Method and device for producing p-phenylenediamine by using liquid phase continuous hydrogenation method
A technology of p-phenylenediamine and hydrogenation method, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of organic compounds, preparation of amino compounds, etc., can solve the problems of low production capacity of equipment, high labor intensity of operation, serious environmental pollution, etc., and achieve Low equipment cost, low labor intensity, and the effect of reducing environmental pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Embodiment 1: produce p-phenylenediamine according to the following steps:
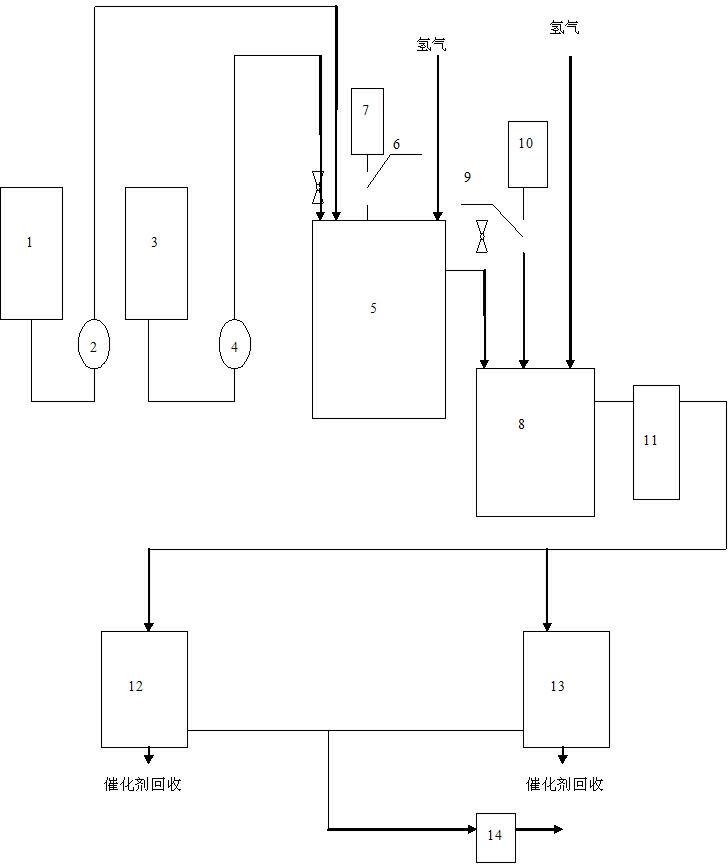
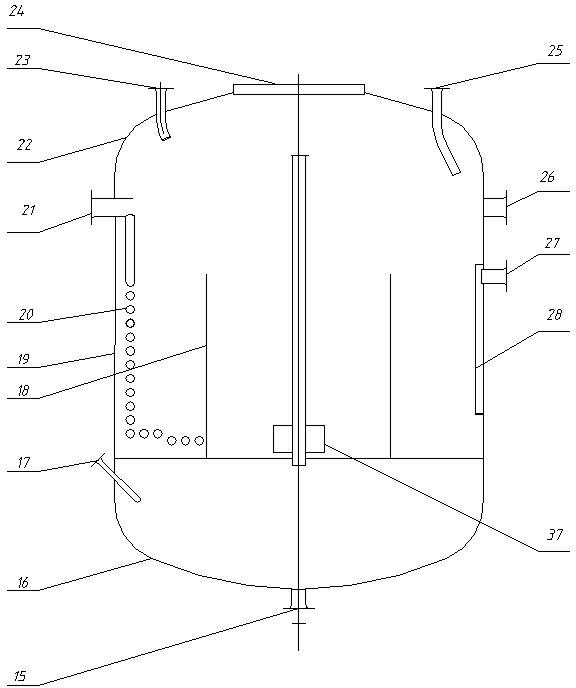
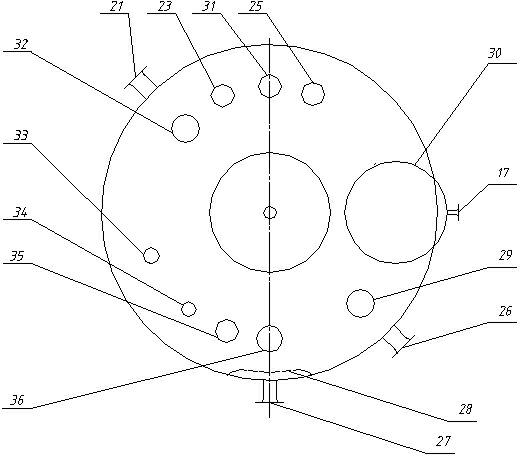
[0041] (1) In the first-stage hydrogenation reactor 5 and the second-stage hydrogenation reactor 8, methanol corresponding to 50% of the total volume of the reactor was first added, and then a nickel catalyst equivalent to 1.5% of the above-mentioned methanol weight was added;
[0042] (2) Turn on the cooling water of the heat exchange coil and keep the reaction temperature at 90°C;
[0043] (3) When stirring at 90°C, continuously feed hydrogen into the primary hydrogenation reactor 5 and the secondary hydrogenation reactor 8; The pressure in the stage hydrogenation reactor 8 remains on 1.3MPa;
[0044] (4) When the hydrogen pressure in the kettle reaches 1.3 MPa, continuously add methanol and p-nitroaniline into the first-stage hydrogenation reactor 5, and the speed of adding methanol is 15.5 minutes when methanol passes through the first-stage hydrogenation reactor 5. Calculated, the volu...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Embodiment 2: produce p-phenylenediamine according to the following steps:
[0050] (1) In the first-stage hydrogenation reactor 5 and the second-stage hydrogenation reactor 8, methanol corresponding to 60% of the total volume of the reactor was first added, and then a nickel-based catalyst equivalent to 1% of the above-mentioned methanol weight was added;
[0051] (2) Turn on the cooling water of the heat exchange coil and keep the reaction temperature at 100°C;
[0052] (3) When stirring at 100°C, continuously feed hydrogen into the primary hydrogenation reactor 5 and the secondary hydrogenation reactor 8; The pressure in the stage hydrogenation reactor 8 remains on 2.0MPa;
[0053] (4) When the hydrogen pressure in the kettle reaches 2.0MPa, continuously add methanol and p-nitroaniline into the primary hydrogenation reactor 5, and the speed of adding methanol is 10 hours when the methanol passes through the primary hydrogenation reactor. Calculated, the volume ra...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Embodiment 3: produce p-phenylenediamine according to the following steps:
[0059] (1) In the first-stage hydrogenation reactor 5 and the second-stage hydrogenation reactor 8, methanol corresponding to 70% of the total volume of the reactor was first added, and then a nickel-based catalyst equivalent to 0.5% of the above-mentioned methanol weight was added;
[0060] (2) Turn on the cooling water of the heat exchange coil and keep the reaction temperature at 120°C;
[0061] (3) At 120°C under agitation, continuously feed hydrogen into the primary hydrogenation reactor 5 and the secondary hydrogenation reactor 8; The pressure in the stage hydrogenation reactor 8 remains on 2.0MPa;
[0062] (4) When the hydrogen pressure in the kettle reaches 2.0MPa, continuously add methanol and p-nitroaniline into the first-stage hydrogenation reactor 5, and the rate of adding methanol is based on the residence time of methanol passing through the first-stage hydrogenation reactor at...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com