Fluorescent dye-containing particles and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of fluorescent pigments and particles, which can be used in medical preparations containing active ingredients, chemical instruments and methods, luminescent materials, etc., and can solve problems such as limitation and increase in manufacturing cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0020] (1) Preparation of sol solution containing pigment
[0021] (2) Formation of particles using a pigment-containing sol solution
[0022] (3) Arbitrary drying of particles
[0023] (1) Preparation of sol solution containing pigment
[0024] The step of preparing a sol solution containing a dye can be divided into a step of preparing a sol solution and a step of dispersing an organic fluorescent dye and a water-soluble polymer in the sol solution.
[0025] An organic fluorescent dye is more easily decomposed when dispersed in a sol solution than when stored as a solid. Therefore, the organic fluorescent pigment can be added to the sol solution immediately before the spray drying method is used to form the particles. Accordingly, decomposition of the organic fluorescent dye is prevented as much as possible. Water-soluble polymers can be directly added to the sol solution, but it often takes time to dissolve them. Therefore, the water-soluble polymer may be dissolved in...
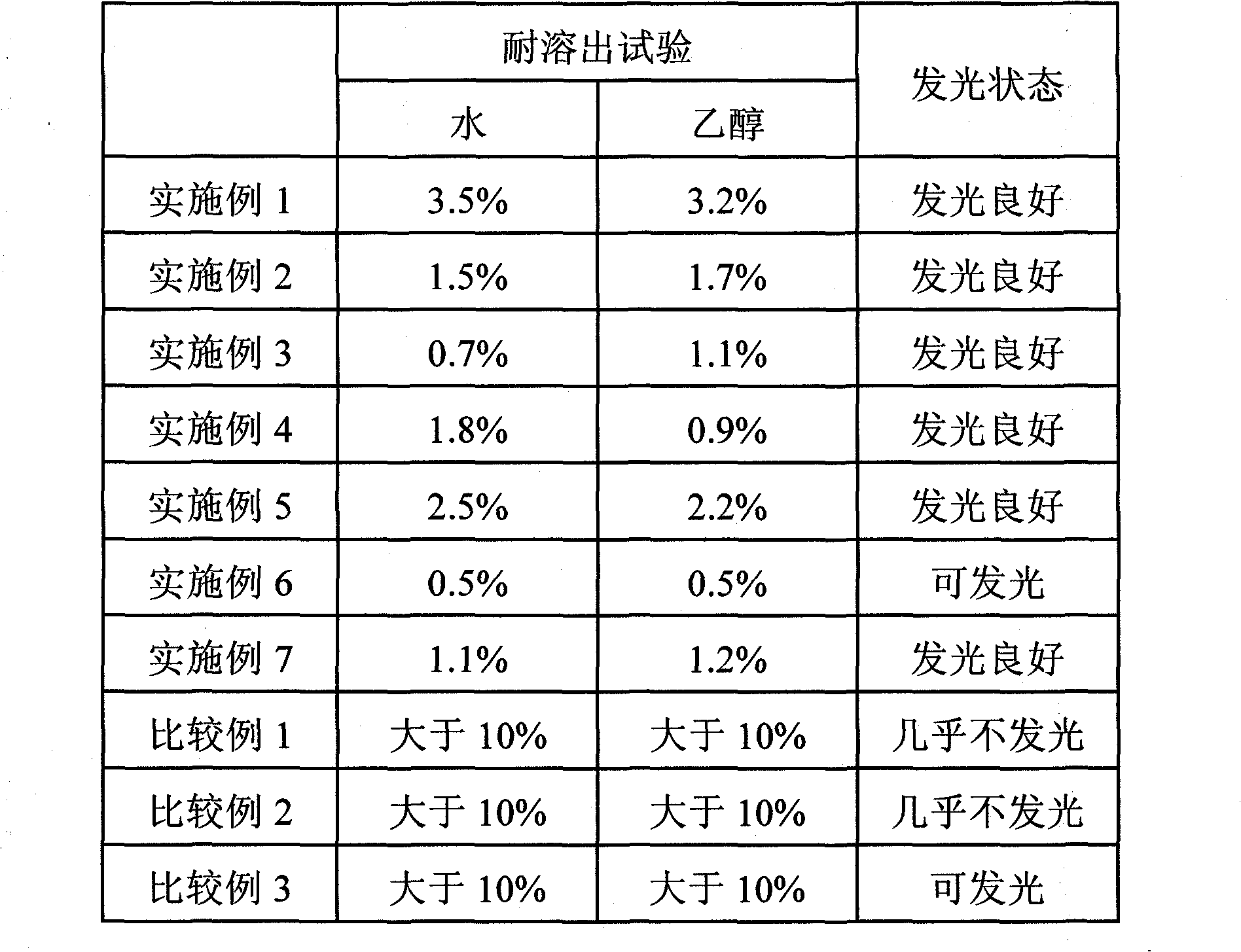
Embodiment 1
[0061] 1.7 g of acetic acid was added to a solution containing 60.0 g of tetramethoxysilane, 39 g of isopropanol, and 56.8 g of purified water, and stirred at room temperature for 12 hours to perform hydrolysis and polymerization to obtain a sol solution. 0.15 g of an organic fluorescent dye (D&C Orange No. 5), 3 g of polyvinylpyrrolidone (K15) and 50 g of isopropanol were added to 100 g of this sol solution, and stirred sufficiently to obtain a sol solution containing a dye. Particles were formed using the sol solution containing the dye using a spray dryer (MDL-050 manufactured by Fujisaki Electric Co., Ltd.). The obtained particles were dried at an atmospheric temperature of 150° C. for 4 hours to remove the solvent remaining in the particles. The average particle diameter of the obtained particles was 5.5 μm. In the measurement of the average particle diameter, a commercially available laser diffraction particle size distribution analyzer (Microtrac HRA manufactured by Ni...
Embodiment 2
[0063] 1.7 g of acetic acid was added to a solution containing 36.0 g of tetramethoxysilane, 21.4 g of methyltrimethoxysilane, 42 g of isopropanol, and 56.8 g of purified water, and stirred at room temperature for 1 hour. The obtained solution was left to stand in a thermostat at 60° C. for 24 hours to perform hydrolysis and polymerization to obtain a sol solution. 0.15 g of an organic fluorescent dye (D&C Orange No. 5), 3 g of polyvinylpyrrolidone (K15), and 50 g of isopropanol were added to 100 g of the sol solution, and stirred sufficiently to obtain a sol solution containing a dye. Using this sol solution containing a pigment, particles were formed by the same method as in Example 1. The obtained particles were dried at an atmospheric temperature of 150° C. for 4 hours. The average particle diameter of the obtained particles was 4.5 μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com