water for 16 hours, intragastric administration twice in one day, with an interval of 6 hours between administrations, each administration giving the maximum concentration (0.085g / ml), Immediately after administration and within 7 days after administration of the medicinal solution of the ethyl acetate part of Populus glabrata leaves with the largest volume (40ml / kg), the symptoms of poisoning and death in mice were observed and recorded. At the end of the observation period, the surviving mice were sacrificed for gross autopsy to observe visceral lesions.
[0022] Table 1 Changes in body weight of mice during the acute toxicity test of the ethyl acetate part of poplar leaves
[0023]
[0024] The maximum dosage of the ethyl acetate part of the leaves of Populus radix L. gavage twice a day was 6....
Embodiment 3
[0025] Example three: the analgesic effect of the ethyl acetate part of poplar leaf
[0026] 1. The analgesic effect of the ethyl acetate part of Populus glabra leaves on mice (hot plate method)
[0027] Set the temperature of the smart hot plate instrument to 55°C, and start the test when the temperature of the hot plate reaches the preset temperature. Select a female mouse with a body weight of 18-22g, put one on the hot plate at a time, take the time (seconds) required for the mouse to lick the hind foot phenomenon as the pain threshold of the mouse, and select the pain threshold between 5s and 30s mice for the experiment. Select 50 qualified mice therefrom, be divided into five groups at random, 10 in every group, be respectively blank control group, tramadol hydrochloride group and the high-dose group of ethyl acetate part of Populus glabrata leaf (according to the mouse acute toxicity test result, this The test set the maximum dose is about 1 / 4 of the acute toxicity te...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com