Method for detecting gigahertz single photon with low time jitter and low noise
A single-photon detection and time jitter technology, applied in instruments and other directions, can solve the problems of large time jitter, difficult to meet the requirements of ranging, and reduce the amplitude of the avalanche signal, so as to maintain the amplitude and integrity, reduce the time jitter, and maintain the avalanche signal. Amplitude effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
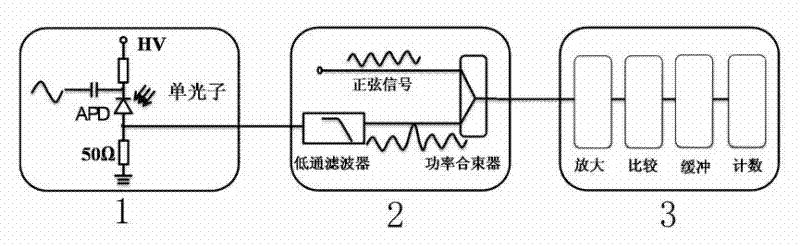
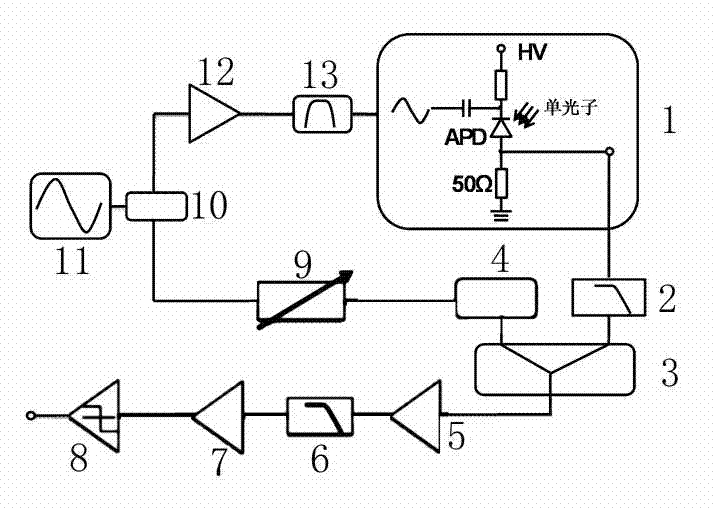
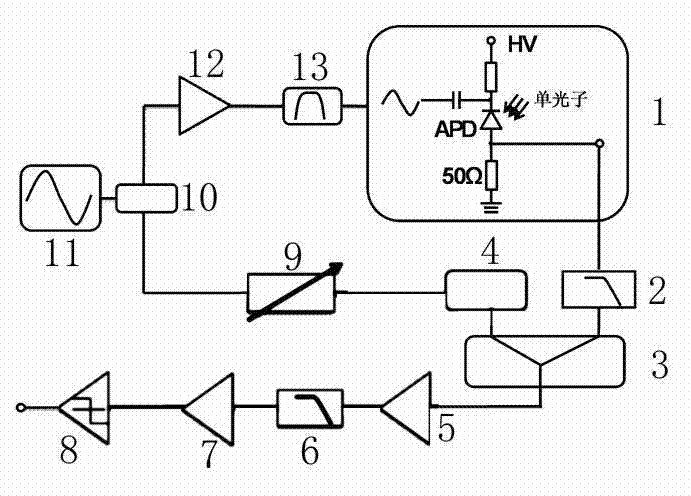
[0017] Example: such as Figure 1-2 As shown, the labels 1-13 represent respectively: detection circuit 1, noise suppression circuit 2, signal processing circuit 3, phase shifter 4, radio frequency amplifier 5, low pass filter 6, radio frequency amplifier 7, comparator 8, adjustable attenuation Device 9, power splitter 10, sinusoidal signal generator 11, high power amplifier 12, band pass filter 13.
[0018] Such as figure 1 As shown, the detection circuit converts the single-photon signal into an electrical signal through the APD. In the converted electrical signal, the avalanche signal is submerged in the spike noise caused by the capacitive effect of the APD, and the avalanche signal is extracted through the noise suppression circuit. The noise suppression circuit is composed of a low-pass filter and a balance circuit. The signal first passes through the low-pass filter and then balances with the attenuated sinusoidal signal to remove the noise and extract the avalan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com