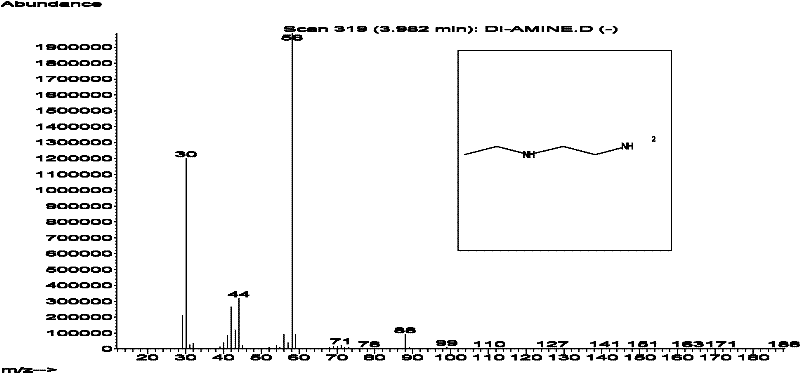
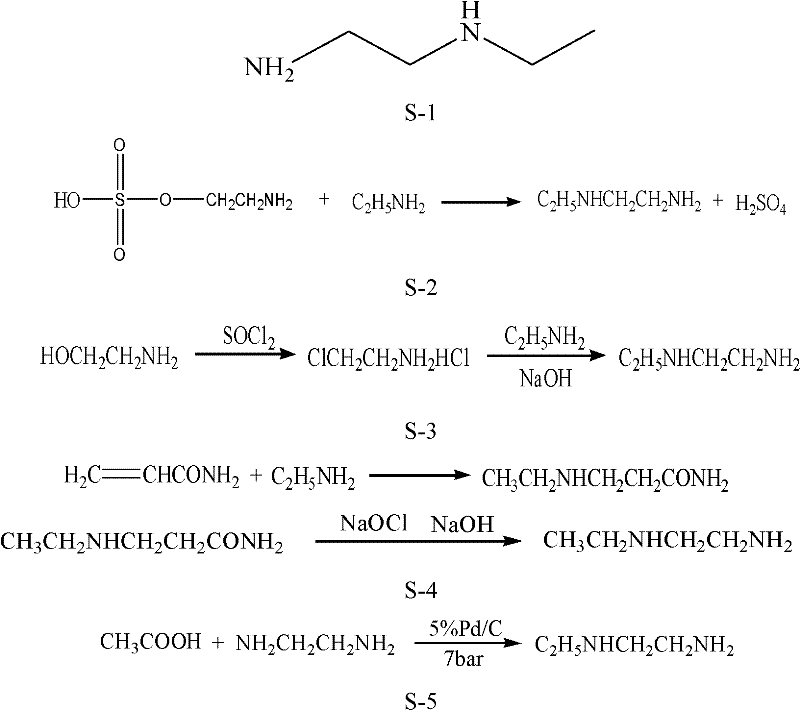
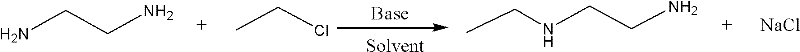The synthetic method of n-ethylethylenediamine
A technology of ethylethylenediamine and a synthesis method, which is applied in the preparation of amino-substituted functional groups, organic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as harsh reaction conditions, and achieve the effects of reducing the burden of post-processing, simple process, and good product selectivity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] The synthetic method of embodiment 1, N-ethylethylenediamine:
[0026] Add 110g (1.6mol) of ethylenediamine, 550g of methanol, and 60g (1.12mol) of sodium methoxide into a high-pressure reactor with a stirring temperature measuring device, and press 52g (0.8mol) of ethyl chloride after closing the lid; The internal temperature is raised to 40°C, and the pressure is 0.5Mpa at this time. Keep the temperature for 6 hours to complete the reaction, and the pressure after the reaction is 0.3Mpa.
[0027] After the reaction, the sodium chloride in the reaction liquid was filtered off, the filtrate was rectified, and the fraction at 128-130°C was collected to obtain 49.3 g of the product N-ethylethylenediamine with a yield of 69.89%.
[0028] The fraction collected at 62-64°C is methanol with a recovery rate of 84.26%; the fraction collected at 114-118°C is ethylenediamine with a recovery rate of 58.25%, both of which can be recycled.
Embodiment 2
[0029] The synthetic method of embodiment 2, N-ethylethylenediamine:
[0030] Add 110g (1.6mol) of ethylenediamine, 220g of methanol, and 47.5g (0.88mol) of sodium methylate into a high-pressure reactor with a stirring temperature measuring device. After closing the lid, press 52g (0.8mol) of ethyl chloride. The temperature was raised to 60°C within 1h, and the pressure was 0.7Mpa at this time. Keep the temperature for 3 hours to complete the reaction, and the pressure after the reaction is 0.36Mpa.
[0031] After the reaction, the sodium chloride in the reaction solution was filtered off, the filtrate was rectified, and the fraction at 128-130°C was collected to obtain 43.2 g of the product N-ethylethylenediamine with a yield of 61.25%.
[0032] At the same time, solvent methanol and excess ethylenediamine were collected, and the recoveries of the two were 84.54% and 58.12% respectively.
Embodiment 3
[0033] The synthetic method of embodiment 3, N-ethylethylenediamine:
[0034] Add 110g (1.6mol) of ethylenediamine, 550g of methanol, and 52g (0.96mol) of sodium methoxide into a high-pressure reaction kettle with a stirring temperature measuring device. After closing the lid of the kettle, press 52g (0.8mol) of ethyl chloride. The internal temperature was raised to 80°C, and the pressure was 1.2Mpa at this time. Keep the temperature for 4 hours to complete the reaction, and the pressure after the reaction is 0.5Mpa.
[0035] After the reaction, the sodium chloride in the reaction solution was filtered off, the filtrate was rectified, and the fraction at 128-130°C was collected to obtain 42.9 g of N-ethylethylenediamine, with a yield of 60.82%.
[0036] At the same time, solvent methanol and excess ethylenediamine were collected, and the recoveries of the two were 86.65% and 59.02% respectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com